Abstract
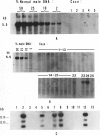
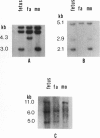
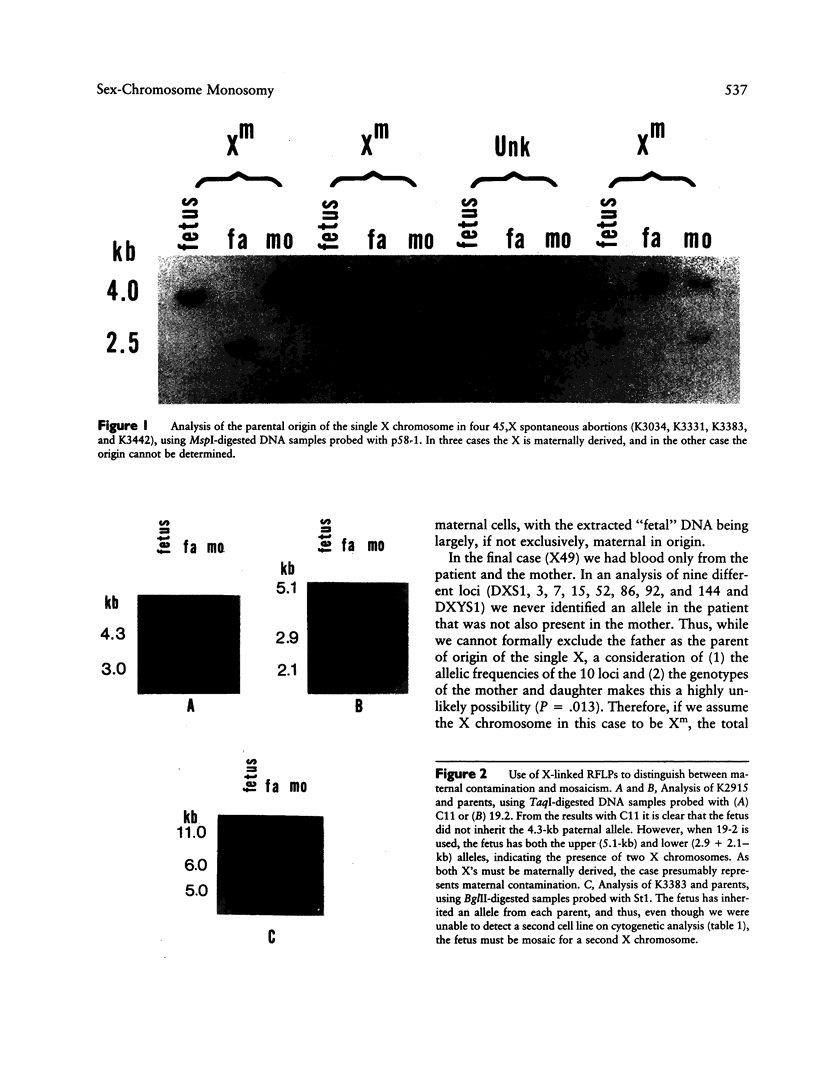
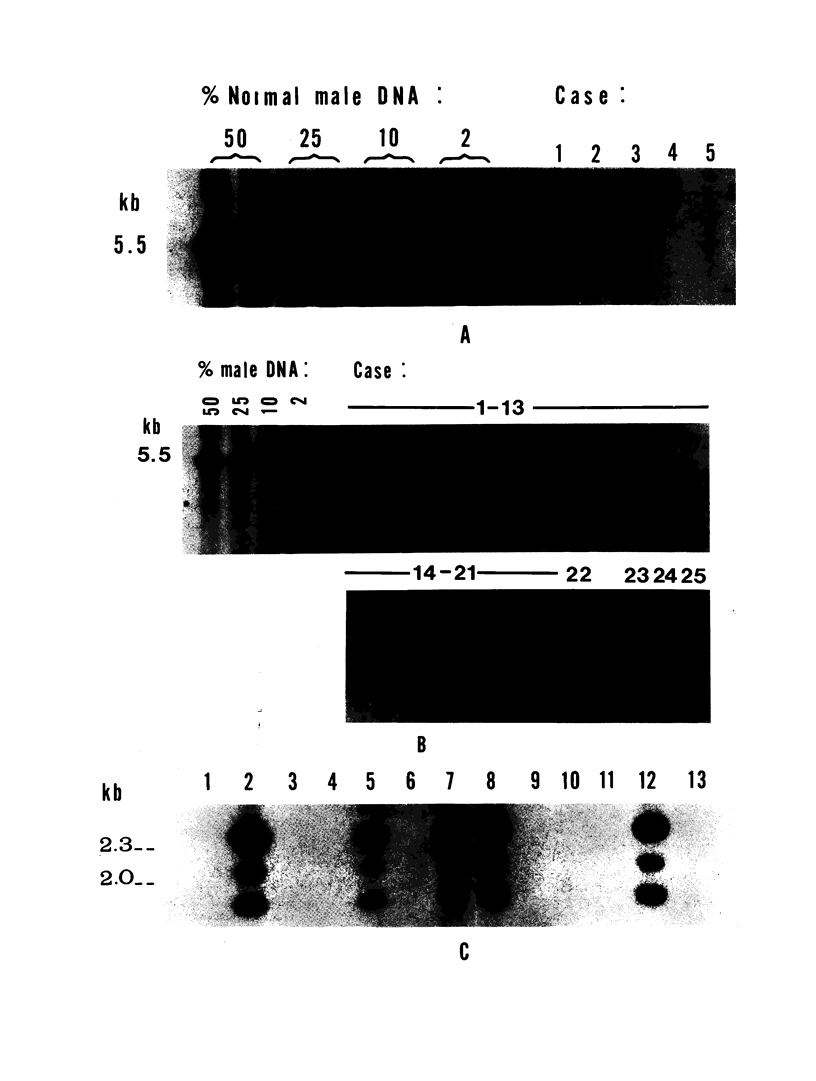
X chromosome- and Y chromosome-specific DNA probes were used to study different aspects of the genesis of sex-chromosome monosomy. Using X-linked RFLPs, we studied the parental origin of the single X chromosome in 35 spontaneously aborted and five live-born 45,X conceptions. We determined the origin in 35 cases; 28 had a maternal X (Xm) and seven had a paternal X (Xp). There was a correlation between parental origin and parental age, with the Xp category having a significantly reduced mean maternal age by comparison with the Xm group. Studies aimed at detecting mosaicism demonstrated the presence of a Y chromosome or a second X chromosome in three of 33 spontaneous abortions, a level of mosaicism much lower than that reported for live-born Turner syndrome individuals.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T., Chen N., Funkhouser J., Jooss T., Manuel B., Matsuura J., Matsuyama A., Wilson C., Yamane J. A., Jacobs P. A. A cytogenetic study of 1000 spontaneous abortions. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Oct;44(Pt 2):151–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T., Kumlin E., Takaesu N., Leppert M. Determination of the parental origin of sex-chromosome monosomy using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):965–972. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T., Quillen S. D., Yamane J. A. Sex ratio in spontaneous abortions. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Jan;47(Pt 1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Exclusion of chromosomal mosaicism: tables of 90%, 95% and 99% confidence limits and comments on use. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Jan;29(1):94–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B., Warburton D. The distribution of chromosomal genotypes associated with Turner's syndrome: livebirth prevalence rates and evidence for diminished fetal mortality and severity in genotypes associated with structural X abnormalities or mosaicism. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):24–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00289473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Donlon T. A., Kunkel S. M., Lalande M., Latt S. A. Y-190, a DNA probe for the sensitive detection of Y-derived marker chromosomes and mosaicism. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):109–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00591069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger R., Tippett P., Gavin J., Teesdale P., Daniels G. L. Xg groups and sex chromosome abnormalities in people of northern European ancestry: an addendum. J Med Genet. 1977 Jun;14(3):210–211. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalvey J. R., Erickson R. P. An improved method for detecting Y chromosomal DNA. Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;76(3):240–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00283615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tippett P., Sanger R. Source of single X in XO Turner syndrome: a comment. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):92–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00389469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D., Kline J., Stein Z., Susser M. Monosomy X: a chromosomal anomaly associated with young maternal age. Lancet. 1980 Jan 26;1(8161):167–169. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90658-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]