Abstract
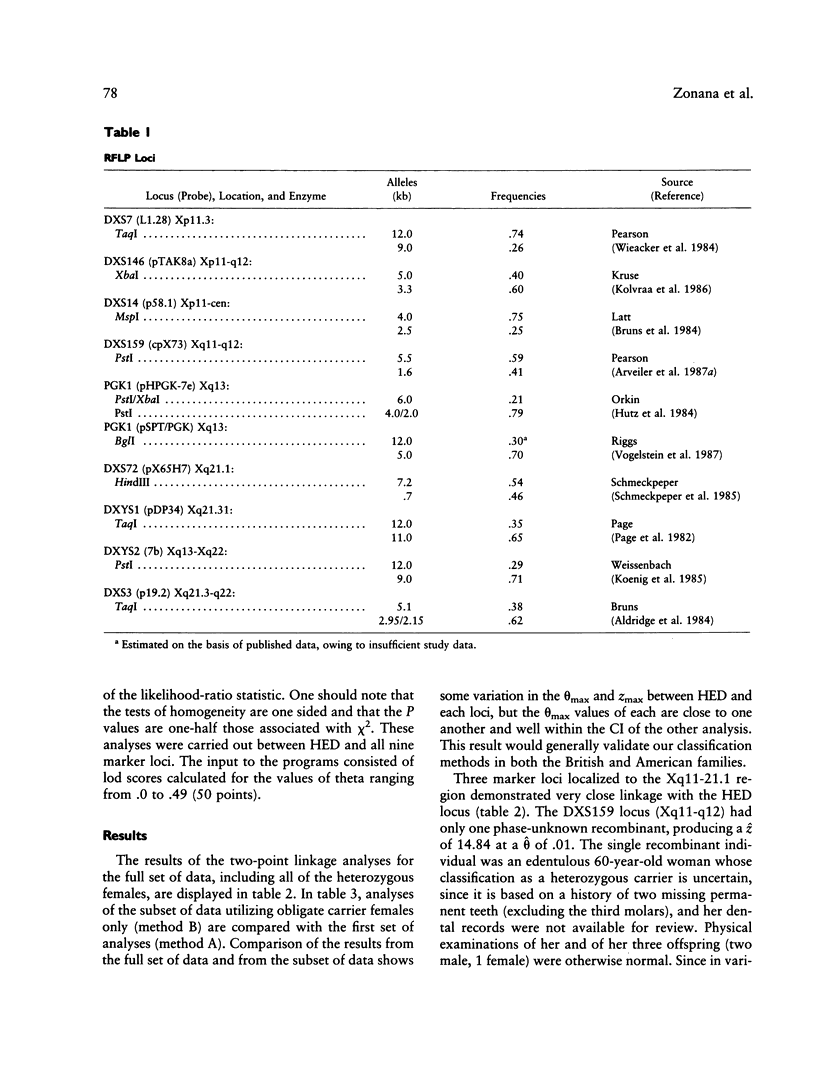
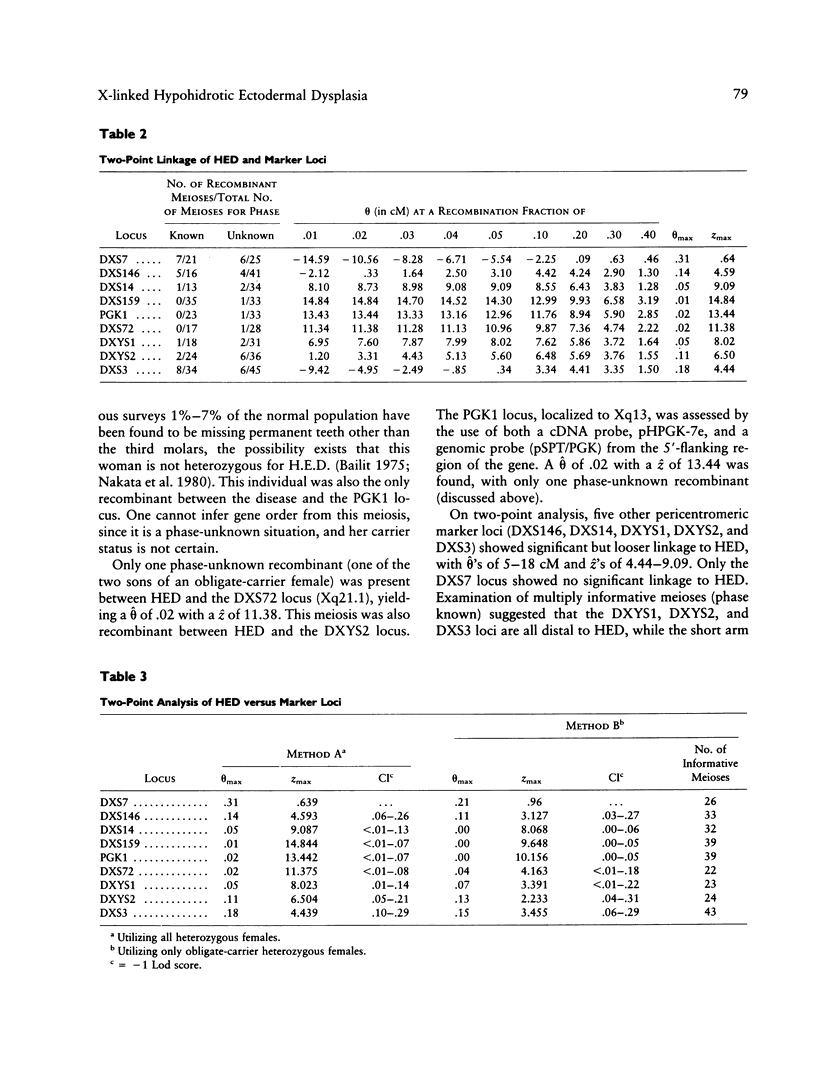
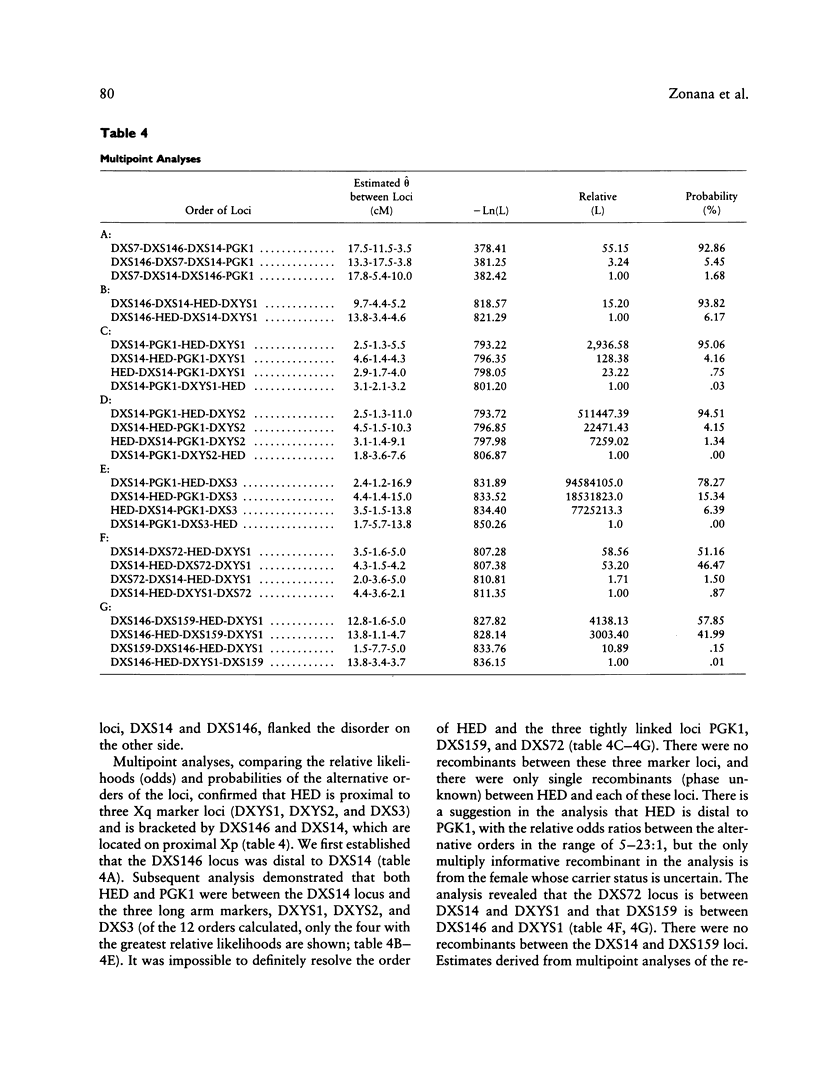
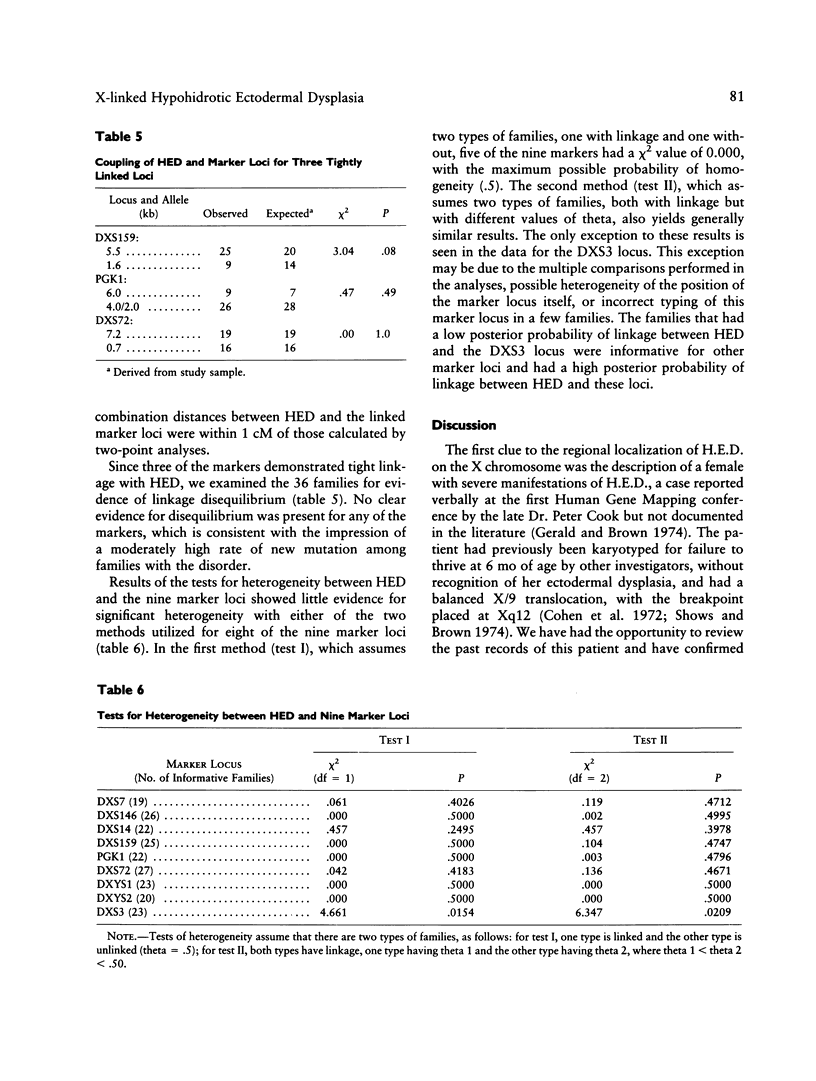
X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (H.E.D.) is a disorder of abnormal morphogenesis of ectodermal structures and is of unknown pathogenesis. Neither relatively accurate carrier detection nor prenatal diagnosis has been available. Previous localization of the disorder by linkage analysis utilizing restriction-fragment polymorphisms, by our group and others, has placed the disorder in the general pericentromeric region. We have extended our previous study by analyzing 36 families by means of 10 DNA probes at nine marker loci and have localized the disorder to the region Xq11-Xq21.1, probably Xq12-Xq13. Three loci--DXS159 (theta = .01, z = 14.84), PGK1 (theta = .02, z = 13.44), and DXS72 (theta = .02, z = 11.38)--show very close linkage to the disorder, while five other pericentromeric loci (DXS146, DXS14, DXYS1, DXYS2, and DXS3) display significant but looser linkage. Analysis of the linkage data yields no significant evidence for nonallelic heterogeneity for the X-linked form of the disorder. Both multipoint analysis and examination of multiply informative meioses with known phase establish that the locus for H.E.D. is flanked on one side by the proximal long arm loci DXYS1, DXYS2, and DXS3 and on the other side by the short arm loci DXS146 and DXS14. Multipoint mapping could not resolve the order of H.E.D. and the three tightly linked loci. This order can be inferred from published data on physical mapping of marker loci in the pericentromeric region, which have utilized somatic cell hybrid lines established from a female with severe manifestations of H.E.D., and an X/9 translocation (breakpoint Xq13.1). If one assumes that the breakpoint of the translocation is within the locus for H.E.D. and that there has not been a rearrangement in the hybrid line, then DXS159 would be proximal to the disorder and PGK1 and DXS72 would be distal to the disorder. Both accurate carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis are now feasible in a majority of families at risk for the disorder.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold M. L., Rauskolb R., Anton-Lamprecht I., Schinzel A., Schmid W. Prenatal diagnosis of anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Prenat Diagn. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):85–98. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970040202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Mandel J. L. A PstI RFLP detected by probe cpX73 (DXS159) in Xq11-q12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5903–5903. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of nine DNA markers in the q11----q22 region of the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailit H. L. Dental variation among populations. An anthropologic view. Dent Clin North Am. 1975 Jan;19(1):125–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blecher S. R. Anhidrosis and absence of sweat glands in mice hemizygous for the Tabby gene: supportive evidence for the hypothesis of homology between Tabby and human anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia (Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome). J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):720–722. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Phillips D. I., Brown R., Harper P. S. Clinical aspects of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):989–996. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A., Sarfarazi M., Thomas N. S., Roberts K., Harper P. S. X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: DNA probe linkage analysis and gene localization. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):378–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00284112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Lin C. C., Sybert V., Orecchio E. J. Two human X-autosome translocations identified by autoradiography and fluorescence. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Sep;24(5):583–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frias J. L., Smith D. W. Diminished sweat pores in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: a new method for assessment. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):606–610. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald P. S., Brown J. A. Proceedings: Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X Chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1974;13(1):29–34. doi: 10.1159/000130228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Siniscalco M. Identification of a de novo chromosome rearrangement in a man-mouse hybrid clone and its bearing on the cytological map of the human X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):149–156. doi: 10.1159/000130577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happle R., Frosch P. J. Manifestation of the lines of Blaschko in women heterozygous for X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Clin Genet. 1985 May;27(5):468–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Robertson M. E., Fear C. N., Goodship J., Malcolm S., Jay B., Bobrow M., Pembrey M. E. Prenatal diagnosis of X-linked choroideremia with mental retardation, associated with a cytologically detectable X-chromosome deletion. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):286–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00281076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutz M. H., Michelson A. M., Antonarakis S. E., Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Restriction site polymorphism in the phosphoglycerate kinase gene on the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00286604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith D. H., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Active X chromosome DNA is unmethylated at eight CCGG sites clustered in a guanine-plus-cytosine-rich island at the 5' end of the gene for phosphoglycerate kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4122–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinebrecht J., Degenhardt K. H., Grubisic A., Günther E., Svejcar J. Sweat pore counts in ectodermal dysplasias. Hum Genet. 1981;57(4):437–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00281701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Moisan J. P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Homologies between X and Y chromosomes detected by DNA probes: localisation and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5485–5501. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kølvraa S., Kruse T. A., Jensen P. K., Linde K. H., Vestergaard S. R., Bolund L. Close linkage between X-linked ectodermal dysplasia and a cloned DNA sequence detecting a two allele restriction fragment length polymorphism in the region Xp11-q12. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):284–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00282550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko J. G., Lewis R. A., Nussbaum R. L. Multipoint linkage analysis of loci in the proximal long arm of the human X chromosome: application to mapping the choroideremia locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):303–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermot K. D., Winter R. M., Malcolm S. Gene localisation of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (C-S-T syndrome). Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):172–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00282084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata M., Koshiba H., Eto K., Nance W. E. A genetic study of anodontia in X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Nov;32(6):908–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. Ancient linkage groups and frozen accidents. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):259–262. doi: 10.1038/244259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Linkage analysis and family classification under heterogeneity. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Oct;47(Pt 4):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb01001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D., de Martinville B., Barker D., Wyman A., White R., Francke U., Botstein D. Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell D. C., Wang H. S., Beckett J., Chan A., Holden J. J., Mulligan L. M., Phillips M. A., Simpson N. E., Wrogemann K., Hamerton J. L. Regional localization of 18 human X-linked DNA sequences. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;42(3):123–128. doi: 10.1159/000132264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Davis J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. An anonymous single-copy X-chromosome RFLP for DXS72 from Xq13-Xq22 [HGM8 provisional no. DXS72]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5724–5724. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Peters J., Lyon M. F., Evans E. P., Edwards J. H., Buckle V. J. Chromosome maps of man and mouse, III. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):3–18. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Show T. B., Brown J. A. Proceedings: An (Xq+; 9p-) translocation suggests the assignment of G6PD, HPRT, and PGK to the long arm of the X chromosome in somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1974;13(1):146–149. doi: 10.1159/000130259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson A. C., Kerr C. B. On the distribution of frequencies of mutation to genes determining harmful traits in man. Mutat Res. 1967 May-Jun;4(3):339–352. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


