Abstract
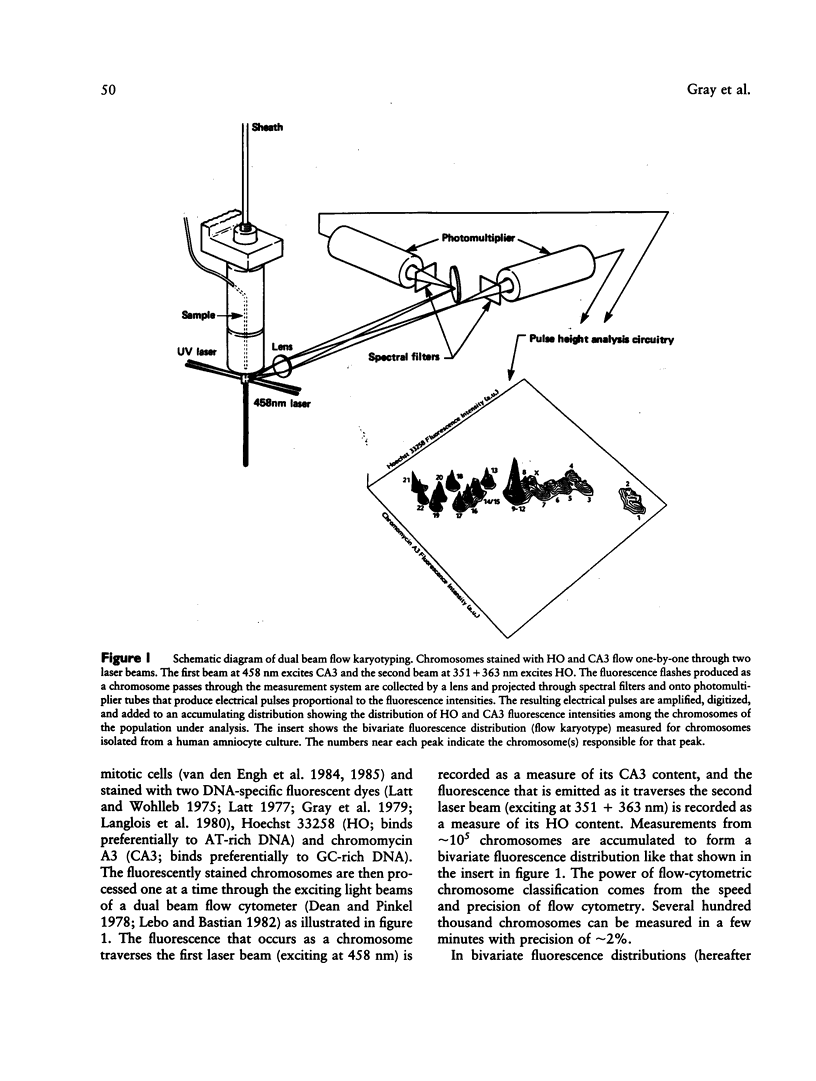
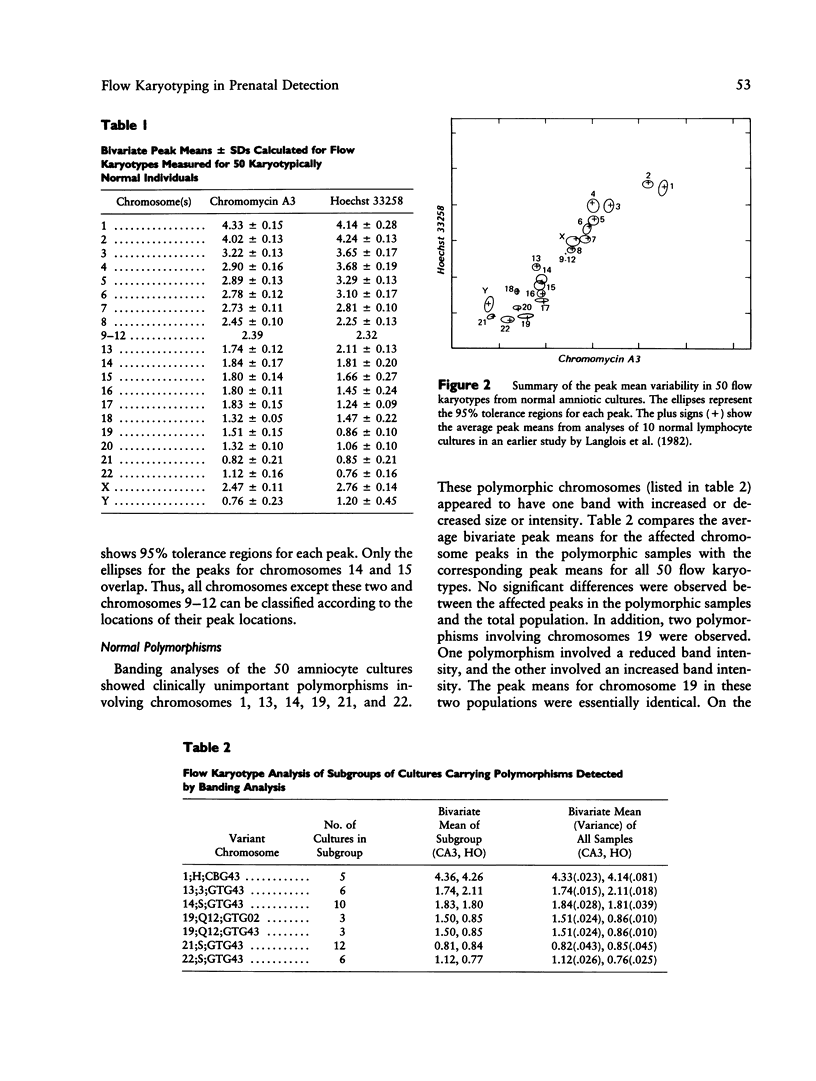
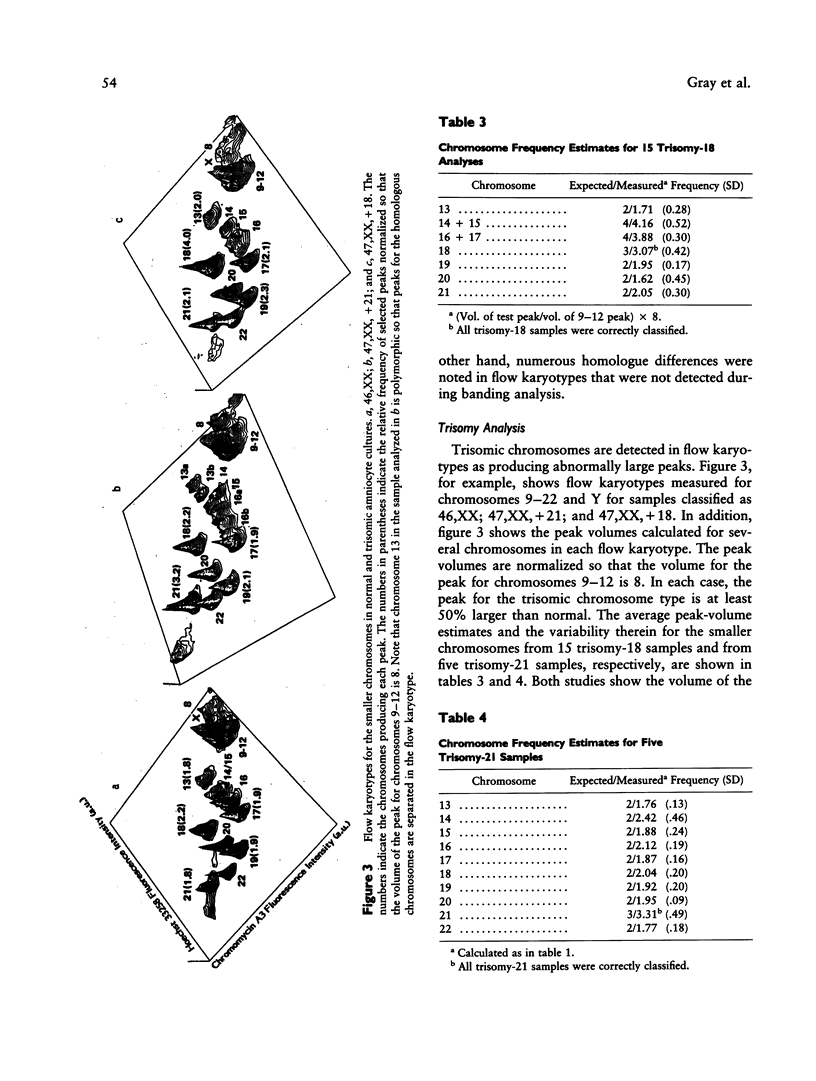
This paper describes the application of bivariate flow karyotyping to (1) classification of chromosomes isolated from cultures of cells taken by amniocentesis and (2) detection of numerical and structural aberrations. Chromosomes were isolated from primary cultures 2-5 wk after amniocentesis, stained with Hoechst 33258 and chromomycin A3, and analyzed using dual beam flow cytometry. Information about chromosome DNA content and DNA base composition was derived from the locations of the peaks in the flow karyotypes, each peak being produced by one or more chromosome types with similar DNA content and DNA base composition. Information about the relative frequency of each chromosome type was determined on the basis of the relative volume of the peak for that chromosome type. Cytogenetic information determined on the basis of flow karyotypes was compared with that obtained by visual analysis following G-banding. Variability among the peak means and volumes in flow karyotypes was determined from analyses of 50 normal amniocyte cultures. Numerical aberrations involving chromosomes 21, 18, and Y were detected correctly in all of 28 analyses, including eight in a blind study. Structural aberrations involving chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 6, 9-12, 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22 were detected in all of seven cultures in a blind study. Flow karyotypes proved to be insensitive to small, normally occurring chromosome polymorphisms detected by banding analysis. In addition, a few samples were erroneously scored as having numerical aberrations.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholdi M., Travis G., Cram L. S., Porreca P., Leavitt J. Flow karyology of neoplastic human fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;468:339–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb42051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Modest E. J. Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00282002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. N., Pinkel D. High resolution dual laser flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):622–627. doi: 10.1177/26.8.357646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Kubień E., Van den Berghe H. Excess of mental retardation and/or congenital malformation in reciprocal translocations in man. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00278808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbus M. S., Loughman W. D., Epstein C. J., Halbasch G., Stephens J. D., Hall B. D. Prenatal genetic diagnosis in 3000 amniocenteses. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 25;300(4):157–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901253000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Carrano A. V., Steinmetz L. L., Van Dilla M. A., Moore D. H., 2nd, Mayall B. H., Mendelsohn M. L. Chromosome measurement and sorting by flow systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1231–1234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Langlois R. G. Chromosome classification and purification using flow cytometry and sorting. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:195–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A. Epidemiology of chromosome abnormalities in man. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Mar;105(3):180–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois R. G., Carrano A. V., Gray J. W., Van Dilla M. A. Cytochemical studies of metaphase chromosomes by flow cytometry. Chromosoma. 1980;77(3):229–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00286050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois R. G., Yu L. C., Gray J. W., Carrano A. V. Quantitative karyotyping of human chromosomes by dual beam flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7876–7880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A. Fluorescent probes of chromosome structure and replication. Can J Genet Cytol. 1977 Dec;19(4):603–623. doi: 10.1139/g77-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Wohlleb J. C. Optical studies of the interaction of 33258 Hoechst with DNA, chromatin, and metaphase chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 11;52(4):297–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00364015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebo R. V., Bastian A. M. Design and operation of a dual laser chromosome sorter. Cytometry. 1982 Nov;3(3):213–219. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Cram S., Deaven L. Flow microfluorometric analysis of isolated Chinese hamster chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Sep;94(2):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90519-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Evans H. J., Buckland R. A. New technique for distinguishing between human chromosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 7;232(27):31–32. doi: 10.1038/newbio232031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. D., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Sillar R., Boyd E. High-resolution analysis of human peripheral lymphocyte chromosomes by flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7727–7731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Aten J., Gray J., Carrano A. V. Human chromosome isolation from short-term lymphocyte culture for flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):154–155. doi: 10.1038/293154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. Mid-prophase human chromosomes. The attainment of 2000 bands. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00274682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G. J., Trask B. J., Gray J. W., Langlois R. G., Yu L. C. Preparation and bivariate analysis of suspensions of human chromosomes. Cytometry. 1985 Mar;6(2):92–100. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G., Trask B., Cram S., Bartholdi M. Preparation of chromosome suspensions for flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1984 Mar;5(2):108–117. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



