Abstract
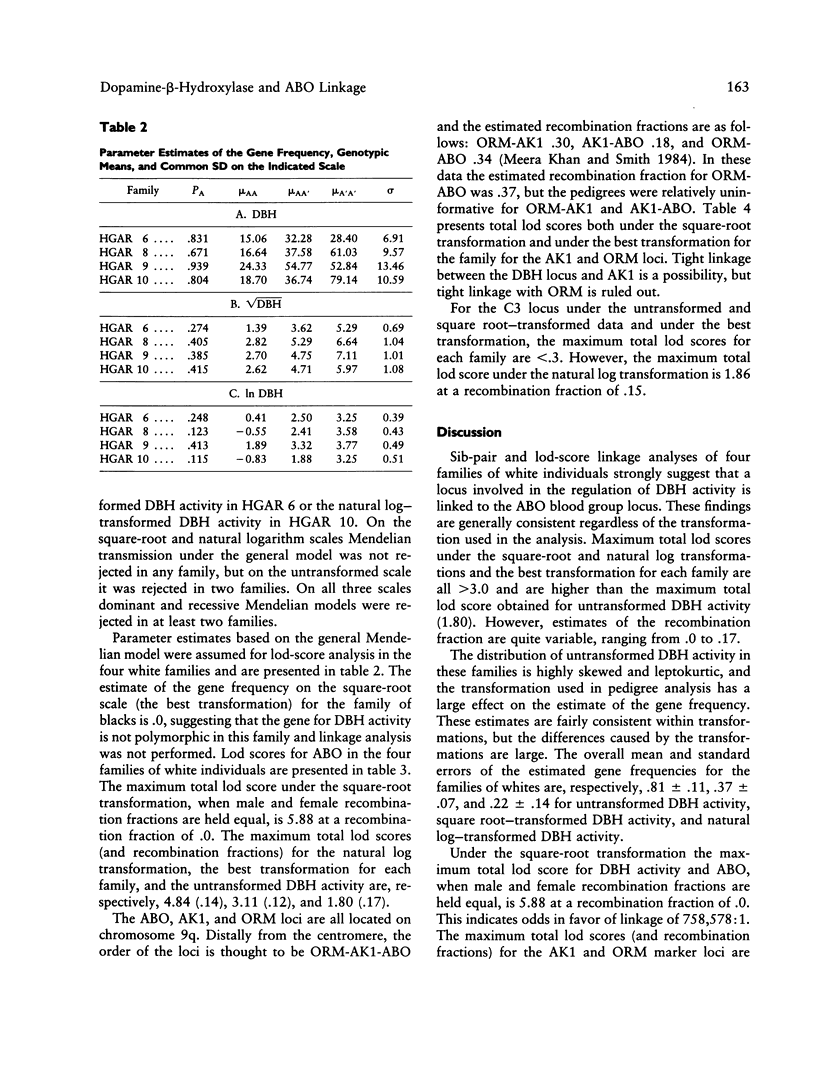
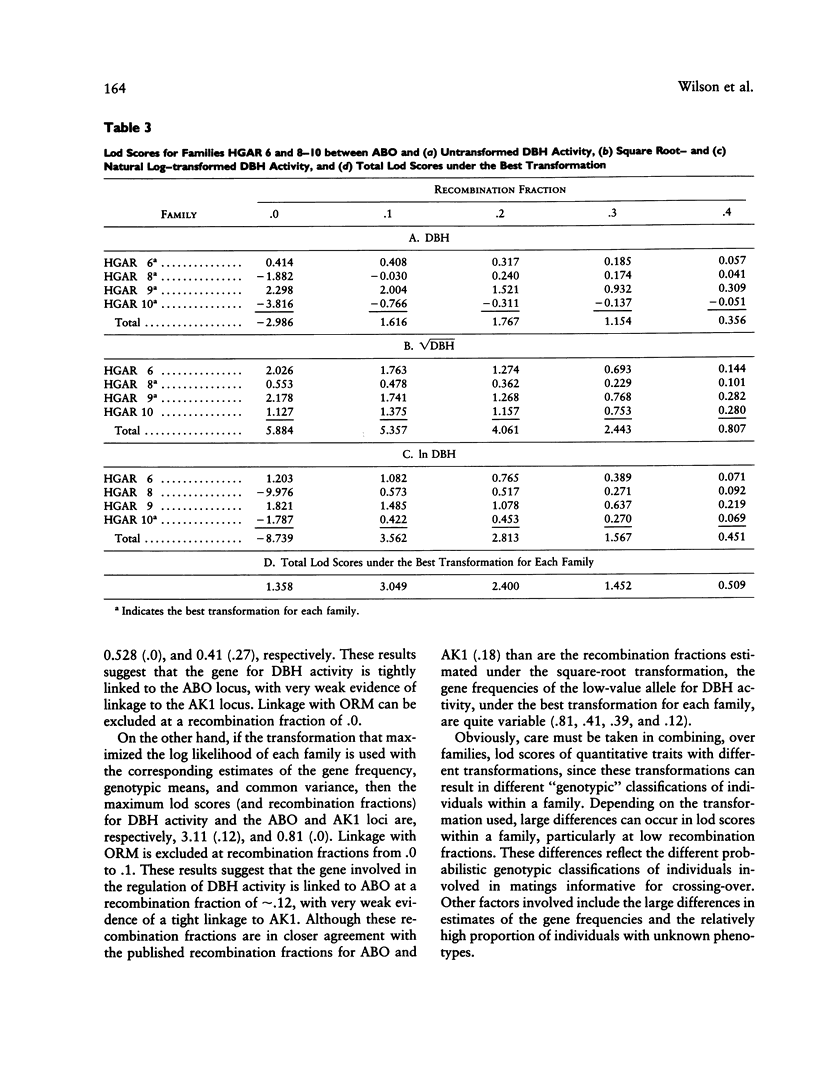
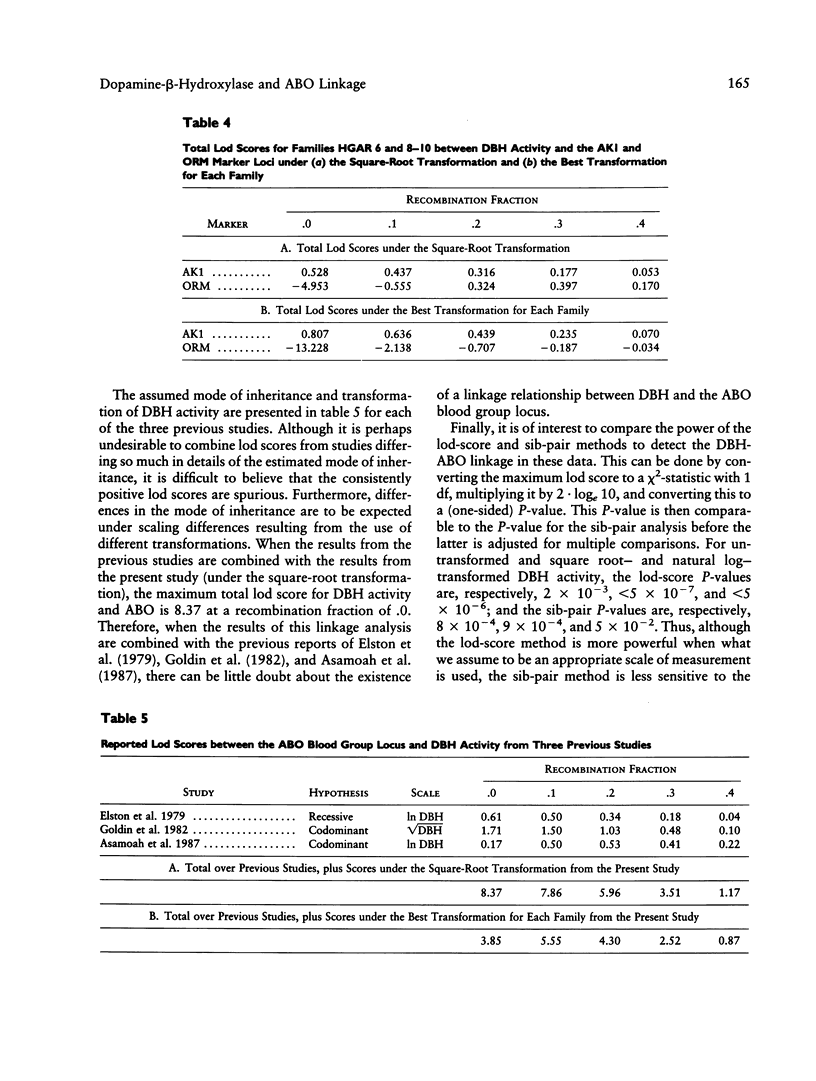
Previous studies have presented evidence suggesting that levels of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH) activity are controlled by a gene linked to the ABO blood group locus. In this study, linkage analyses in four large families of whites and one family of blacks were performed on the untransformed and on the square root--and natural log--transformed DBH activity. In the families of white individuals, the results of both the sib-pair and lod-score linkage analyses strongly indicate that a gene regulating DBH activity is linked to the ABO blood group locus on chromosome 9q (i.e., lod score 5.88 at a recombination fraction of .0). However, the transformation used has a large effect on the maximum lod score and estimated recombination fraction. This putative gene does not appear to be polymorphic in the family of blacks.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asamoah A., Wilson A. F., Elston R. C., Dalferes E., Jr, Berenson G. S. Segregation and linkage analyses of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in a six-generation pedigree. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;27(3):613–621. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwelder W. C., Elston R. C. A comparison of sib-pair linkage tests for disease susceptibility loci. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(1):85–97. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C. Genetic Analysis Workshop II: sib pair screening tests for linkage. Genet Epidemiol. 1984;1(2):175–178. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Namboodiri K. K., Hames C. G. Segregation and linkage analyses of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity. Hum Hered. 1979;29(5):284–292. doi: 10.1159/000153059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Stewart J. A general model for the genetic analysis of pedigree data. Hum Hered. 1971;21(6):523–542. doi: 10.1159/000152448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon E. S., Jonas W. Z. Erythrocyte soluble catechol-O-methyl transferase activity in primary affective disorder. A clinical and genetic study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975 Nov;32(11):1351–1356. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760290019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin L. R., Gershon E. S., Lake C. R., Murphy D. L., McGinniss M., Sparkes R. S. Segregation and linkage studies of plasma dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH), erythrocyte catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), and platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO): possible linkage between the ABO locus and a gene controlling DBH activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):250–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Freedman L. S., Bonnay M. An assay for dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in tissues and serum. Experientia. 1971 Jun;27(6):632–633. doi: 10.1007/BF02136929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseman J. K., Elston R. C. The investigation of linkage between a quantitative trait and a marker locus. Behav Genet. 1972 Mar;2(1):3–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01066731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S., FRIEDMAN S. DOPAMINE-BETA-HYDROXYLASE. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Jun;17:71–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Smith M. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 7, 8 and 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):71–102. doi: 10.1159/000132005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. A sensitive enzymatic assay for dopamine- -hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Sep;178(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T., Udenfriend S. Photometric assay of dopamine- -hydroxylase activity in human blood. Clin Chem. 1972 Sep;18(9):980–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siervogel R. M., Frey M. A., Kezdi P., Roche A. F., Stanley E. L. Blood pressure, electrolytes, and body size: their relationships in young relatives of men with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4 Pt 2):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siervogel R. M., Weinshilboum R., Wilson A. F., Elston R. C. Major gene model for the inheritance of catechol-O-methyltransferase activity in five large families. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Oct;19(2):315–323. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R. M., Schorott H. G., Raymond F. A., Weidman W. H., Elveback L. R. Inheritance of very low serum dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):573–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R. M. Serum dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Jun;30(2):133–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. F., Elston R. C., Siervogel R. M., Weinshilboum R., Ward L. J. Linkage relationships between a major gene for catechol-o-methyltransferase activity and 25 polymorphic marker systems. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Nov;19(3):525–532. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


