Abstract
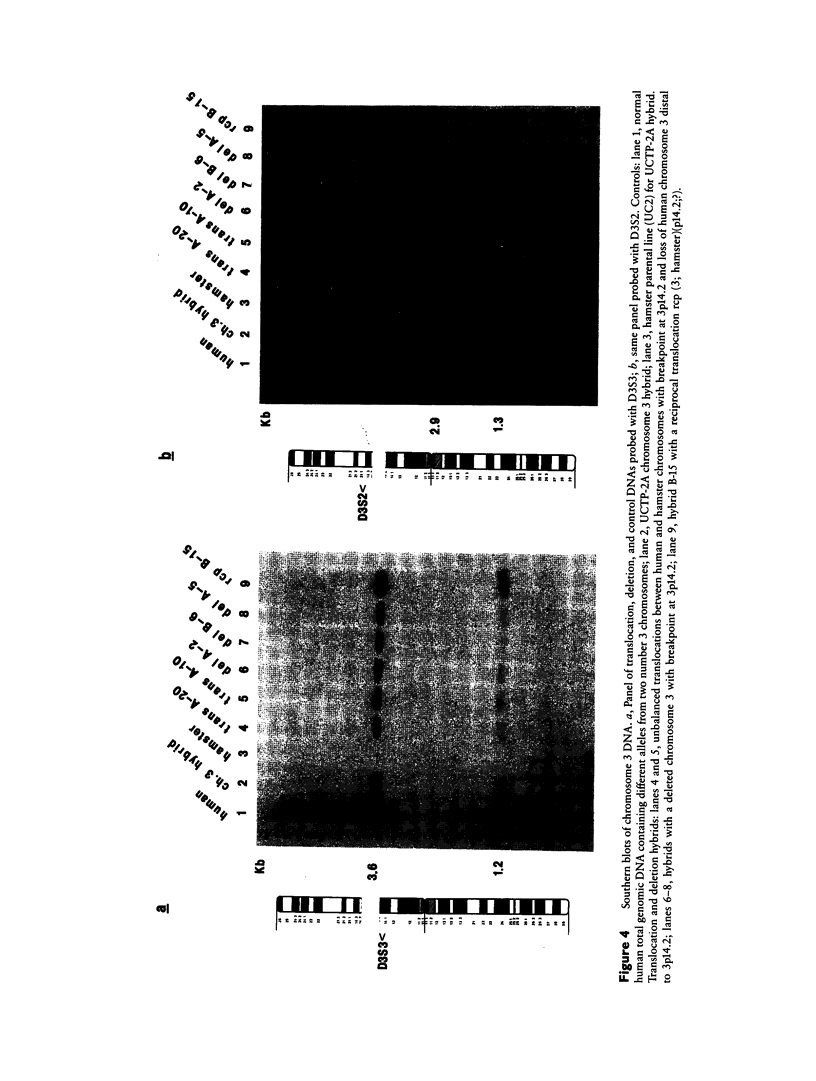
Chromosomal fragile sites are points on chromosomes that usually appear as nonstaining chromosome or chromatid gaps. It has frequently been suggested that fragile sites may be involved in chromosome breakage and recombination events. We and others have previously shown that fragile sites predispose to intrachromosomal recombination as measured by sister-chromatid exchanges. These findings suggested that fragile site expression often, if not always, is accompanied by DNA strand breakage. In the present report, fragile sites are shown to predispose to deletions and interchromosomal recombination. By use of somatic cell hybrids containing either human chromosome 3 or the fragile X chromosome, deletions and translocations were induced by FUdR or aphidicolin with breakpoints at the fragile sites Xq27 or 3p14.2 (FRA3B) or at points so close to the fragile sites as to be cytogenetically indistinguishable. Southern blot analysis of DNA from a panel of chromosome 3 deletion and translocation hybrids was then utilized to detect loss or retention of markers flanking FRA3B and to corroborate the cytogenetic evidence that the breakpoints were at this fragile site. One cell line with a reciprocal translocation between human chromosome 3 (with breakpoint at 3p14.2) and a hamster chromosome showed cytogenetically that the fragile site was expressed on both derivative chromosomes, supporting the hypothesis that the fragile site represents a repeated sequence. The approach described provides a means of generating specific rearrangements in somatic cell hybrids with a breakpoint at a fragile site.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur D. C., Bloomfield C. D. Banded chromosome analysis in patients with treatment-associated acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Jul;12(3):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. J., Miller Y. E., Drabkin H. A., Scoggin C. H. Regional assignment of the polymorphic probe D3S3 to 3p14 by molecular hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;42(1-2):72–74. doi: 10.1159/000132254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W., Berger C., Coyle J., Echo B. DNA polymerase alpha inhibition by aphidicolin induces gaps and breaks at common fragile sites in human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):136–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00272988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W. FUdR induction of the X chromosome fragile site: evidence for the mechanism of folic acid and thymidine inhibition. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Mar;33(2):234–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W., Stein C. K. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges at common fragile sites. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;41(5):882–890. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Morton C. C., Guglielmi P., Li F., Kelly K., Latt S. A. Mapping by chromosome sorting of several gene probes, including c-myc, to the derivative chromosomes of a 3;8 translocation associated with familial renal cancer. Cytometry. 1986 Nov;7(6):589–594. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., Glover T. W. Cancer chromosome breakpoints and common fragile sites induced by aphidicolin. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Oct;13(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBeau M. M., Rowley J. D. Heritable fragile sites in cancer. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):607–608. doi: 10.1038/308607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S. A., Nussbaum R. L. Implications of fragile X expression in normal males for the nature of the mutation. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):161–163. doi: 10.1038/324161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Johnson B. E., Minna J. D., Sakaguchi A. Y. Loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 3p markers in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):451–454. doi: 10.1038/329451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Barker D., White R., Shows T. B. DNA polymorphic loci mapped to human chromosomes 3, 5, 9, 11, 17, 18, and 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. Recombination and amplification of pyrimidine-rich sequences may be responsible for initiation and progression of the Xq27 fragile site: an hypothesis. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):715–721. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Jones C., Morse H., Rumsby P., Miller Y., Davis R. Structural gene coding for multifunctional protein carrying orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and OMP decarboxylase activity is located on long arm of human chromosome 3. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 May;9(3):359–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01539144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Fratini A. Excess thymidine induces folate sensitive fragile sites. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Oct;22(2):433–443. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320220234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommerup N., Poulsen H., Brøndum-Nielsen K. 5-Fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine induction of the fragile site on Xq28 associated with X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1981 Oct;18(5):374–376. doi: 10.1136/jmg.18.5.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Zhang F., Licameli G. R., Peters J. F. The fragile X site in somatic cell hybrids: an approach for molecular cloning of fragile sites. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):420–423. doi: 10.1126/science.3603029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyandt H. E., Wysham D. G., Minden S. K., Anderson R. S., Hecht F. Mechanisms of giemsa banding of chromosomes. I. Giemsa-11 banding with azure and eosin. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L. Constitutive fragile sites and cancer. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1199–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.6239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]