Abstract
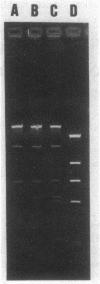
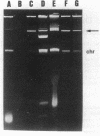
We report the recovery of Salmonella typhi that acquired resistance to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and gentamicin subsequent to multiple antibiotic therapy. Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates which were recovered from the same stool sample displayed identical resistance patterns. Agarose gel electrophoresis revealed that S. typhi and laboratory-derived transconjugants contained a high-molecular-weight plasmid present in the resistant intestinal bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Linh N. N., Arnold K., Pollack M. Chloramphenicol-resistant typhoid fever in Vietnam associated with R factor. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Tauxe R. V. Drug-resistant Salmonella in the United States: an epidemiologic perspective. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.3535069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. L., Wylie B. A., Sooka A., Koornhof H. J. Bacteremia caused by a lactose-fermenting, multiply resistant Salmonella typhi strain in a patient recovering from typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1516–1518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1516-1518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Richards H., Datta C. Salmonella typhi in vivo acquires resistance to both chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1981 May 30;1(8231):1181–1183. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. W., Chumpitaz J. C., Guevara J. M., Papadopoulou B., Acar J. F., Vieu J. F. Plasmid-mediated resistance to multiple antibiotics in Salmonella typhi. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):261–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Cortes A., Bessudo D., Sanchez-Leyva R., Fragoso R., Hinojosa M., Becerril P. Water-borne transmission of chloramphenicol-resistant Salmonella typhi in Mexico. Lancet. 1973 Sep 15;2(7829):605–607. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of R factor compatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):387–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.387-398.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Salmonella typhi: identification, antibiograms, serology, and bacteriophage typing. Am J Med Technol. 1978 Dec;44(12):1149–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Eyckmans L., Rocha H., Prata A., Hook E. W. Comparison of parenteral ampicillin and parenteral chloramphenicol in the treatment of typhoid fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Takahashi M., Yabuuchi E. Lactose-fermenting, multiple drug-resistant Salmonella typhi strains isolated from a patient with postoperative typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):920–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.920-925.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe R. M., Mansuwan P., Duangmani C. Letter: Chloramphenicol--resistant typhoid. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):623–624. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92678-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATNEY T. S., ACHENBACH N. E. New uses for membrane filters III. Bacterial mating procedure. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:874–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.874-875.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olarte J., Galindo E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniker C. K., Vimala K. N. Transferable chloramphenicol resistance in Salmonella typhi. Nature. 1972 Sep 8;239(5367):109–110. doi: 10.1038/239109b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H., Datta N. Plasmids and transposons acquired by Salmonella typhi in man. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Wahab M. F., Raasch F. O. Evaluation of chloramphenicol and ampicillin in salmonella enteric fever. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jan 25;278(4):171–176. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196801252780401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusu V., Baron-Dorobă O., Diamandi S. Salmonella typhi strain with transmissible multiple resistance. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 May;234(4):502–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scragg J. N., Rubidge C. J. Trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole in typhoid fever in children. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 25;3(5777):738–741. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5777.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z., Green P. Thermosensitive antibiotic resistance plasmids in enterobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Chumpitaz J. C., Goldstein F. Variability of IncHI1 plasmids from Salmonella typhi with special reference to Peruvian plasmids encoding resistance to trimethoprim and other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):452–455. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., Rowe B., Threlfall E. J. Incidence of trimethoprim resistance in salmonellae isolated in Britain: a twelve year study. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):705–706. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90723-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley M., Taylor D. E. Identification of DNA homologies among H incompatibility group plasmids by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern transfer hybridization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):194–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]