Abstract
Mutations in the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene result in the autosomal dominant disorder familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Many different LDL receptor mutations have been identified and characterized, demonstrating a high degree of allelic heterogeneity at this locus. The ability to identify mutant LDL receptor genes for prenatal diagnosis of homozygous FH or to study the role of the LDL receptor gene in polygenic hypercholesterolemia requires the use of closely linked RFLPs. In the present study we used 10 different RFLPs, including three newly described polymorphisms, to construct 123 independent haplotypes from 20 Caucasian American pedigrees. Our sample contained 31 different haplotypes varying in frequency from 0.8% to 29.3%; the five most common haplotypes account for 67.5% of the sample. The heterozygosity and PIC of each site were determined, and these values disclosed that eight of the RFLPs were substantially polymorphic. Linkage-disequilibrium analysis of the haplotype data revealed strong nonrandom associations among all 10 RFLPs, especially among those sites clustered in the 3' region of the gene. Evolutionary analysis suggests the occurrence of both mutational and recombinational events in the generation of the observed haplotypes. A strategy for haplotype analysis of the LDL receptor gene in individuals of Caucasian American descent is presented.
Full text
PDF


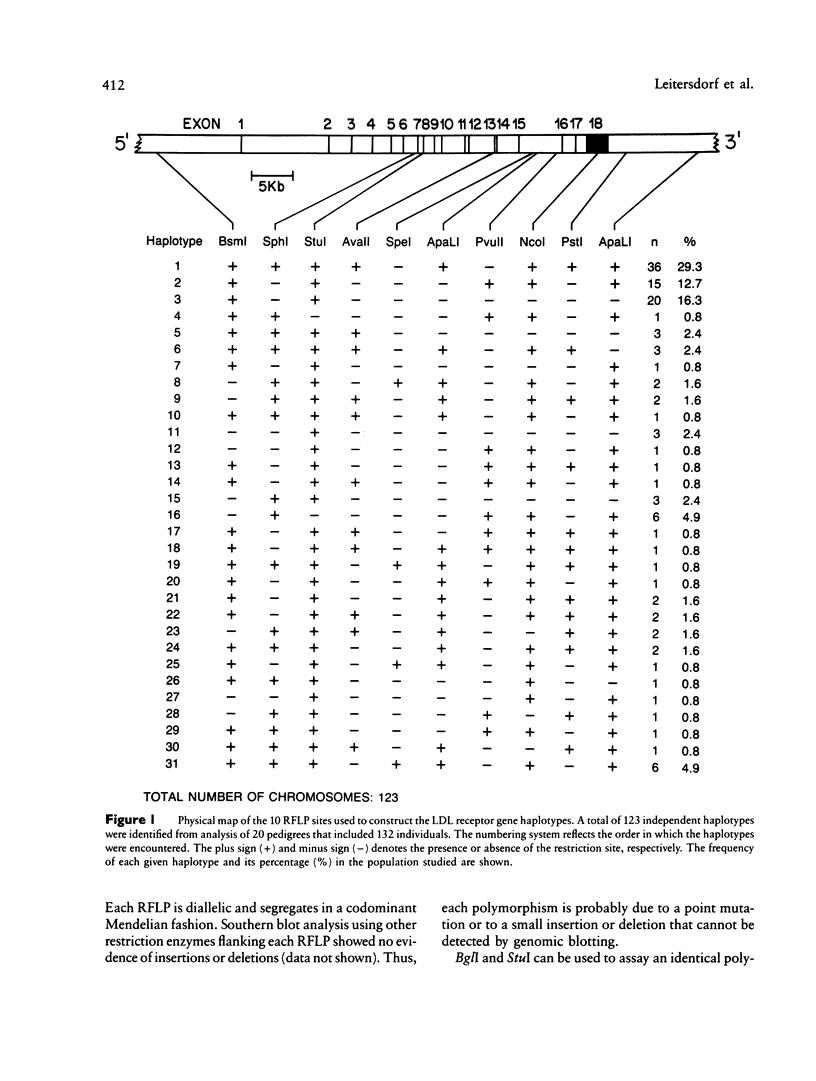

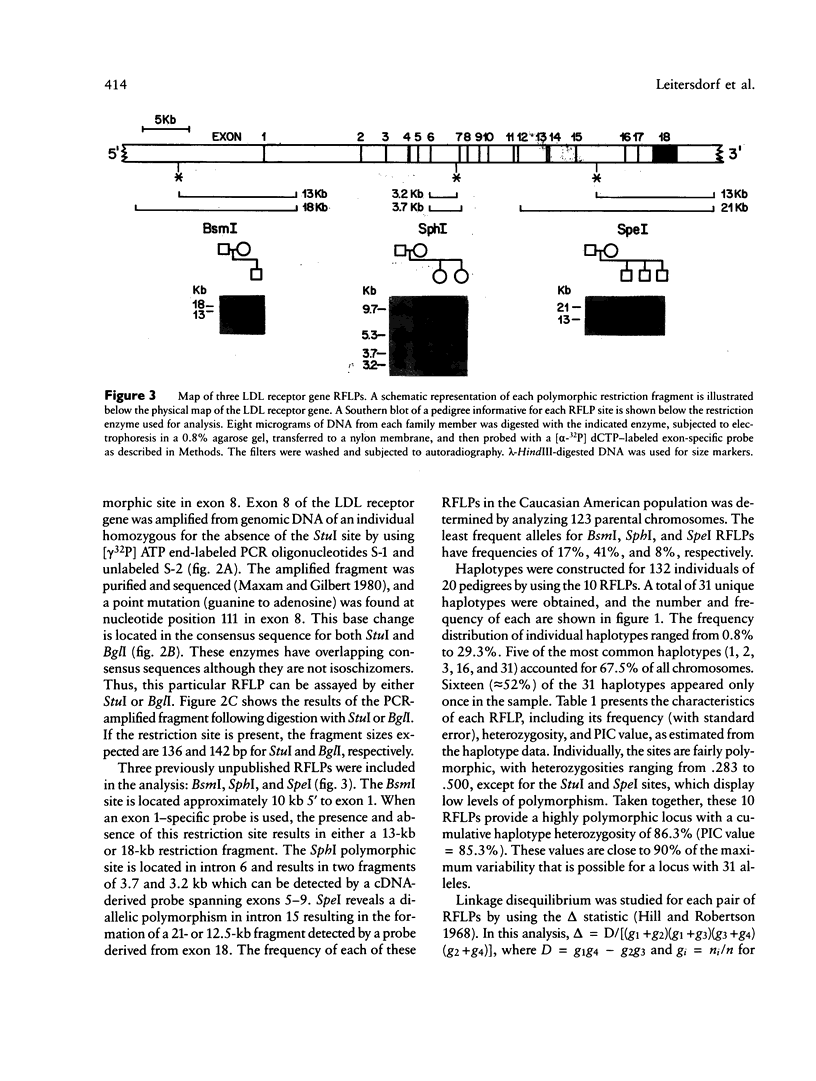
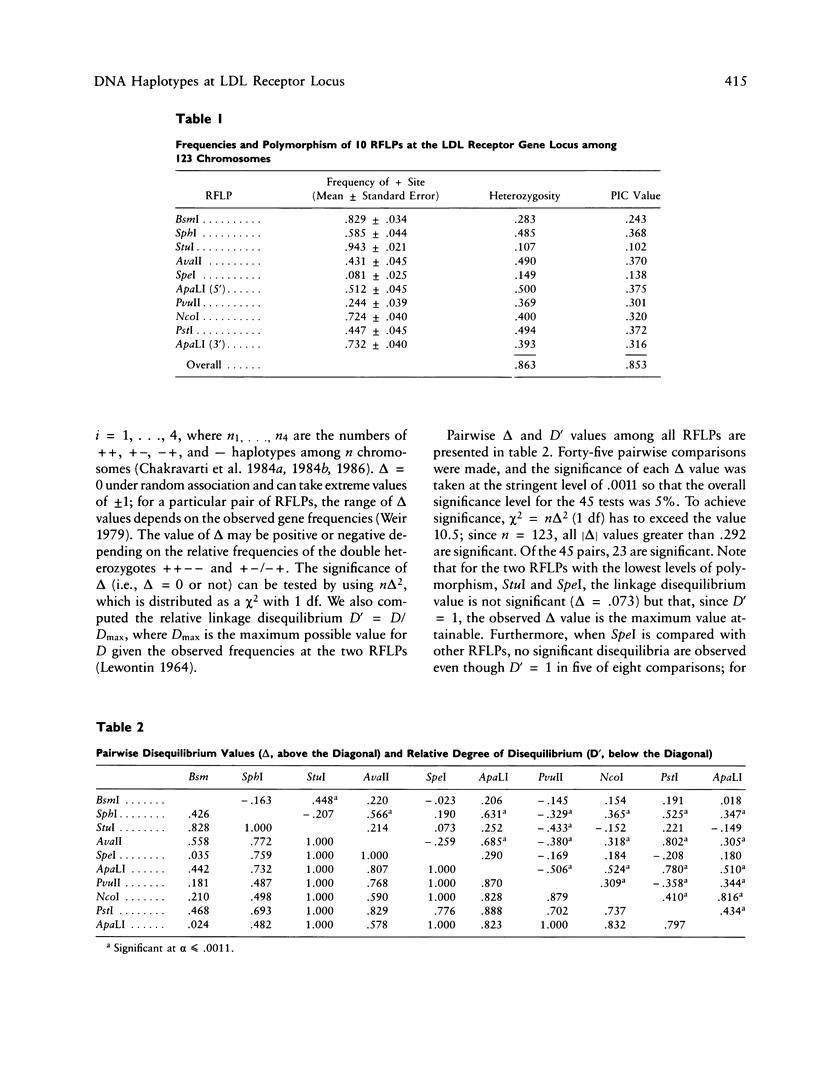




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Oettgen P., Chakravarti A., Halloran S. L., Hudson R. R., Feisee L., Karathanasis S. K. DNA polymorphism haplotypes of the human apolipoprotein APOA1-APOC3-APOA4 gene cluster. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):265–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01790095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Holm T., White R. A locus on chromosome 11p with multiple restriction site polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1159–1171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Apolipoprotein genetic variation and human disease. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jan;68(1):85–132. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Lidsky A. S., Daiger S. P., Güttler F., Sullivan S., Dilella A. G., Woo S. L. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and their relationship with phenylketonuria. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00283048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H. A strategy for using multiple linked markers for genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):984–997. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Elbein S. C., Permutt M. A. Evidence for increased recombination near the human insulin gene: implication for disease association studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Mellits K. H., Buetow K. H., Seeburg P. H. Patterns of polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium suggest independent origins of the human growth hormone gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6085–6089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The J.D. mutation in familial hypercholesterolemia: amino acid substitution in cytoplasmic domain impedes internalization of LDL receptors. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90533-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Brayton K., Woo S. L. An amino-acid substitution involved in phenylketonuria is in linkage disequilibrium with DNA haplotype 2. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):333–336. doi: 10.1038/327333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funke H., Klug J., Frossard P., Coleman R., Assmann G. Pst I RFLP close to the LDL receptor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7820–7820. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Schrott H. G., Hazzard W. R., Bierman E. L., Motulsky A. G. Hyperlipidemia in coronary heart disease. II. Genetic analysis of lipid levels in 176 families and delineation of a new inherited disorder, combined hyperlipidemia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1544–1568. doi: 10.1172/JCI107332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion of exon encoding cysteine-rich repeat of low density lipoprotein receptor alters its binding specificity in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13114–13120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Russell D. W., Davignon J., Goldstein J. L. Deletion in the gene for the low-density-lipoprotein receptor in a majority of French Canadians with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 17;317(12):734–737. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709173171204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Esser V., Russell D. W. AvaII polymorphism in the human LDL receptor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):379–379. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Lehrman M. A., Yamamoto T., Russell D. W. Polymorphism and evolution of Alu sequences in the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7651–7655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Leitersdorf E., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. Multiple crm- mutations in familial hypercholesterolemia. Evidence for 13 alleles, including four deletions. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):909–917. doi: 10.1172/JCI113402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B., Beisiegel U., Dunning A., Havinga J. R., Williamson R., Humphries S. Unequal crossing-over between two alu-repetitive DNA sequences in the low-density-lipoprotein-receptor gene. A possible mechanism for the defect in a patient with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S. E., Kessling A. M., Horsthemke B., Donald J. A., Seed M., Jowett N., Holm M., Galton D. J., Wynn V., Williamson R. A common DNA polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene and its use in diagnosis. Lancet. 1985 May 4;1(8436):1003–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91611-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W. New application for DNA polymorphism. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):478–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotze M. J., Langenhoven E., Dietzsch E., Retief A. E. A RFLP associated with the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene (LDLR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):376–376. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotze M. J., Retief A. E., Brink P. A., Weich H. F. A DNA polymorphism in the human low-density lipoprotein receptor gene. S Afr Med J. 1986 Jul 19;70(2):77–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Internalization-defective LDL receptors produced by genes with nonsense and frameshift mutations that truncate the cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Duplication of seven exons in LDL receptor gene caused by Alu-Alu recombination in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Exon-Alu recombination deletes 5 kilobases from the low density lipoprotein receptor gene, producing a null phenotype in familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3679–3683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S., Davis C. G., Elhammer A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L. The Lebanese allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus. Nonsense mutation produces truncated receptor that is retained in endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Hobbs H. H. Human LDL receptor gene: two ApaLI RFLPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2782–2782. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewontin R C. The Interaction of Selection and Linkage. I. General Considerations; Heterotic Models. Genetics. 1964 Jan;49(1):49–67. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul H., Galton D., Stocks J. DNA polymorphic patterns and haplotype arrangements of the apo A-1, apo C-III, apo A-IV gene cluster in different ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):264–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00281071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Deeb S., Walker D., Motulsky A. G. The detection of linkage disequilibrium between closely linked markers: RFLPs at the AI-CIII apolipoprotein genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):113–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Goldstein J. L., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S. Posttranslational processing of the LDL receptor and its genetic disruption in familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Hobgood K. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The LDL receptor locus in familial hypercholesterolemia: multiple mutations disrupt transport and processing of a membrane receptor. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainscoat J. S., Bell J. I., Thein S. L., Higgs D. R., Sarjeant G. R., Peto T. E., Weatherall D. J. Multiple origins of the sickle mutation: evidence from beta S globin gene cluster polymorphisms. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Sep;1(2):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson G. A., Guess H. A. Is the most frequent allele the oldest? Theor Popul Biol. 1977 Apr;11(2):141–160. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(77)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S. Inferences about linkage disequilibrium. Biometrics. 1979 Mar;35(1):235–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]