Abstract
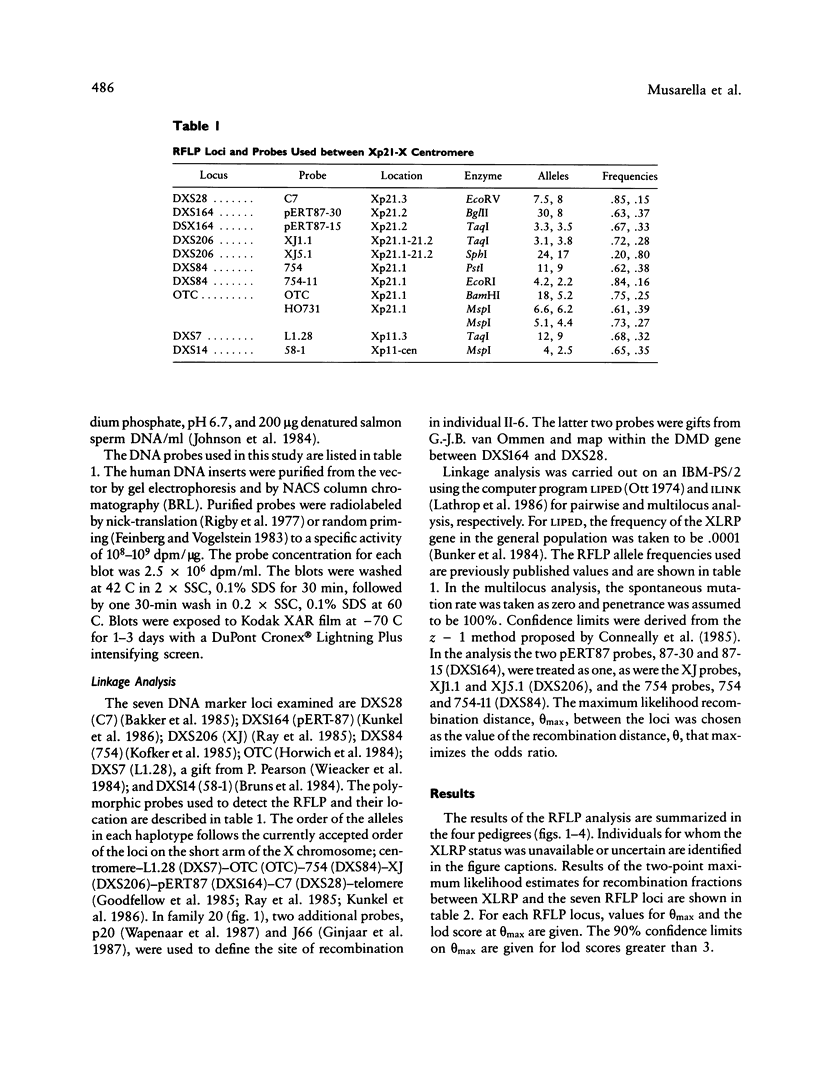
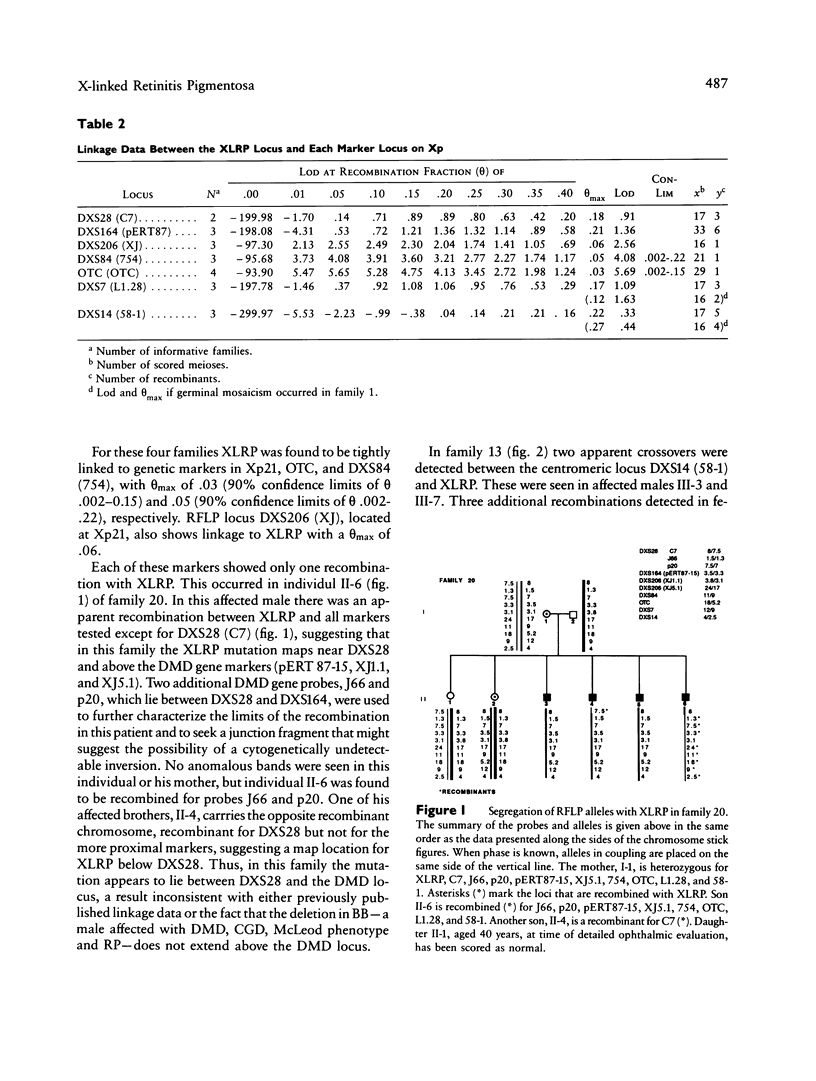
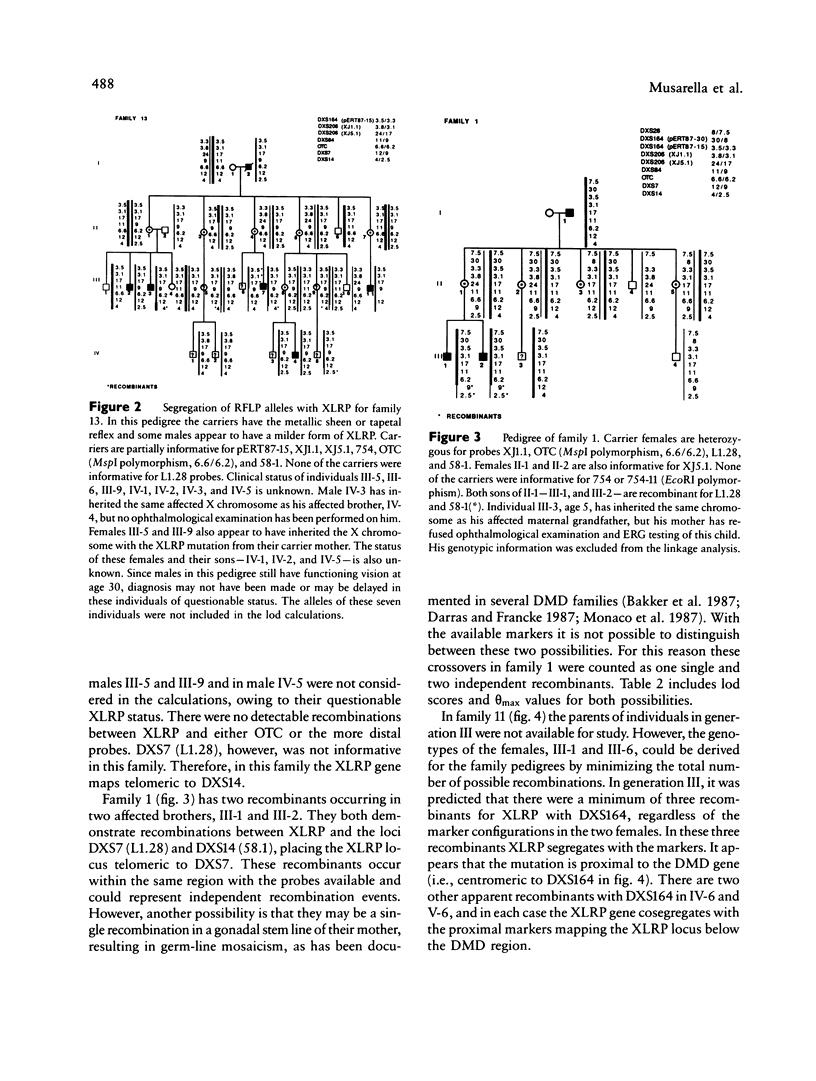
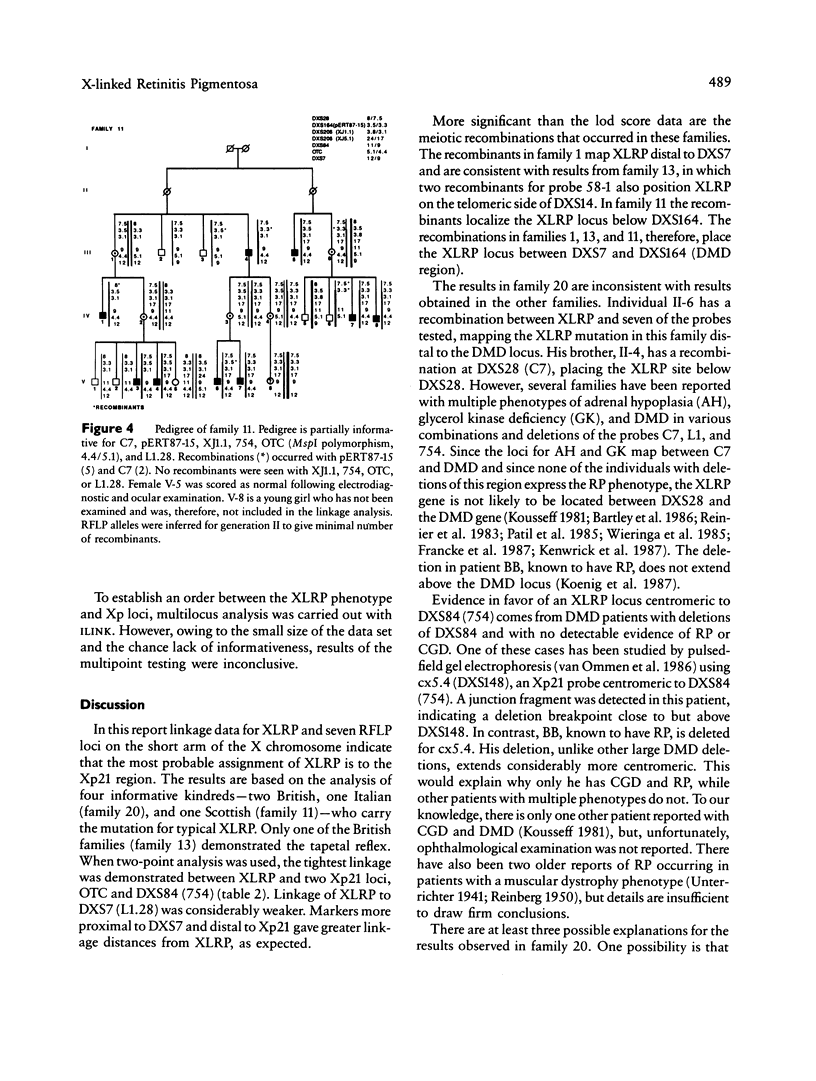
The X-linked recessive type of retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP) causes progressive night blindness, visual field constriction, and eventual blindness in affected males by the third or fourth decade of life. The biochemical basis of the disease is unknown, and prenatal diagnosis and definitive carrier diagnosis remain elusive. Heterogeneity in XLRP has been suggested by linkage studies of families affected with XLRP and by phenotypic differences observed in female carriers. Localization of XLRP near Xp11.3 has been suggested by close linkage to an RFLP at the locus DXS7 (Xp11.3) detected by probe L1.28. In other studies a locus for XLRP with metallic sheen has been linked to the ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) locus mapping to the Xp21 region. In this study, by linkage analysis using seven RFLP markers between Xp21 and Xcen, we examined four families with multiple affected individuals. Close linkage was found between XLRP and polymorphic sites OTC (theta = .06 with lod 5.69), DXS84 (theta = .05 with lod 4.08), and DXS206 (theta = .06 with lod 2.56), defined by probes OTC, 754, and XJ, respectively. The close linkage of OTC, 754, and XJ to XLRP localizes the XLRP locus to the Xp21 region. Data from recombinations in three of four families place the locus above L1.28 and below the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene, consistent with an Xp21 localization. In one family, however, one affected male revealed a crossover between XLRP and all DNA markers, except for the more distal DXS28 (C7), while his brother is recombined for this marker (C7) and not other, more proximal markers. This suggests that in this family the XLRP mutation maps near DXS28 and above the DMD locus.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Van Broeckhoven C., Bonten E. J., van de Vooren M. J., Veenema H., Van Hul W., Van Ommen G. J., Vandenberghe A., Pearson P. L. Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):554–556. doi: 10.1038/329554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley J. A., Patil S., Davenport S., Goldstein D., Pickens J. Duchenne muscular dystrophy, glycerol kinase deficiency, and adrenal insufficiency associated with Xp21 interstitial deletion. J Pediatr. 1986 Feb;108(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80980-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Simonoff E. Risk factors for genetic typing and detection in retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Jun;89(6):763–775. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelson C. J., Pogo A. O., Chaudhuri A., Marsh W. L., Redman C. M., Banerjee D., Symmans W. A., Simon T., Frey D., Kunkel L. M. Localization of the McLeod locus (XK) within Xp21 by deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):703–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S. S., Wright A. F., Clayton J. F., Price W. H., Phillips C. I., McKeown C. M., Jay M., Bird A. C., Pearson P. L., Southern E. M. Close genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and a restriction fragment length polymorphism identified by recombinant DNA probe L1.28. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):253–255. doi: 10.1038/309253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. C., Blach R. K. X-linked recessive fundus dystrophies and their carrier states. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1970;90:127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. C. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Apr;59(4):177–199. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.4.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughman J. A., Conneally P. M., Nance W. E. Population genetic studies of retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):223–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunker C. H., Berson E. L., Bromley W. C., Hayes R. P., Roderick T. H. Prevalence of retinitis pigmentosa in Maine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Mar;97(3):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Logan C., Hu X., Belfall B., Worton R. G., Ray P. N. A cDNA clone from the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy gene. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):434–437. doi: 10.1038/328434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton J. F., Wright A. F., Jay M., McKeown C. M., Dempster M., Jay B. S., Bird A. C., Bhattacharya S. S. Genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and DNA probe DXS7 (L1.28): further linkage data, heterogeneity testing, and risk estimation. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00282083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Francke U. A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):556–558. doi: 10.1038/329556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton M. J., Chen J. D., Serravalle S., Colley P., Halliday F. B., Donald J. Analysis of linkage relationships of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa with the following Xp loci: L1.28, OTC, 754, XJ-1.1, pERT87, and C7. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):60–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00291236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS J. Chorioretinal degeneration or retinitis pigmentosa of intermediate sex-linked heredity. Doc Ophthalmol. 1962;16:111–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00146722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A. Retinitis pigmentosa. Genetic percentages. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 May;96(5):822–826. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910050428005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A., Weinberg A. B., McMahon T. T. X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Clinical characteristics of carriers. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Sep;104(9):1329–1335. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050210083030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Harper J. F., Darras B. T., Cowan J. M., McCabe E. R., Kohlschütter A., Seltzer W. K., Saito F., Goto J., Harpey J. P. Congenital adrenal hypoplasia, myopathy, and glycerol kinase deficiency: molecular genetic evidence for deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;40(3):212–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Warburg M., Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Gal A., Ropers H. H. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa: linkage with the centromere and a cloned DNA sequence from the proximal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):93–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00283360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Williams K. R., Kalousek F., Kraus J. P., Doolittle R. F., Konigsberg W., Rosenberg L. E. Structure and expression of a complementary DNA for the nuclear coded precursor of human mitochondrial ornithine transcarbamylase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1068–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.6372096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R. L., Bunt-Milam A. H., Chang M. L., Beavo J. A. cGMP phosphodiesterase in rod and cone outer segments of the retina. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):568–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay B. Hereditary aspects of pigmentary retinopathy. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1972;92:173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Patterson M., Speer A., Fischbeck K., Davies K. Molecular analysis of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy region using pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousseff B. Linkage between chronic granulomatous disease and Duchenne's muscular dystrophy? Am J Dis Child. 1981 Dec;135(12):1149–1149. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130360053025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Eisenhard M., Latt S. A. Regional localization on the human X of DNA segments cloned from flow sorted chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1557–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. L. Construction of human linkage maps: likelihood calculations for multilocus linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):39–52. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae W. G. Retinitis pigmentosa in Ontario - a survey. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1982;18(6):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn L. J., Lischner H. W., Pileggi A. J., Harley R. D. Chorioretinal lesions in familial chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Mar;73(3):403–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Colletti-Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Localization and cloning of Xp21 deletion breakpoints involved in muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00281063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai S., Dryja T. P., Bruns G. A., Aldridge J. F., Berson E. L. Linkage between the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa locus and the L1.28 locus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985 Aug 15;100(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(85)90786-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lewis R. A., Lesko J. G., Ferrell R. Mapping X-linked ophthalmic diseases: II. Linkage relationship of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa to X chromosomal short arm markers. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00389458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINBERG M. H. Progressive muscular dystrophy associated with retinitis pigmentosa. Calif Med. 1950 Sep;73(3):266–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Belfall B., Duff C., Logan C., Kean V., Thompson M. W., Sylvester J. E., Gorski J. L., Schmickel R. D., Worton R. G. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):672–675. doi: 10.1038/318672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renier W. O., Nabben F. A., Hustinx T. W., Veerkamp J. H., Otten B. J., Ter Laak H. J., Ter Haar B. G., Gabreëls F. J. Congenital adrenal hypoplasia, progressive muscular dystrophy, and severe mental retardation, in association with glycerol kinase deficiency, in male sibs. Clin Genet. 1983 Oct;24(4):243–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAPPERT-KIMMIJSER J. LES D'EG'EN'ERESCENCES TAP'ETO-R'ETINIENNES DU TYPE X CHROMOSOMAL AUX PAYS-BAS. Bull Mem Soc Fr Ophtalmol. 1963;76:122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieving P. A., Fishman G. A. Refractive errors of retinitis pigmentosa patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 1978 Mar;62(3):163–167. doi: 10.1136/bjo.62.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szamier R. B., Berson E. L., Klein R., Meyers S. Sex-linked retinitis pigmentosa: ultrastructure of photoreceptors and pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979 Feb;18(2):145–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Davies K. E., Cooke H. J., Pearson P. L., Williamson R., Bhattacharya S., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward a complete linkage map of the human X chromosome: regional assignment of 16 cloned single-copy DNA sequences employing a panel of somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hustinx T., Scheres J., Renier W., ter Haar B. Complex glycerol kinase deficiency syndrome explained as X-chromosomal deletion. Clin Genet. 1985 May;27(5):522–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Baugher B. W., Mattes P. M., Daddona P. E., Kelley W. N. Human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Demonstration of structural variants in lymphoblastoid cells derived from patients with a deficiency of the enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):706–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI110499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S. S., Clayton J. F., Dempster M., Tippett P., McKeown C. M., Jay M., Jay B., Bird A. C. Linkage relationships between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and nine short-arm markers: exclusion of the disease locus from Xp21 and localization to between DXS7 and DXS14. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;41(4):635–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S., Price W. H., Phillips C. I., McKeown C., Crews S. J., Jay M., Bird A. C. DNA probes in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1983;103(Pt 4):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Verkerk J. M., Hofker M. H., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Ray P., Worton R., Wieringa B., Bakker E., Pearson P. L. A physical map of 4 million bp around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the human X-chromosome. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


