Abstract
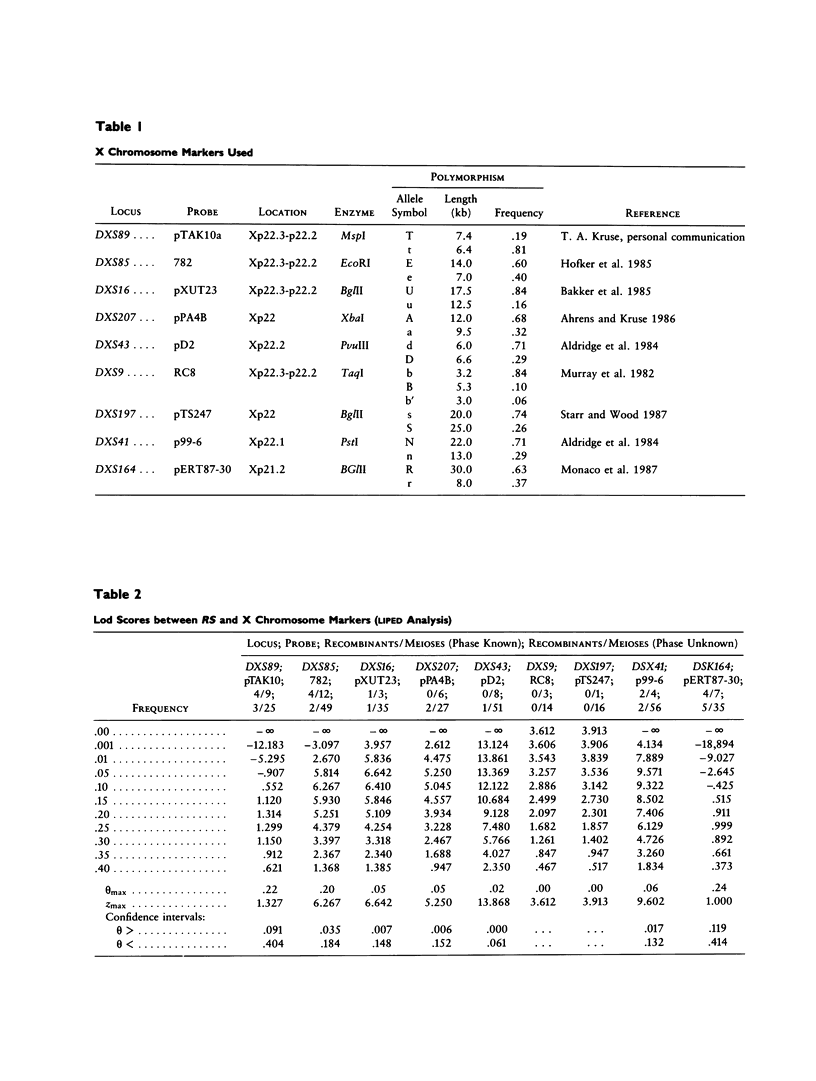
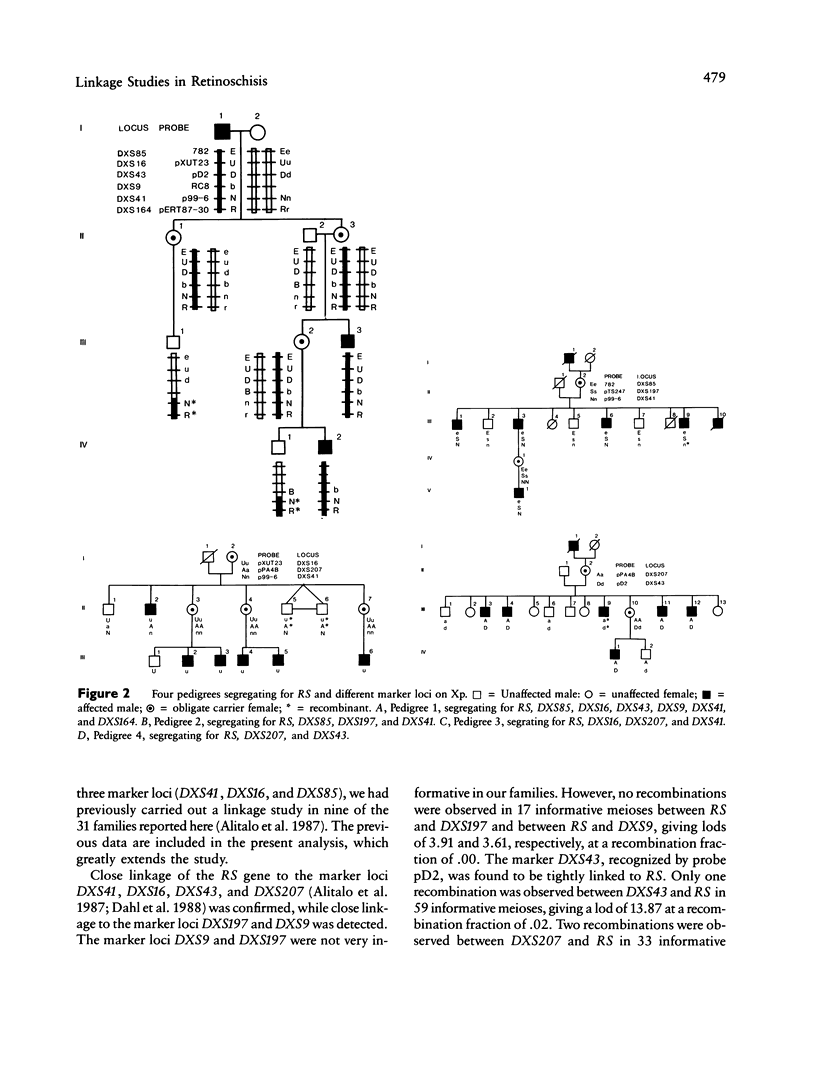
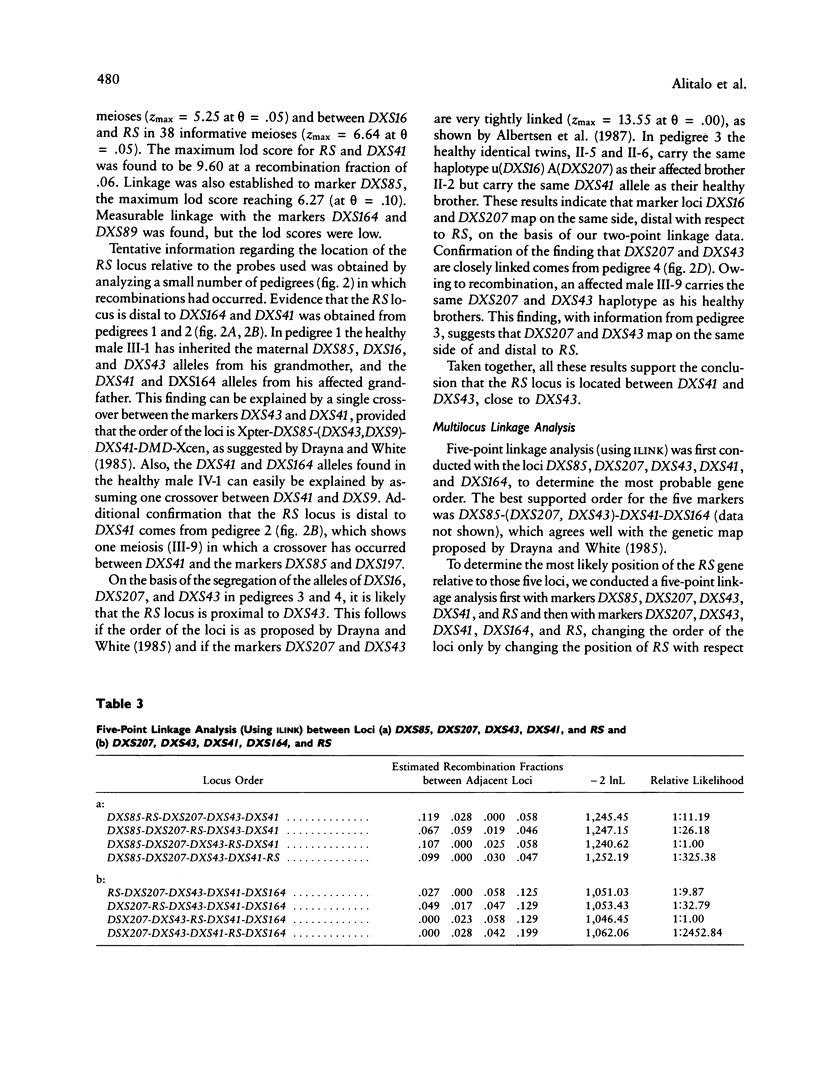
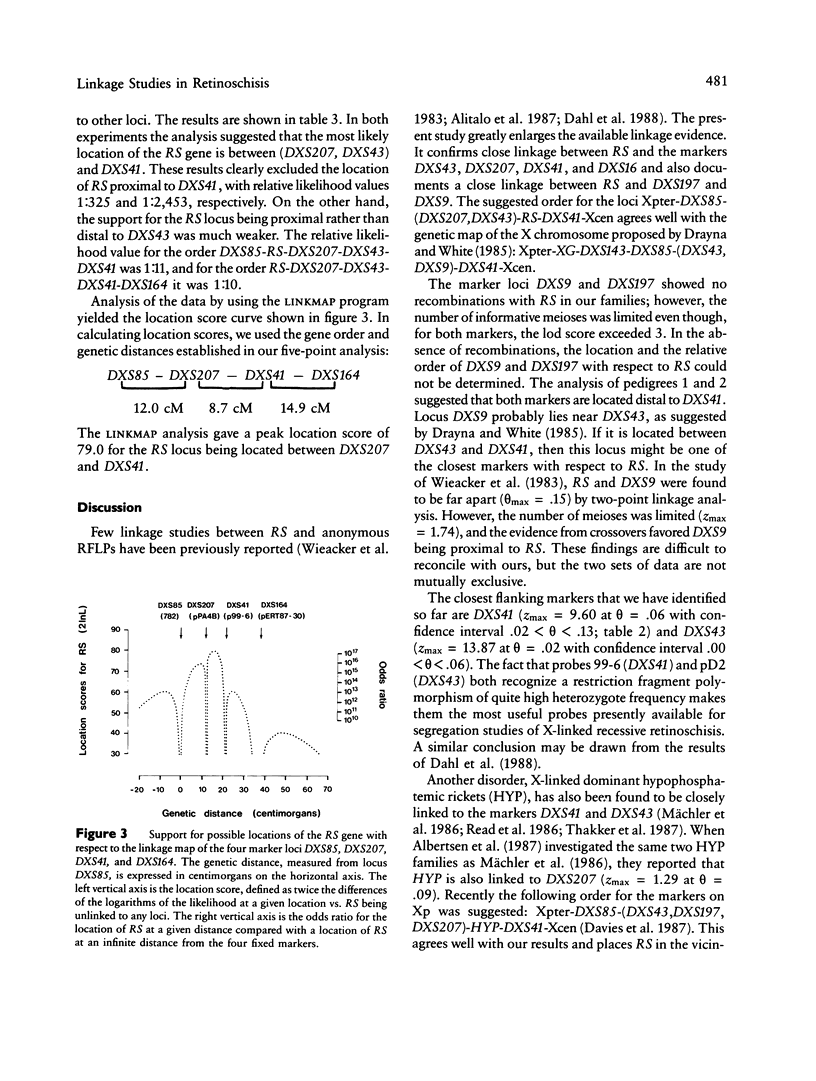
X-linked recessive retinoschisis (RS) is a hereditary disorder with variable clinical features. The main symptoms are poor sight; radial, cystic macula degeneration; and peripheral superficial retinal detachment. The disease is quite common in Finland, where at least 300 hemizygous males have been diagnosed. We used nine polymorphic DNA markers to study the localization of RS on the short arm of the X chromosome in 31 families comprising 88 affected persons. Two-point linkage results confirmed close linkage of the RS gene to the marker loci DXS43, DXS16, DXS207, and DXS41 and also revealed close linkage to the marker loci DXS197 and DXS9. Only one recombination was observed between DXS43 and RS in 59 informative meioses, giving a maximum lod score of 13.87 at the recombination fraction .02. No recombinations were observed between the RS locus and DXS9 and DXS197 (lods between 3 and 4), but at neither locus was the number of informative meioses sufficient to provide reliable estimates of recombination fractions. The most likely gene order on the basis of multilocus analysis was Xpter-DXS85-(DXS207,DXS43)-RS-DXS41-DXS 164-Xcen. Because multilocus linkage analysis indicated that the most probable location of RS is proximal to DXS207 and DXS43 and distal to DXS41, these three flanking markers are the closest and most informative markers currently available for carrier detection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrens P., Kruse T. A. An anonymous X-chromosomal clone identifying a frequent RFLP at Xp21-22 (HGM8 provisional no. DXS207). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7819–7819. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo T., Kärnä J., Forsius H., de la Chapelle A. X-linked retinoschisis is closely linked to DXS41 and DXS16 but not DXS85. Clin Genet. 1987 Sep;32(3):192–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Hofker M. H., Goor N., Mandel J. L., Wrogemann K., Davies K. E., Kunkel L. M., Willard H. F., Fenton W. A., Sandkuyl L. Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with closely linked RFLPs. Lancet. 1985 Mar 23;1(8430):655–658. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91325-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H., Heilig P., Kolder H. E., Giblett E. R., Fialkow P. J. Hereditary retinoschisis linkage studies in a family and considerations in genetic counselling. Can J Ophthalmol. 1976 Jan;11(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Goonewardena P., Chotai J., Anvret M., Pettersson U. DNA linkage analysis of X-linked retinoschisis. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):228–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00291666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Weissenbach J., Fellous M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X and Y chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):277–315. doi: 10.1159/000132481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing C. C., Cullen A. P. Fluorescein angiography in X-chromosomal maculopathy with retinoschisis (juvenile hereditary retinoschisis). Can J Ophthalmol. 1972 Jan;7(1):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsius H., Krause U., Helve J., Vuopala V., Mustonen E., Vainio-Mattila B., Fellman J., Eriksson A. W. Visual acuity in 183 cases of X-chromosomal retinoschisis. Can J Ophthalmol. 1973 Jul;8(3):385–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. S., Yeung J. Maculopathy of sex-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Can J Ophthalmol. 1976 Jan;11(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon T. T., Rosenthal B. P. X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. J Am Optom Assoc. 1983 Jan;54(1):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Colletti-Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Localization and cloning of Xp21 deletion breakpoints involved in muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00281063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Harper P. S., Meredith L., Mueller C. R., Williamson R. Linkage relationship of a cloned DNA sequence on the short arm of the X chromosome to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):69–71. doi: 10.1038/300069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mächler M., Frey D., Gal A., Orth U., Wienker T. F., Fanconi A., Schmid W. X-linked dominant hypophosphatemia is closely linked to DNA markers DXS41 and DXS43 at Xp22. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):271–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00401243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read A. P., Thakker R. V., Davies K. E., Mountford R. C., Brenton D. P., Davies M., Glorieux F., Harris R., Hendy G. N., King A. Mapping of human X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets by multilocus linkage analysis. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00401242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr T., Wood S. Isolation and characterization of DNA probes from the short arm of the human X chromosome that detect restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genome. 1987 Feb;29(1):201–205. doi: 10.1139/g87-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanino T., Katsumi O., Hirose T. Electrophysiological similarities between two eyes with X-linked recessive retinoschisis. Doc Ophthalmol. 1985 Aug 30;60(2):149–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00158030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker R. V., Read A. P., Davies K. E., Whyte M. P., Weksberg R., Glorieux F., Davies M., Mountford R. C., Harris R., King A. Bridging markers defining the map position of X linked hypophosphataemic rickets. J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;24(12):756–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.12.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio-Mattila B., Eriksson A. W., Forsius H. X-chromosomal recessive retinoschisis in the Region of Pori. An ophthalmo-genetical analysis of 103 cases. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1969;47(5):1135–1148. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1969.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdaguer J. Juvenile retinal detachment. Pan American Association of Ophthalmology and American Journal of Ophthalmology Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982 Feb;93(2):145–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Dallapiccola B., Bender K., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Linkage relationships between Retinoschisis, Xg, and a cloned DNA sequence from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):143–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00327111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


