Abstract
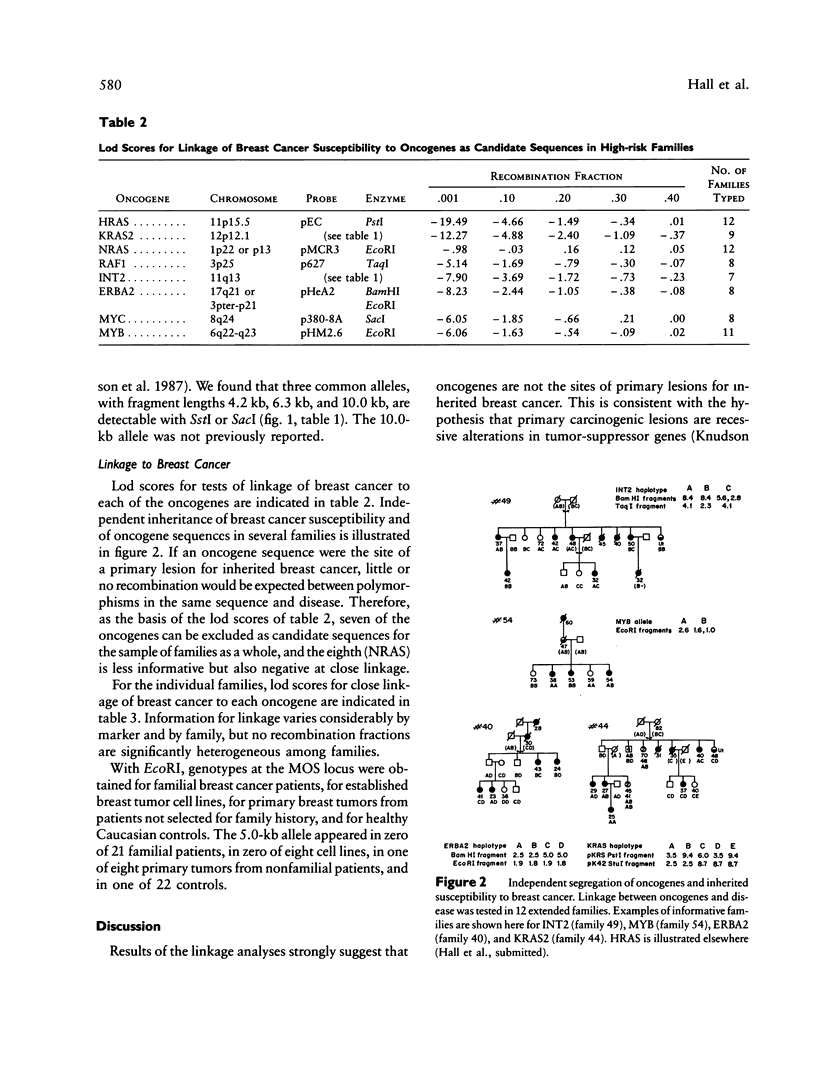
The role of oncogenes in breast tumorigenesis is unclear. Alterations and/or amplification of several oncogene sequences have been observed in primary human breast tumors, in breast tumor cell lines, and in mammary tumors in model systems. In principle, such alterations could be sites of primary lesions for human breast cancer, causes of tumor progression or metastasis, or simply secondary lesions of highly aberrant tumor genomes. The present study tested genetic linkage of breast cancer susceptibility to nine oncogenes in 12 extended families including 87 affected individuals. Lod scores for close linkage of each candidate sequence to breast cancer were -19.6 for HRAS, -12.3 for KRAS2, -1.0 for NRAS, -6.0 for MYC, -6.1 for MYB, -8.2 for ERBA2, -7.9 for INT2, and -5.1 for RAF1. Regions of chromosome 11p associated with tumor homozygosity and the region of 3p carrying the gene for Von Hippel-Lindau disease could also be excluded from linkage to human breast cancer. The 5-kb allele of the MOS oncogene, previously proposed to be associated with breast cancer, was absent in these families, suggesting that polymorphism at this locus is not associated with inherited susceptibility. These results strongly suggest that oncogenes are not the sites of primary alterations leading to breast cancer. On the other hand, alterations in one or more of these sequences may be associated with tumor progression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Lidereau R., Theillet C., Callahan R. Reduction to homozygosity of genes on chromosome 11 in human breast neoplasia. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.3659909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. A., Gusella J. F. Use of cyclosporin A in establishing Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoblastoid cell lines. In Vitro. 1984 Nov;20(11):856–858. doi: 10.1007/BF02619631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., McCoy M., Weinberg R., Goldfarb M., Wigler M., Burt R., Gardner E., White R. A test of the role of two oncogenes in inherited predisposition to colon cancer. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Sep;1(2):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., McGuire W. L. Nuclear thyroid hormone receptors in a human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3769–3773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. L., Corle D. K., Micozzi M. S., Schatzkin A., Taylor P. R. A prospective study of the development of breast cancer in 16,692 women with benign breast disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Sep;128(3):467–477. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey G., Smith R., McGillivray D., Peters G., Dickson C. Characterization and chromosome assignment of the human homolog of int-2, a potential proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):502–510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Brookes S., Peters G. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: proviral activation of a cellular gene in the common integration region int-2. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escot C., Theillet C., Lidereau R., Spyratos F., Champeme M. H., Gest J., Callahan R. Genetic alteration of the c-myc protooncogene (MYC) in human primary breast carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4834–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Middleton P. G., Rout D., De Angelis C. Chromosomal localization of the human oncogene ERBA2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(3-4):150–153. doi: 10.1159/000132313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heighway J., Geurts van Kessel A. H. Anonymous genomic fragment co-amplified with c-Ki-ras 2 detects frequent polymorphism (pK42). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8700–8700. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):820–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Croce C. M. Amplification of the c-myc oncogene in one of five human breast carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):438–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., DiMartino N. A., Colb M., Parkinson D. R. Unique allelic restriction fragments of the human Ha-ras locus in leukocyte and tumour DNAs of cancer patients. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):369–374. doi: 10.1038/313369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidereau R., Callahan R., Dickson C., Peters G., Escot C., Ali I. U. Amplification of the int-2 gene in primary human breast tumors. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidereau R., Cole S. T., Larsen C. J., Mathieu-Mahul D. A single point mutation responsible for c-mos polymorphism in cancer patients. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):235–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidereau R., Mathieu-Mahul D., Theillet C., Renaud M., Mauchauffé M., Gest J., Larsen C. J. Presence of an allelic EcoRI restriction fragment of the c-mos locus in leukocyte and tumor cell DNAs of breast cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7068–7070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse B., Rotherg P. G., South V. J., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):87–90. doi: 10.1038/333087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B., Austin M. A., Lee M., King M. C. Inheritance of human breast cancer: evidence for autosomal dominant transmission in high-risk families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3044–3048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
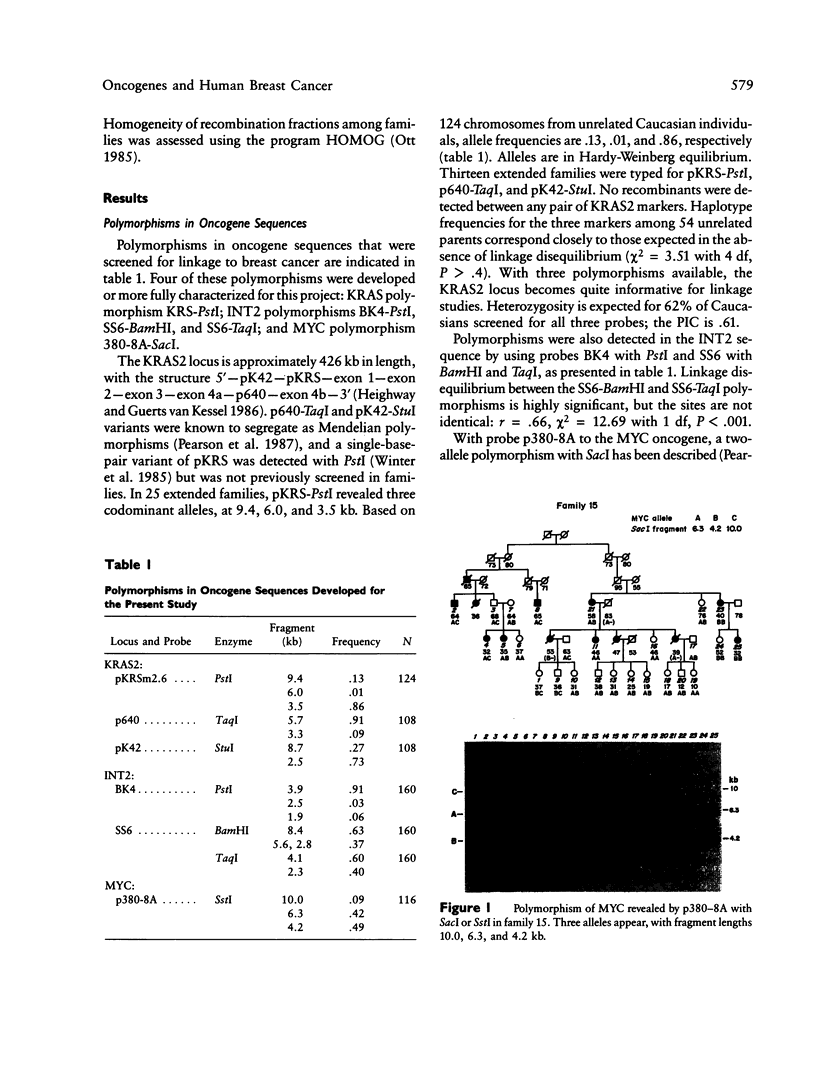
- Pearson P. L., Kidd K. K., Willard H. F. Report of the committee on human gene mapping by recombinant DNA techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):390–566. doi: 10.1159/000132487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosperi M. T., Even J., Calvo F., Lebeau J., Goubin G. Two adjacent mutations at position 12 activate the K-ras2 oncogene of a human mammary tumor cell line. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider S. H., Gorman P. A., Shipley J. M., Moore G., Vennstrom B., Solomon E., Sheer D. Localization of the oncogene c-erbA2 to human chromosome 3. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 May;51(Pt 2):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Ozelius L. J., Lane A. H., Farmer G. E., Lamiell J. M., Haines J., Yuen J. W., Collins D., Majoor-Krakauer D. Von Hippel-Lindau disease maps to the region of chromosome 3 associated with renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):268–269. doi: 10.1038/332268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M. Amplification of c-erbB-2 and aggressive human breast tumors? Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1795–1798. doi: 10.1126/science.3289120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M. In Reply: Amplification c-erbB-2 and Aggressive Human Breast Tumors? Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1796–1798. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4860.1796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Voss R., Hall V., Bodmer W. F., Jass J. R., Jeffreys A. J., Lucibello F. C., Patel I., Rider S. H. Chromosome 5 allele loss in human colorectal carcinomas. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):616–619. doi: 10.1038/328616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Swallow J. E., Brammar W. J., Whittaker J. L., Walker R. A. Alterations to either c-erbB-2(neu) or c-myc proto-oncogenes in breast carcinomas correlate with poor short-term prognosis. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Battifora H., Le Fevre C., Cline M. J. Alterations of myc, myb, and rasHa proto-oncogenes in cancers are frequent and show clinical correlation. Science. 1986 Jan 17;231(4735):261–265. doi: 10.1126/science.3941898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Battifora H., Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Cline M. J. Association of multiple copies of the c-erbB-2 oncogene with spread of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):6123–6125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Mooi W. J., Peterse J. L., Nusse R. Amplification and over-expression of the neu oncogene in human breast carcinomas. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1988 Apr;14(2):111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]