Abstract
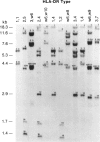
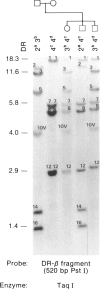
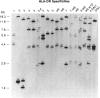
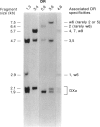
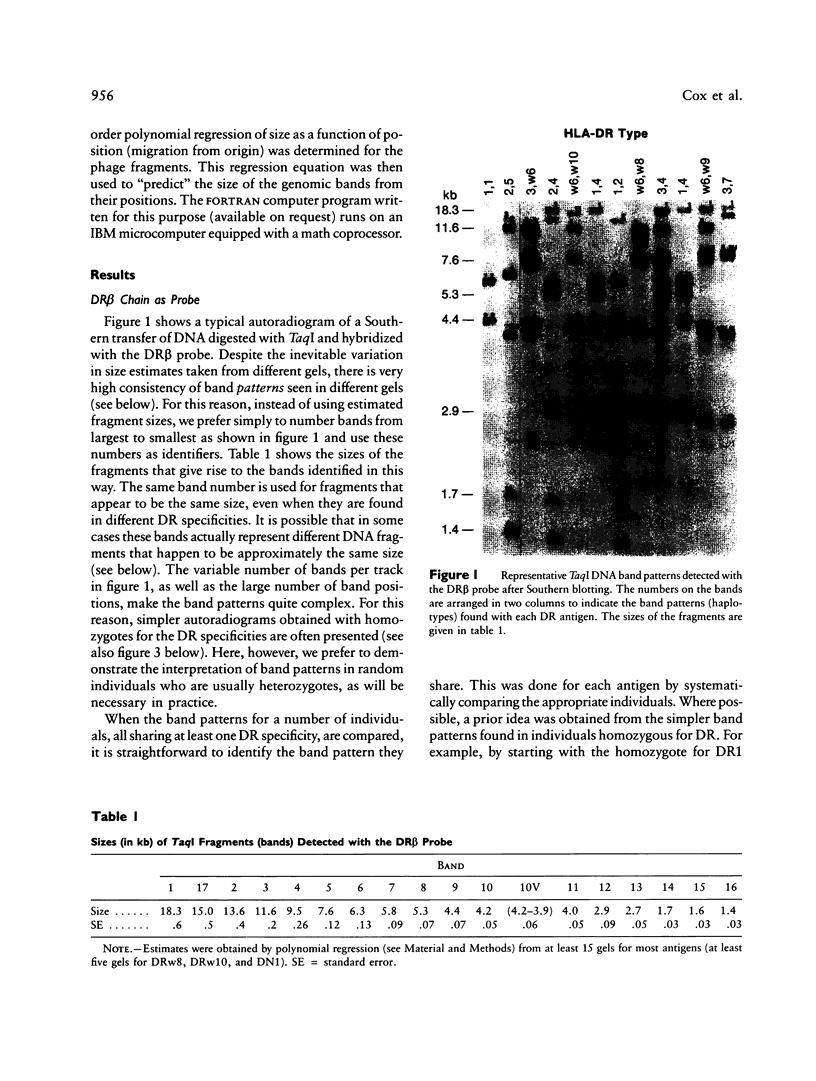
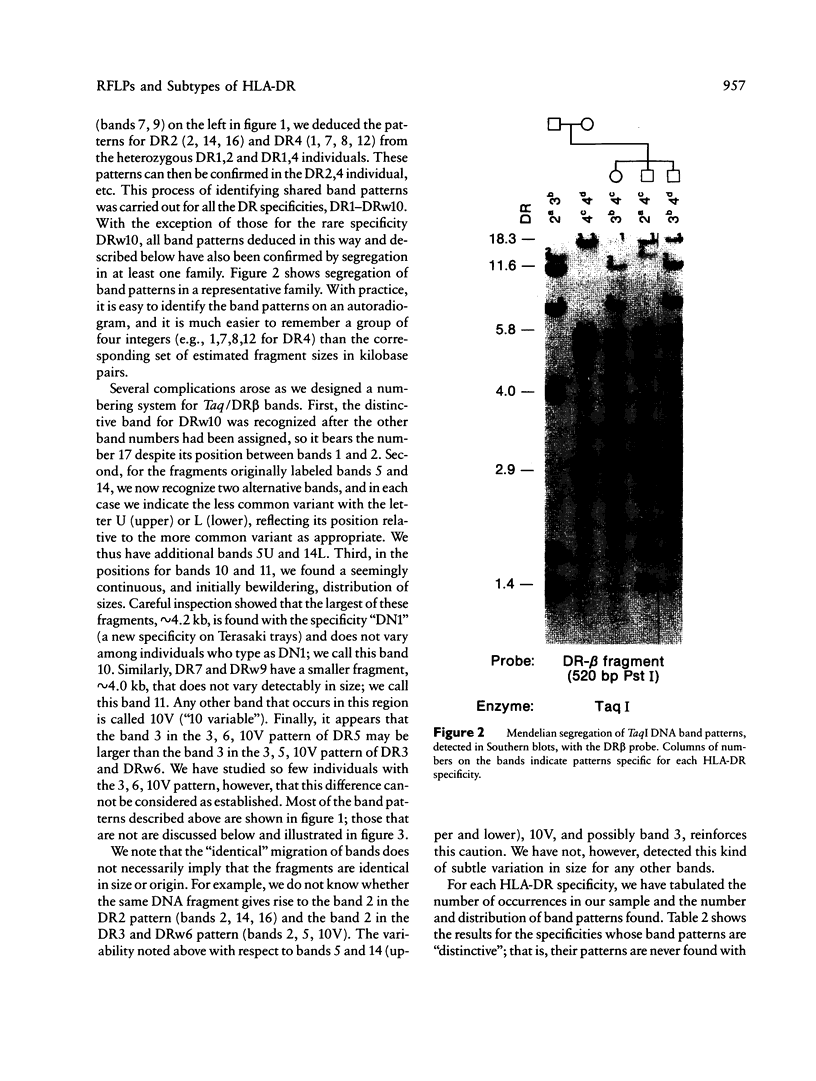
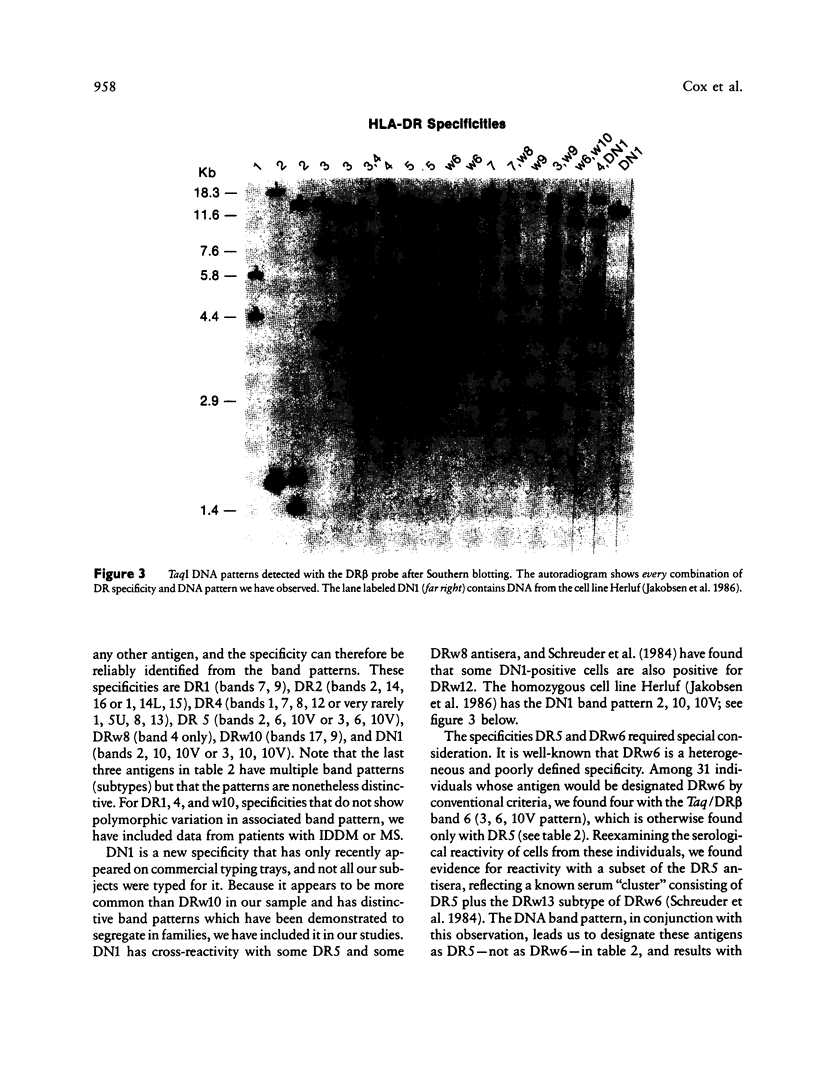
The HLA-DR beta gene, used as a hybridization probe, detects RFLPs that correlate with HLA-DR specificities. Using genomic DNA from more than 200 individuals, we have carried out a population study with a cDNA probe for the DR beta chain, which, under appropriate conditions, does not cross-hybridize with genes from other HLA-D subregions (e.g., DP and DQ). We first assessed the correspondence between serologically defined HLA-DR types and DNA patterns obtained after digestion with TaqI and found that DNA patterns allowed us to identify most specificities. Only two pairs of antigens are not distinguishable: with the DR beta probe alone we cannot distinguish DR3 from DRw6 or DR7 from DRw9. However, the correct assignment can always be made for the first pair by hybridizing the same digests with a DQ alpha or DQ beta probe. Thus DR typing from the DNA patterns is practical and accurate. We also looked for serologically undetectable subtypes. RFLPs revealed high-frequency subtypes for the specificities DR 2, 3, 5, w6, 7, and w9. Some of these are more accurately viewed as variant haplotypes, since the relevant variation is probably not at the DR beta locus that determines the serological specificities but rather at other closely linked and highly homologous DR beta loci such as DR beta-III. Nevertheless, the existence of variant haplotypes for so many specificities indicates a wealth of polymorphic variation beyond that detected serologically and provides more specific markers for studies of various diseases associated with HLA-DR specificities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Böhme J., Andersson G., Möller E., Thorsby E., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Genomic hybridization with class II transplantation antigen cDNA probes as a complementary technique in tissue typing. Hum Immunol. 1984 Oct;11(2):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelini G., de Preval C., Gorski J., Mach B. High-resolution analysis of the human HLA-DR polymorphism by hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4489–4493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, MacMurray A., Foster L., Watling D., McDevitt H. O. Molecular mapping of class II polymorphisms in the human major histocompatibility complex. I. DR beta. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):562–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch M. L., Fei H., Bontrop R. E., Gerrets R., Tilanus M. G., Termijtelen A., Giphart M. J. Polymorphisms within the HLA-DRw6 haplotype. III. DQ alpha and DQ beta polymorphism associated with HLA-D. Hum Immunol. 1987 Jun;19(2):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme J., Andersson M., Andersson G., Möller E., Peterson P. A., Rask L. HLA-DR beta genes vary in number between different DR specificities, whereas the number of DQ beta genes is constant. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2149–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Le Gall I., Marcadet A., Font M. P., Lalouel J. M., Dausset J. Clusters of HLA class II beta restriction fragments describe allelic series. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7870–7874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Mach B. Polymorphism of human Ia antigens: gene conversion between two DR beta loci results in a new HLA-D/DR specificity. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):67–70. doi: 10.1038/322067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbeck S. L., Nepom G. T. Exon-specific oligonucleotide probes localize HLA-DQ beta allelic polymorphisms. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(4):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00364529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A. A new homozygous typing cell with HLA-D"H" (DB6) specificity. Evidence that the DN-1 monoclonal antibody 9w925 is specific for the HLA-D"H" determinant. Tissue Antigens. 1986 May;27(5):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E., Andreas-Zietz A., McNicholas A., Grooms A., Scholz S., Albert E. D. Characterization of DR blank alleles by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). Tissue Antigens. 1987 Mar;29(3):154–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1987.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen-Corish M. R., Serjeantson S. W. HLA-DR beta gene DNA polymorphisms revealed by Taq I correlate with HLA-DR specificities. Hum Immunol. 1986 Mar;15(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Wake C. T., Gorski J., Mach B. Complete sequence of an HLA-dR beta chain deduced from a cDNA clone and identification of multiple non-allelic DR beta chain genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):389–394. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Lernmark A., Rask L., Peterson P. A., Platz P., Svejgaard A. Detection of HLA-D/DR-related DNA polymorphism in HLA-D homozygous typing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3758–3761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine S., Cascino I., Zeevi A., Duquesnoy R. J., Trucco M. DQ alpha and beta RFLP reveals the composition of the DQ molecule recognized by T-cell clones. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(3):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00373820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., Lee J., Bodmer W. F., Bodmer J. G., Trowsdale J. Six HLA-D region alpha-chain genes on human chromosome 6: polymorphisms and associations of DC alpha-related sequences with DR types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3461–3465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilanus M. G., Hongming F., van Eggermond M. C., vd Bijl M., D'Amaro J., Schreuder G. M., de Vries R. R., Giphart M. J. An overview of the restriction fragment length polymorphism of the HLA-D region: its application to individual D-, DR- typing by computerized analyses. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Oct;28(4):218–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Lee J., Carey J., Grosveld F., Bodmer J., Bodmer W. Sequences related to HLA-DR alpha chain on human chromosome 6: restriction enzyme polymorphism detected with DC alpha chain probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1972–1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Young J. A., Kelly A. P., Austin P. J., Carson S., Meunier H., So A., Erlich H. A., Spielman R. S., Bodmer J. Structure, sequence and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:5–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Mach B. Allelic polymorphism and complexity of the genes for HLA-DR beta-chains--direct analysis by DNA-DNA hybridization. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):372–374. doi: 10.1038/300372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]