Abstract
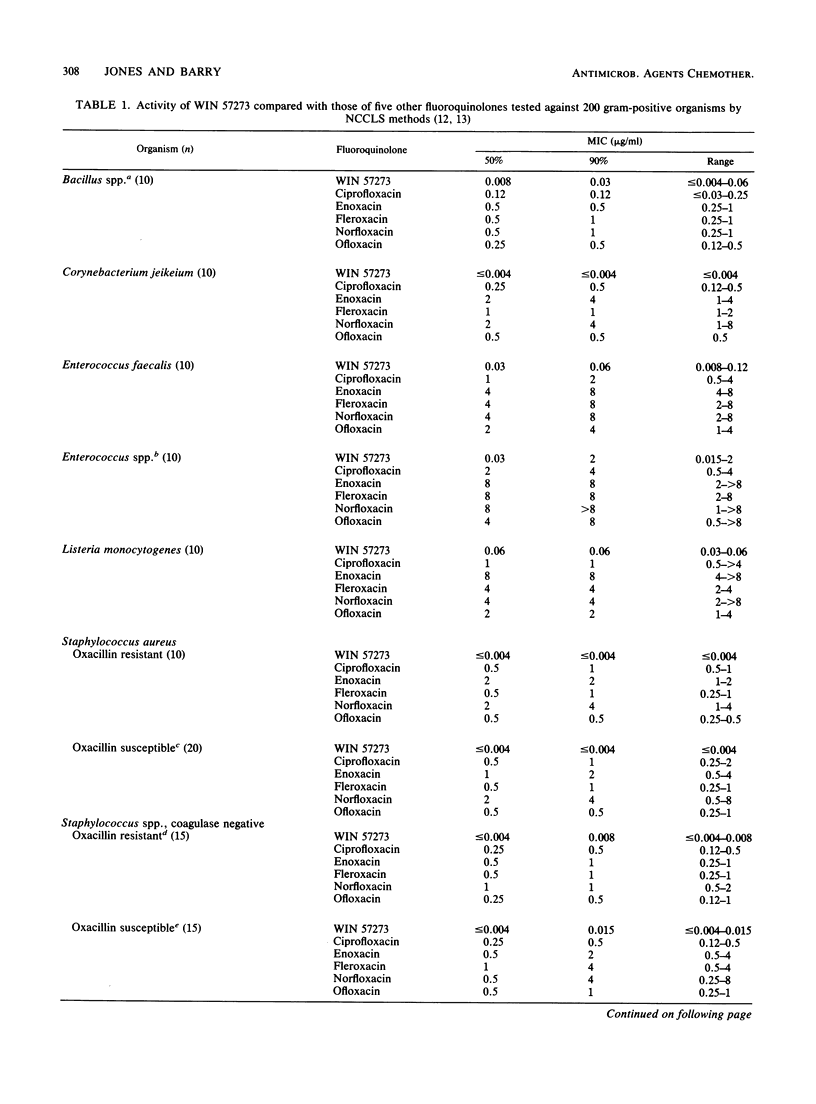
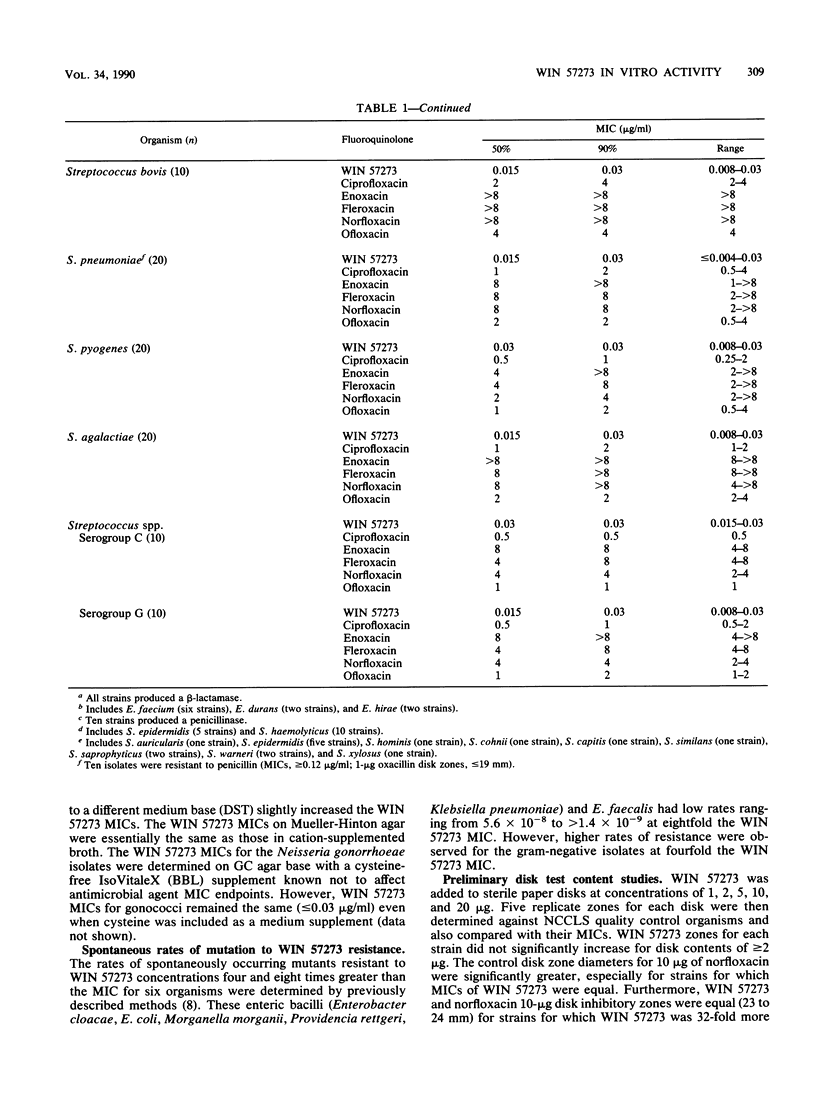
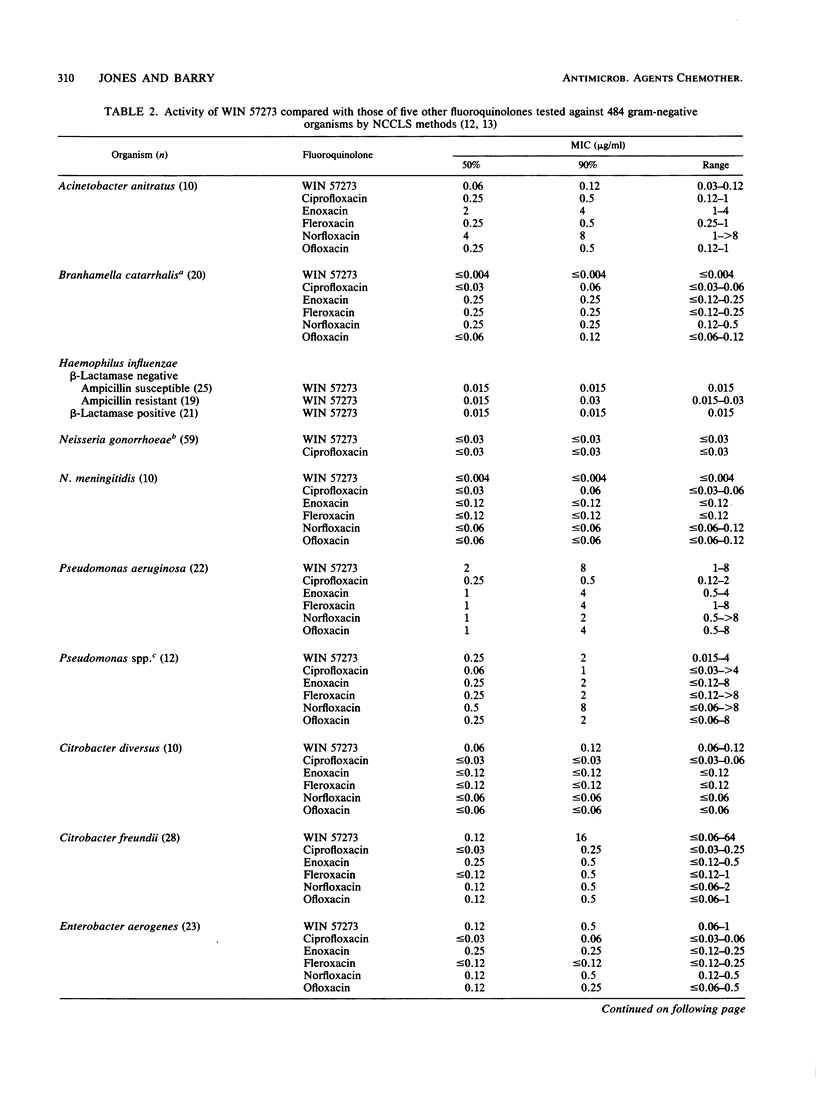
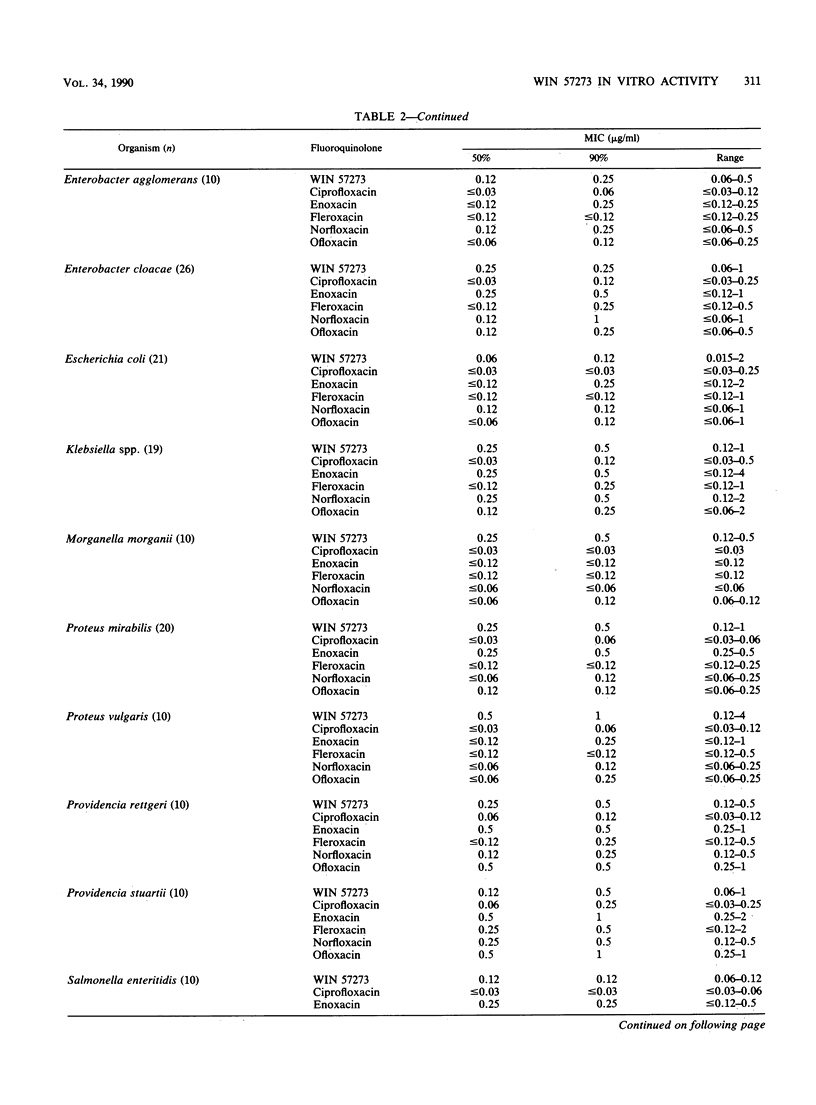
WIN 57273 is a new fluoroquinolone that has an expanded spectrum of activity against Staphylococcus spp. (MIC for 90% of isolates [MIC90], 0.008 microgram/ml), Enterococcus faecalis (MIC90, 0.06 microgram/ml), Bacillus spp. (MIC90, 0.03 micrograms/ml), Listeria monocytogenes (MIC90, 0.06 microgram/ml), Streptococcus spp. (MIC90, 0.03 microgram/ml), and Bacteroides fragilis group strains (MIC90, 0.5 microgram/ml). Like other fluoroquinolone compounds, WIN 57273 was active against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae (97% of strains inhibited by less than or equal to 2 micrograms/ml), Haemophilus, Branhamella, and Neisseria strains (100% susceptible), Acinetobacter spp. (100% susceptible), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (68% susceptible). We observed that WIN 57273 was very active against cephalosporin- or aminoglycoside-resistant gram-negative strains but shared cross-resistance with other fluoroquinolones. Increasing inoculum concentrations had minimal effects on WIN 57273 MICs, and the drug was considered to be bactericidal based on reference MBC and kill curve analyses. Unlike most previously studied drugs in this class, WIN 57273 had increased activity (three- to fourfold) at low pH. Rates of mutation to WIN 57273 resistance at eight times its MIC were in the range of 5.6 x 10(-8) to greater than 1.4 x 10(-9). This new compound possesses a wide potential spectrum of use, and it should be evaluated further by in vitro and in vivo studies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza A. M., Chin N. X., Novelli A., Neu H. C. Comparative in vitro activity of a new fluorinated 4-quinolone, T-3262 (A-60969). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):663–670. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Chu D. T., Swanson R. N., Ramer N. R., Hanson C. W., Bower R. R., Stamm J. M., Hardy D. J. A-61827 (A-60969), a new fluoronaphthyridine with activity against both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. C., Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C. Evaluation of in vitro antibacterial activity of enoxacin: comparison with other orally absorbed antimicrobial agents, proposed disk diffusion test interpretive criteria, and quality control limits. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 May;3(3):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargallo D., Moros M., Coll R., Esteve M., Parés J., Xicota M. A., Guinea J. Activity of E-3846, a new fluoroquinolone, in vitro and in experimental cystitis and pyelonephritis in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):636–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Aldridge K. E., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gerlach E. H., Pfaller M. A., Washington J. A., 2nd Multicenter in vitro evaluation of lomefloxacin (NY-198, SC-47111), including tests against nearly 7,000 bacterial isolates and preliminary recommendations for susceptibility testing. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;10(4):221–240. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L. Susceptibility of stably derepressed beta-lactamase producing strains to imipenem and four quinolones. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;7(1):82–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01962184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Baltch A. L., Hammer M. C., Conroy J. V. In vitro activities of PD 117,596 and reference antibiotics against 448 clinical bacterial strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1450–1455. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Ashby J. P., Andrews J. M. In vitro activity of PD 127,391, an enhanced-spectrum quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1251–1256. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


