Abstract
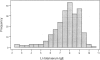
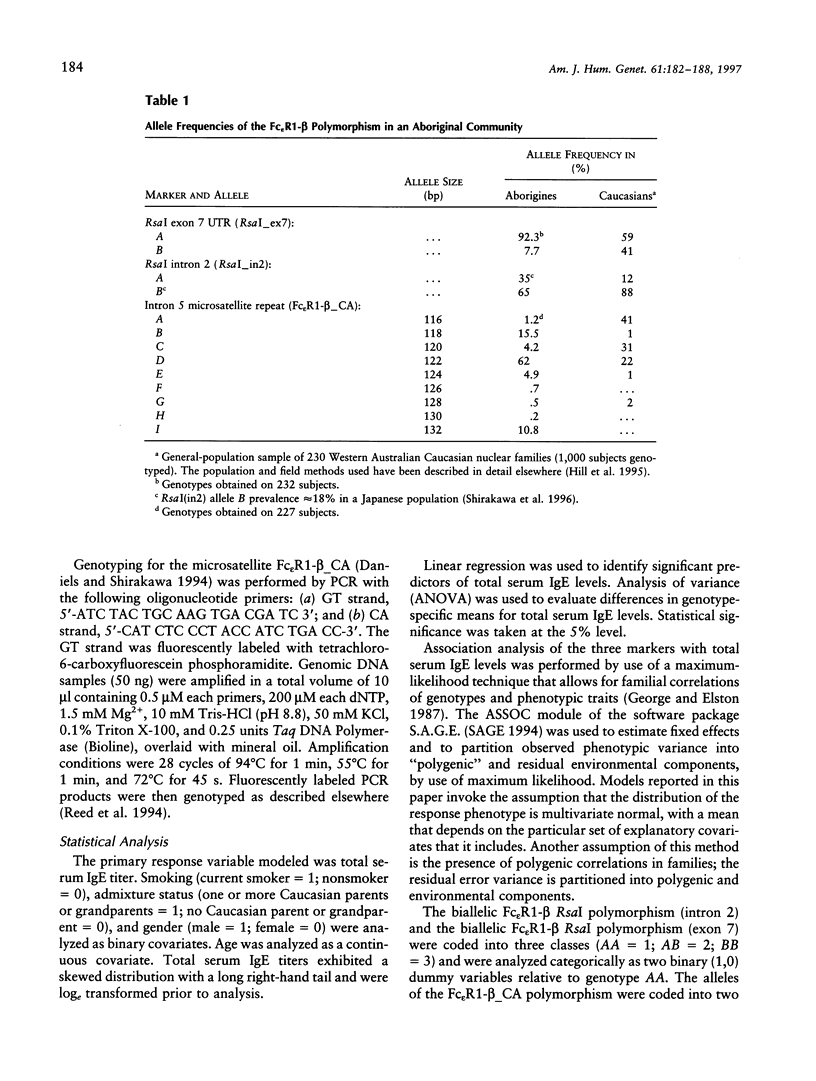
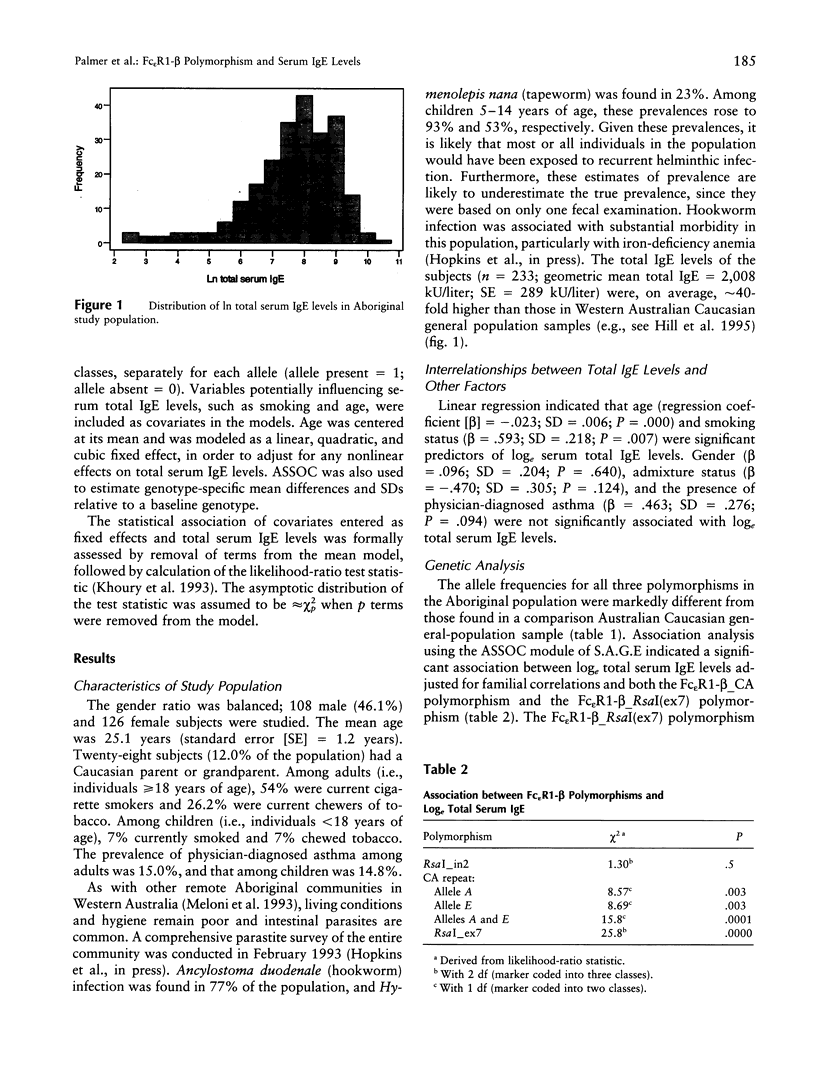
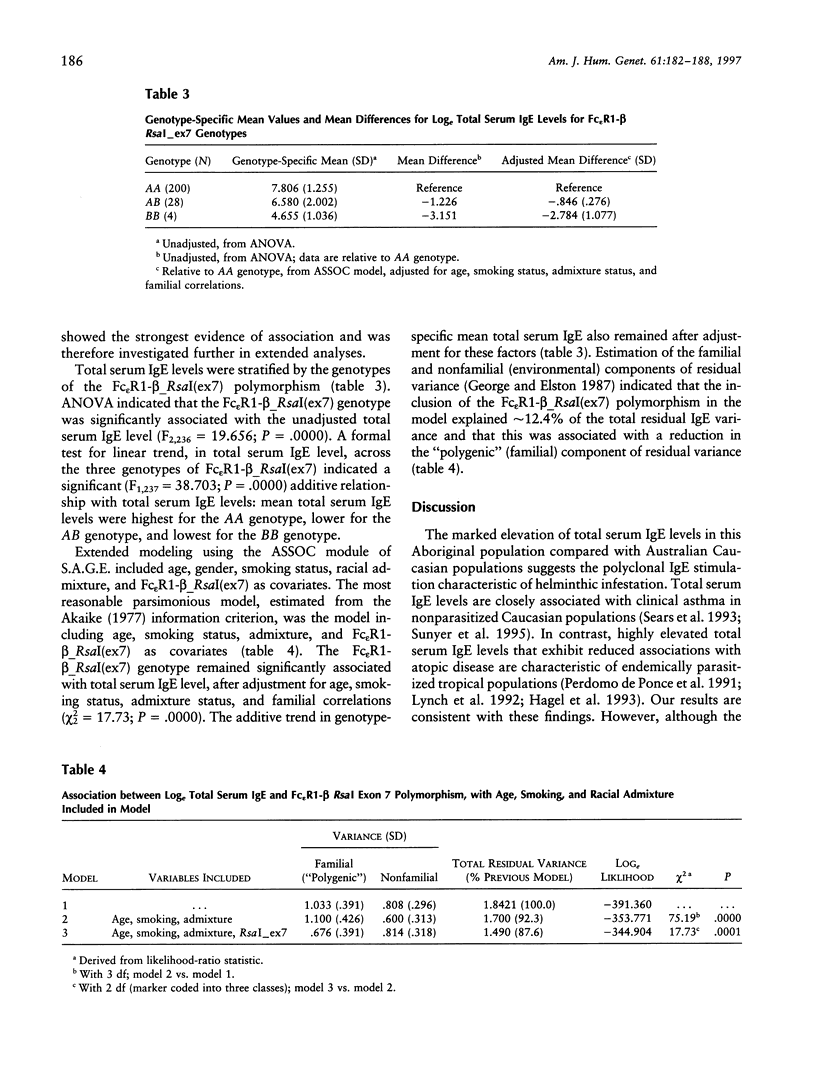
Endemic helminthic infection is a major public-health problem and affects a large proportion of the world's population. In Australia, helminthic infection is endemic in Aboriginal communities living in tropical northern regions of the continent. Such infection is associated with nonspecific (polyclonal) stimulation of IgE synthesis and highly elevated total serum IgE levels. There is evidence that worm-infection variance (i.e., human capacity of resistance) and total serum IgE levels may be related to the presence of a major codominant gene. The beta chain of the high-affinity IgE receptor, Fc epsilon R1-beta, has been previously identified as a candidate for the close genetic linkage of the 11q13 region to IgE responses in several populations. We show a biallelic RsaI polymorphism in Fc epsilon R1-beta to be associated with total serum IgE levels (P = .0001) in a tropical population of endemically parasitized Australian Aborigines (n = 234 subjects). The polymorphism explained 12.4% of the total residual variation in serum total IgE and showed a significant (P = .0000) additive relationship with total serum IgE levels, across the three genotypes. These associations were independent of familial correlations, age, gender, racial admixture, or smoking status. Alleles of a microsatellite repeat in intron 5 of the same gene showed similar associations. The results suggest that variation in Fc epsilon R1-beta may regulate IgE-mediated immune responses in this population.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boguniewicz M., Hayward A. Atopy, airway responsiveness, and genes. Thorax. 1996 Aug;51 (Suppl 2):S55–S59. doi: 10.1136/thx.51.suppl_2.s55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collée J. M., ten Kate L. P., de Vries H. G., Kliphuis J. W., Bouman K., Scheffer H., Gerritsen J. Allele sharing on chromosome 11q13 in sibs with asthma and atopy. Lancet. 1993 Oct 9;342(8876):936–936. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91988-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Sharp P. A., Faux J. A., Hopkin J. M. Linkage between immunoglobulin E responses underlying asthma and rhinitis and chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1292–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92687-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. E., Bhattacharrya S., James A., Leaves N. I., Young A., Hill M. R., Faux J. A., Ryan G. F., le Söuef P. N., Lathrop G. M. A genome-wide search for quantitative trait loci underlying asthma. Nature. 1996 Sep 19;383(6597):247–250. doi: 10.1038/383247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. E., Shirakawa T. A dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the FCERIB gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):213–213. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A. J., Couissinier P., Demeure C., Rihet P., Kohlstaedt S., Carneiro-Carvalho D., Ouattara M., Goudot-Crozel V., Dessein H., Bourgois A. Environmental, genetic and immunological factors in human resistance to Schistosoma mansoni. Immunol Invest. 1992 Aug;21(5):423–453. doi: 10.3109/08820139209069383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizier M. H., Hill M., James A., Faux J., Ryan G., le Souef P., Lathrop M., Musk A. W., Demenais F., Cookson W. Detection of a recessive major gene for high IgE levels acting independently of specific response to allergens. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(1):93–105. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George V. T., Elston R. C. Testing the association between polymorphic markers and quantitative traits in pedigrees. Genet Epidemiol. 1987;4(3):193–201. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370040304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M. Diarrhoea in Australian Aborigines. Aust J Public Health. 1992 Sep;16(3):216–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-6405.1992.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagel I., Lynch N. R., Pérez M., Di Prisco M. C., López R., Rojas E. Modulation of the allergic reactivity of slum children by helminthic infection. Parasite Immunol. 1993 Jun;15(6):311–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1993.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., Cookson W. O. A new variant of the beta subunit of the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (Fc epsilon RI-beta E237G): associations with measures of atopy and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jul;5(7):959–962. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., James A. L., Faux J. A., Ryan G., Hopkin J. M., le Söuef P., Musk A. W., Cookson W. O. Fc epsilon RI-beta polymorphism and risk of atopy in a general population sample. BMJ. 1995 Sep 23;311(7008):776–779. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7008.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizawa N., Yamaguchi E., Furuya K., Ohnuma N., Kodama N., Kojima J., Ohe M., Kawakami Y. Association between high serum total IgE levels and D11S97 on chromosome 11q13 in Japanese subjects. J Med Genet. 1995 May;32(5):363–369. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. L., Low C. C., Nutman T. B. IgE production in human helminth infection. Reciprocal interrelationship between IL-4 and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1873–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., Hagel I., Di Prisco M. C., Lopez R. I., Garcia N. M., Perez M. Serum IgE levels, helminth infection and socioeconomic change. Parasitol Today. 1992 May;8(5):166–167. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90011-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch N. R., López R., Istúriz G., Tenías-Salazar E. Allergic reactivity and helminthic infection in Amerindians of the Amazon Basin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;72(4):369–372. doi: 10.1159/000234899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquet S., Abel L., Hillaire D., Dessein H., Kalil J., Feingold J., Weissenbach J., Dessein A. J. Genetic localization of a locus controlling the intensity of infection by Schistosoma mansoni on chromosome 5q31-q33. Nat Genet. 1996 Oct;14(2):181–184. doi: 10.1038/ng1096-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez F. D., Holberg C. J., Halonen M., Morgan W. J., Wright A. L., Taussig L. M. Evidence for Mendelian inheritance of serum IgE levels in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white families. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;55(3):555–565. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni B. P., Thompson R. C., Hopkins R. M., Reynoldson J. A., Gracey M. The prevalence of Giardia and other intestinal parasites in children, dogs and cats from aboriginal communities in the Kimberley. Med J Aust. 1993 Feb 1;158(3):157–159. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1993.tb121692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. A., Bias W. B., Marsh D. G. A genetic study of total IgE levels in the Amish. Hum Hered. 1982;32(1):15–23. doi: 10.1159/000153262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninan T. K., Russell G. Respiratory symptoms and atopy in Aberdeen schoolchildren: evidence from two surveys 25 years apart. BMJ. 1992 Apr 4;304(6831):873–875. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6831.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peat J. K., van den Berg R. H., Green W. F., Mellis C. M., Leeder S. R., Woolcock A. J. Changing prevalence of asthma in Australian children. BMJ. 1994 Jun 18;308(6944):1591–1596. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6944.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdomo de Ponce D., Benarroch L., Aldrey O., Rodríguez D., Rosales A., Avila E., Bianco N. The influence of environment and parasitism on the prevalence of asthma in two Venezuelan regions. Invest Clin. 1991;32(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. I., Quinnell R. J., Walsh E. A. Immunity in humans to Necator americanus: IgE, parasite weight and fecundity. Parasite Immunol. 1995 Feb;17(2):71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1995.tb00968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V. Atopy and Fc receptors: mutation is the message? Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):117–118. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Davies J. L., Copeman J. B., Bennett S. T., Palmer S. M., Pritchard L. E., Gough S. C., Kawaguchi Y., Cordell H. J., Balfour K. M. Chromosome-specific microsatellite sets for fluorescence-based, semi-automated genome mapping. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):390–395. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues V., Jr, Abel L., Piper K., Dessein A. J. Segregation analysis indicates a major gene in the control of interleukine-5 production in humans infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Aug;59(2):453–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandford A. J., Shirakawa T., Moffatt M. F., Daniels S. E., Ra C., Faux J. A., Young R. P., Nakamura Y., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O. Localisation of atopy and beta subunit of high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) on chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Burrows B., Flannery E. M., Herbison G. P., Holdaway M. D. Atopy in childhood. I. Gender and allergen related risks for development of hay fever and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 Nov;23(11):941–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Coffman R. L. Regulation of immunity to parasites by T cells and T cell-derived cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:385–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Hashimoto T., Furuyama J., Takeshita T., Morimoto K. Linkage between severe atopy and chromosome 11q13 in Japanese families. Clin Genet. 1994 Sep;46(3):228–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Li A., Dubowitz M., Dekker J. W., Shaw A. E., Faux J. A., Ra C., Cookson W. O., Hopkin J. M. Association between atopy and variants of the beta subunit of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):125–129. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa T., Mao X. Q., Sasaki S., Kawai M., Morimoto K., Hopkin J. M. Association between Fc epsilon RI beta and atopic disorder in a Japanese population. Lancet. 1996 Feb 10;347(8998):394–395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90570-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. R., Welburn S. C. Genetic processes within an epidemic of sleeping sickness in Uganda. Parasitol Res. 1993;79(5):421–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00931833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunyer J., Antó J. M., Sabrià J., Roca J., Morell F., Rodríguez-Roisin R., Rodrigo M. J. Relationship between serum IgE and airway responsiveness in adults with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Mar;95(3):699–706. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. P., Sharp P. A., Lynch J. R., Faux J. A., Lathrop G. M., Cookson W. O., Hopkin J. M. Confirmation of genetic linkage between atopic IgE responses and chromosome 11q13. J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):236–238. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]