Full text
PDF



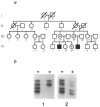
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Zoghbi H. Y., Moseley A. B., Rosenblatt H. M., Belmont J. W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1229–1239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arngrimsson R., Dokal I., Luzzatto L., Connor J. M. Dyskeratosis congenita: three additional families show linkage to a locus in Xq28. J Med Genet. 1993 Jul;30(7):618–619. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.7.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont J. W. Genetic control of X inactivation and processes leading to X-inactivation skewing. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1101–1108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busque L., Mio R., Mattioli J., Brais E., Blais N., Lalonde Y., Maragh M., Gilliland D. G. Nonrandom X-inactivation patterns in normal females: lyonization ratios vary with age. Blood. 1996 Jul 1;88(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. M., Gatherer D., Gray F. C., Pirrit L. A., Affara N. A. Assignment of the gene for dyskeratosis congenita to Xq28. Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;72(4):348–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00290963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriendt K., Matthijs G., Legius E., Schollen E., Blockmans D., van Geet C., Degreef H., Cassiman J. J., Fryns J. P. Skewed X-chromosome inactivation in female carriers of dyskeratosis congenita. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Mar;60(3):581–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokal I. Dyskeratosis congenita: an inherited bone marrow failure syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1996 Mar;92(4):775–779. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.355881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris A. M., Mangerini R., Gaetani G. F., Romei C., Pinchera A., Pacini F. Polyclonal origin of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. Hum Genet. 1997 Feb;99(2):202–205. doi: 10.1007/s004390050339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni G. L., Melevendi C., Jappelli S., Rasore-Quartino A. Dyskeratosis congenita: unusual presenting features within a kindred. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993 Apr-Jun;10(2):145–149. doi: 10.3109/08880019309016548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gealy W. J., Dwyer J. M., Harley J. B. Allelic exclusion of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in platelets and T lymphocytes from a Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome carrier. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):63–65. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. W., Vulliamy T., Forni G. L., Oscier D., Mason P. J., Dokal I. Fine mapping of the dyskeratosis congenita locus in Xq28. J Med Genet. 1996 Dec;33(12):993–995. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.12.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. C., Will A. J., Hows J. M., Sartori P., Darbyshire P. J., Williamson P. J., Oscier D. G., Dexter T. M., Testa N. G. "Stem cell" origin of the hematopoietic defect in dyskeratosis congenita. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3138–3144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumova A. K., Plenge R. M., Bird L. M., Leppert M., Morgan K., Willard H. F., Sapienza C. Heritability of X chromosome--inactivation phenotype in a large family. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1111–1119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Conley M. E. Carrier detection in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency based on patterns of X chromosome inactivation. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1172/JCI112967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willman C. L., Busque L., Griffith B. B., Favara B. E., McClain K. L., Duncan M. H., Gilliland D. G. Langerhans'-cell histiocytosis (histiocytosis X)--a clonal proliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jul 21;331(3):154–160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199407213310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]