Abstract
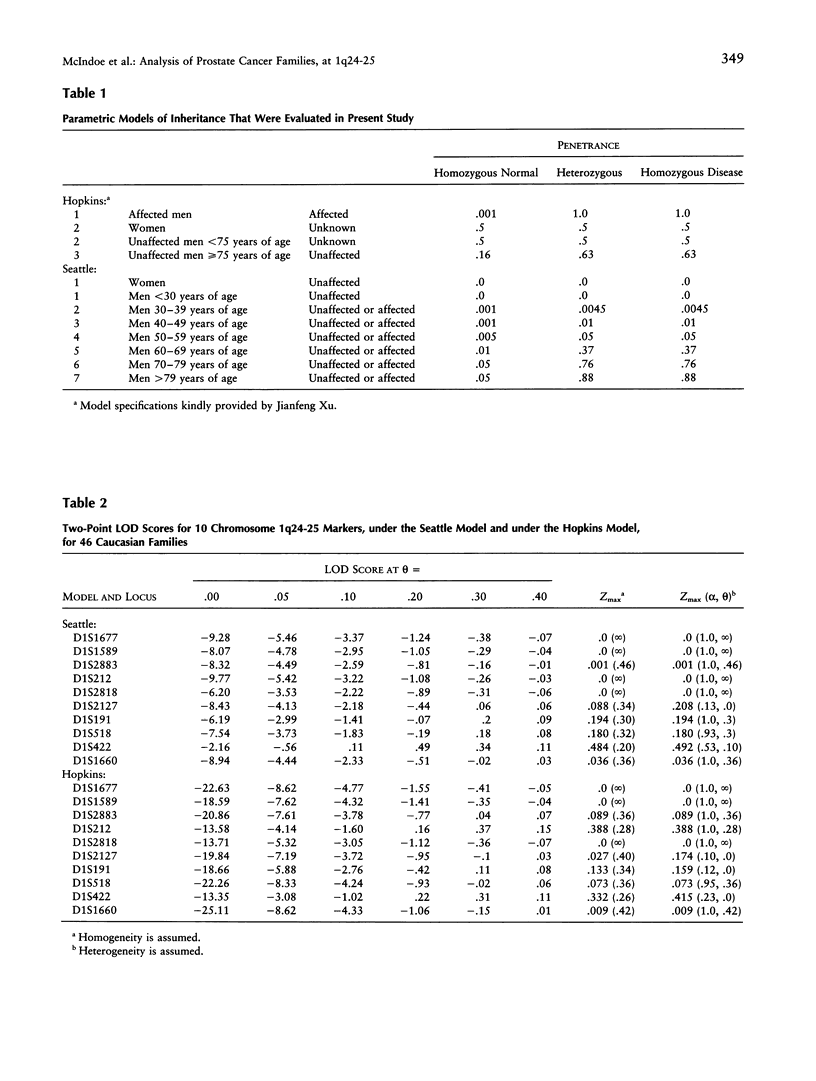
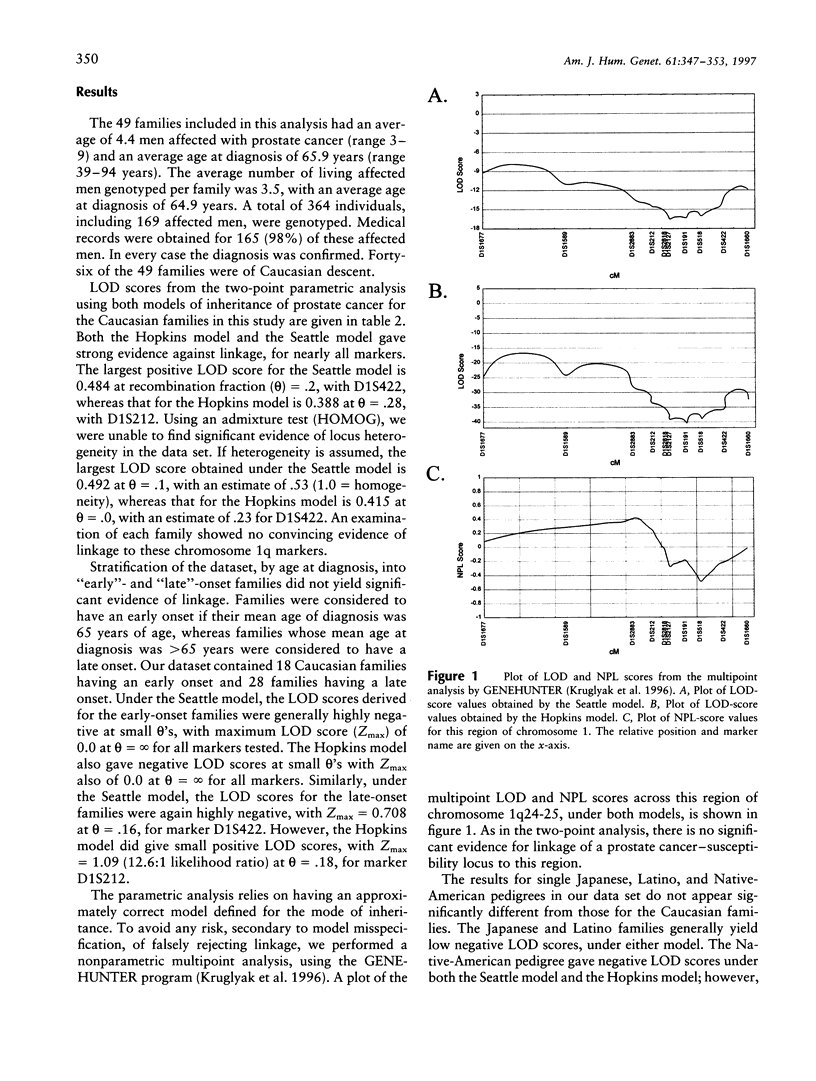
Linkage of a putative prostate cancer-susceptibility locus (HPC1) to chromosome 1q24-25 has recently been reported. Confirmation of this linkage in independent data sets is essential because of the complex nature of this disease. Here we report the results of a linkage analysis using 10 polymorphic markers spanning approximately 37 cM in the region of the putative HPC1 locus in 49 high-risk prostate cancer families. Data were analyzed by use of two parametric models and a nonparametric method. For the parametric LOD-score method, the first model was identical to the original report by Smith and coworkers ("Hopkins"), and the second was based on a segregation analysis previously reported by Carter and coworkers ("Seattle"). In both cases, our results do not confirm the linkage reported for this region. Calculated LOD scores from the two-point analysis for each marker were highly negative at small recombination fractions. Multipoint LOD scores for this linkage group were also highly negative. Additionally, we were unable to demonstrate heterogeneity within the data set, using HOMOG. Although these data do not formally exclude linkage of a prostate cancer-susceptibility locus at HPC1, it is likely that other prostate cancer-susceptibility loci play a more critical role in the families that we studied.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bookstein R., MacGrogan D., Hilsenbeck S. G., Sharkey F., Allred D. C. p53 is mutated in a subset of advanced-stage prostate cancers. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 15;53(14):3369–3373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R. Tumor suppressor genes in prostatic oncogenesis. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1994;19:217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bova G. S., Carter B. S., Bussemakers M. J., Emi M., Fujiwara Y., Kyprianou N., Jacobs S. C., Robinson J. C., Epstein J. I., Walsh P. C. Homozygous deletion and frequent allelic loss of chromosome 8p22 loci in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 1;53(17):3869–3873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bova G. S., MacGrogan D., Levy A., Pin S. S., Bookstein R., Isaacs W. B. Physical mapping of chromosome 8p22 markers and their homozygous deletion in a metastatic prostate cancer. Genomics. 1996 Jul 1;35(1):46–54. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. D., Bova G. S., Ewing C. M., Piantadosi S., Carter B. S., Robinson J. C., Epstein J. I., Isaacs W. B. An uncertain role for p53 gene alterations in human prostate cancers. Cancer Res. 1996 Aug 15;56(16):3814–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. S., Beaty T. H., Steinberg G. D., Childs B., Walsh P. C. Mendelian inheritance of familial prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3367–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. S., Bova G. S., Beaty T. H., Steinberg G. D., Childs B., Isaacs W. B., Walsh P. C. Hereditary prostate cancer: epidemiologic and clinical features. J Urol. 1993 Sep;150(3):797–802. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35617-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. S., Ewing C. M., Ward W. S., Treiger B. F., Aalders T. W., Schalken J. A., Epstein J. I., Isaacs W. B. Allelic loss of chromosomes 16q and 10q in human prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8751–8755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., King M. C. Detecting linkage for genetically heterogeneous diseases and detecting heterogeneity with linkage data. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 May;38(5):599–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong J. T., Suzuki H., Pin S. S., Bova G. S., Schalken J. A., Isaacs W. B., Barrett J. C., Isaacs J. T. Down-regulation of the KAI1 metastasis suppressor gene during the progression of human prostatic cancer infrequently involves gene mutation or allelic loss. Cancer Res. 1996 Oct 1;56(19):4387–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle L. R., Yin X., Brothman A. R., Williams B. J., Atkin N. B., Prochownik E. V. Mutation of the MXI1 gene in prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):249–255. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa T., Nihei N., Kuramochi H., Kawana Y., Killary A. M., Rinker-SchaefferCW, Barrett J. C., Isaacs J. T., Kugoh H., Oshimura M. Metastasis suppressor genes for prostate cancer. Prostate Suppl. 1996;6:31–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. A., Yu M. C., Ross R. K., Coetzee G. A. The CAG and GGC microsatellites of the androgen receptor gene are in linkage disequilibrium in men with prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 May 1;55(9):1937–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan J., Stein J., Babaian R. J., Joe Y. S., Pisters L. L., Glassman A. B., von Eschenbach A. C., Troncoso P. Homozygous deletions at 8p22 and 8p21 in prostate cancer implicate these regions as the sites for candidate tumor suppressor genes. Oncogene. 1995 Nov 16;11(10):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Reeve-Daly M. P., Lander E. S. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1347–1363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macoska J. A., Trybus T. M., Benson P. D., Sakr W. A., Grignon D. J., Wojno K. D., Pietruk T., Powell I. J. Evidence for three tumor suppressor gene loci on chromosome 8p in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 15;55(22):5390–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massenkeil G., Oberhuber H., Hailemariam S., Sulser T., Diener P. A., Bannwart F., Schäfer R., Schwarte-Waldhoff I. P53 mutations and loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes 8p, 16q, 17p, and 18q are confined to advanced prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 1994 Nov-Dec;14(6B):2785–2790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. A., Ewing C. M., Nagafuchi A., Tsukita S., Isaacs W. B. Reduction of E-cadherin levels and deletion of the alpha-catenin gene in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3585–3590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. L., Tong T., Bolden S., Wingo P. A. Cancer statistics, 1996. CA Cancer J Clin. 1996 Jan-Feb;46(1):5–27. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.46.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Moore D. K., Boehnke M., Bryant E. M., Lampe T. H., Nochlin D., Sumi S. M., Deeb S. S. Absence of linkage of chromosome 21q21 markers to familial Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1507–1510. doi: 10.1126/science.3420406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. R., Freije D., Carpten J. D., Grönberg H., Xu J., Isaacs S. D., Brownstein M. J., Bova G. S., Guo H., Bujnovszky P. Major susceptibility locus for prostate cancer on chromosome 1 suggested by a genome-wide search. Science. 1996 Nov 22;274(5291):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Haines J. L., Nee L., Watkins P. C., Myers R. H., Feldman R. G., Pollen D., Drachman D. The genetic defect causing familial Alzheimer's disease maps on chromosome 21. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):885–890. doi: 10.1126/science.2880399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg G. D., Carter B. S., Beaty T. H., Childs B., Walsh P. C. Family history and the risk of prostate cancer. Prostate. 1990;17(4):337–347. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990170409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbas R., Schalken J. A., Aalders T. W., Carter B. S., Karthaus H. F., Schaafsma H. E., Debruyne F. M., Isaacs W. B. Expression of the cellular adhesion molecule E-cadherin is reduced or absent in high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):5104–5109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B., Figgs L. W., Zahm S. H. Differences in cancer incidence, mortality, and survival between African Americans and whites. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Nov;103 (Suppl 8):275–281. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s8275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. J., Jones E., Zhu X. L., Steele M. R., Stephenson R. A., Rohr L. R., Brothman A. R. Evidence for a tumor suppressor gene distal to BRCA1 in prostate cancer. J Urol. 1996 Feb;155(2):720–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenklusen J. C., Thompson J. C., Troncoso P., Kagan J., Conti C. J. Loss of heterozygosity in human primary prostate carcinomas: a possible tumor suppressor gene at 7q31.1. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6370–6373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


