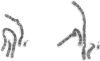Abstract
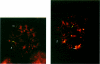
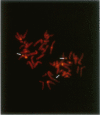
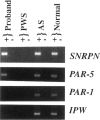
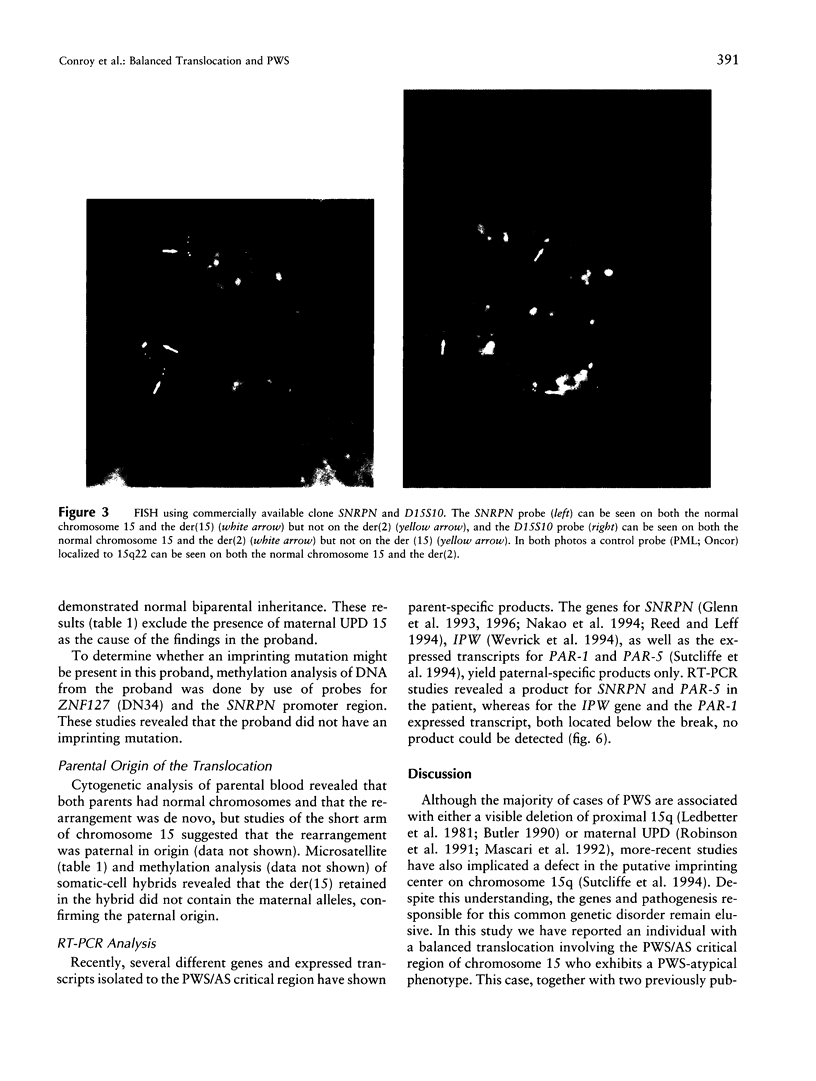
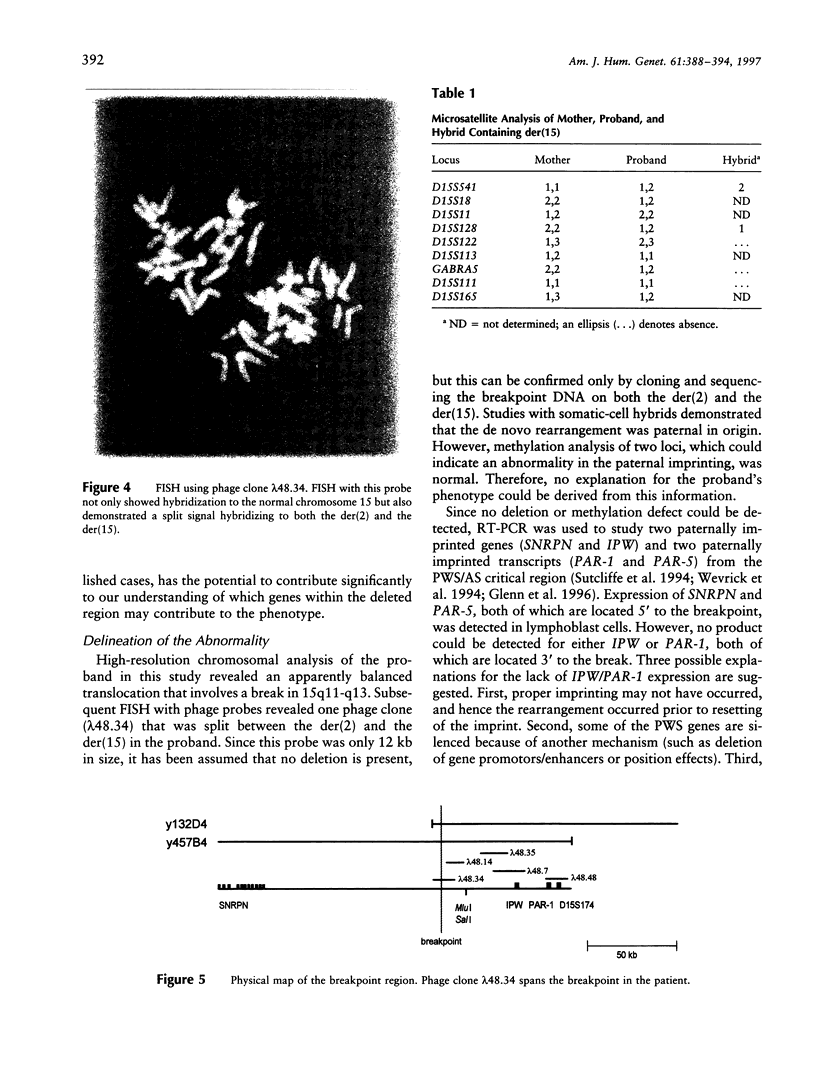
The lack of normally active paternal genes in 15q11-q13, as an outcome of either a paternal deletion or maternal disomy, accounts for >95% of all patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Other mechanisms, including imprinting mutations and unbalanced translocations involving pat 15q11-q13, have been described elsewhere. In this study, we present a patient with a rare balanced, de novo translocation-46,XY,t(2;15)(q37.2;q11.2)-involving breakage within the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region of the paternal homologue, without an apparent deletion. The patient demonstrated several manifestations of the Prader-Willi syndrome but was clinically atypical. Cytogenetic and molecular studies of this case demonstrated the translocation breakpoint to be between SNRPN and IPW, with mRNA expression of SNRPN and PAR-5 but absence of IPW and PAR-1 expression. These results suggest that disruption of either IPW expression or a nearby gene by an upstream break may contribute to the Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype and that expression of SNRPN or other upstream genes is responsible for other aspects of the classical Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedell M. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Good genes in bad neighbourhoods. Nat Genet. 1996 Mar;12(3):229–232. doi: 10.1038/ng0396-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Dittrich B., Gross S., Greger V., Lalande M., Robinson W., Mutirangura A., Ledbetter D., Horsthemke B. Molecular definition of the Prader-Willi syndrome chromosome region and orientation of the SNRPN gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):1991–1994. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Saitoh S., Gross S., Dittrich B., Schwartz S., Nicholls R. D., Horsthemke B. Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting centre on human chromosome 15. Nat Genet. 1995 Apr;9(4):395–400. doi: 10.1038/ng0495-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy S. B. Prader-Willi syndrome. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984 Jan;14(1):1–55. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(84)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn C. C., Porter K. A., Jong M. T., Nicholls R. D., Driscoll D. J. Functional imprinting and epigenetic modification of the human SNRPN gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2001–2005. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn C. C., Saitoh S., Jong M. T., Filbrandt M. M., Surti U., Driscoll D. J., Nicholls R. D. Gene structure, DNA methylation, and imprinted expression of the human SNRPN gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Feb;58(2):335–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm V. A., Cassidy S. B., Butler M. G., Hanchett J. M., Greenswag L. R., Whitman B. Y., Greenberg F. Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):398–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi T. Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):56–61. doi: 10.1159/000132030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Riccardi V. M., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J., Keenan B. S., Crawford J. D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascari M. J., Gottlieb W., Rogan P. K., Butler M. G., Waller D. A., Armour J. A., Jeffreys A. J., Ladda R. L., Nicholls R. D. The frequency of uniparental disomy in Prader-Willi syndrome. Implications for molecular diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 11;326(24):1599–1607. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206113262404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micale M. A., Haren J. M., Conroy J. M., Crowe C. A., Schwartz S. Parental origin of De Novo chromosome 9 deletions in del(9p) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995 May 22;57(1):79–81. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320570118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milot E., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Position effects and genetic disease. Trends Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(96)30019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Greenberg F., Butler M. G., Malcolm S., Nicholls R. D., Chakravarti A., Ledbetter D. H. Multiplex PCR of three dinucleotide repeats in the Prader-Willi/Angelman critical region (15q11-q13): molecular diagnosis and mechanism of uniparental disomy. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Sutcliffe J. S., Durtschi B., Mutirangura A., Ledbetter D. H., Beaudet A. L. Imprinting analysis of three genes in the Prader-Willi/Angelman region: SNRPN, E6-associated protein, and PAR-2 (D15S225E). Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):309–315. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. C., Rogers R. C., Clarkson K. B., Bowyer F. P., Levine M. A., Estabrooks L. L., Severson M. C., Dobyns W. B. Albright hereditary osteodystrophy and del(2) (q37.3) in four unrelated individuals. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jul 31;58(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320580102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. L., Leff S. E. Maternal imprinting of human SNRPN, a gene deleted in Prader-Willi syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):163–167. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bottani A., Xie Y. G., Balakrishman J., Binkert F., Mächler M., Prader A., Schinzel A. Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1219–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Buiting K., Cassidy S. B., Conroy J. M., Driscoll D. J., Gabriel J. M., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Glenn C. C., Greenswag L. R., Horsthemke B. Clinical spectrum and molecular diagnosis of Angelman and Prader-Willi syndrome patients with an imprinting mutation. Am J Med Genet. 1997 Jan 20;68(2):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Buiting K., Rogan P. K., Buxton J. L., Driscoll D. J., Arnemann J., König R., Malcolm S., Horsthemke B., Nicholls R. D. Minimal definition of the imprinting center and fixation of chromosome 15q11-q13 epigenotype by imprinting mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7811–7815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze A., Hansen C., Skakkebaek N. E., Brøndum-Nielsen K., Ledbeter D. H., Tommerup N. Exclusion of SNRPN as a major determinant of Prader-Willi syndrome by a translocation breakpoint. Nat Genet. 1996 Apr;12(4):452–454. doi: 10.1038/ng0496-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan B. A., Jenkins L. S., Karson E. M., Leana-Cox J., Schwartz S. Evidence for structural heterogeneity from molecular cytogenetic analysis of dicentric Robertsonian translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jul;59(1):167–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Nicholls R. D., Butler M. G., Saitoh S., Hainline B. E., Palmer C. G. Breakage in the SNRPN locus in a balanced 46,XY,t(15;19) Prader-Willi syndrome patient. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Apr;5(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. S., Nakao M., Christian S., Orstavik K. H., Tommerup N., Ledbetter D. H., Beaudet A. L. Deletions of a differentially methylated CpG island at the SNRPN gene define a putative imprinting control region. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):52–58. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevrick R., Kerns J. A., Francke U. Identification of a novel paternally expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1877–1882. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. C., Leverton K., Oude Luttikhuis M. E., Oley C. A., Flint J., Wolstenholme J., Duckett D. P., Barrow M. A., Leonard J. V., Read A. P. Brachydactyly and mental retardation: an Albright hereditary osteodystrophy-like syndrome localized to 2q37. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):400–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]