Abstract
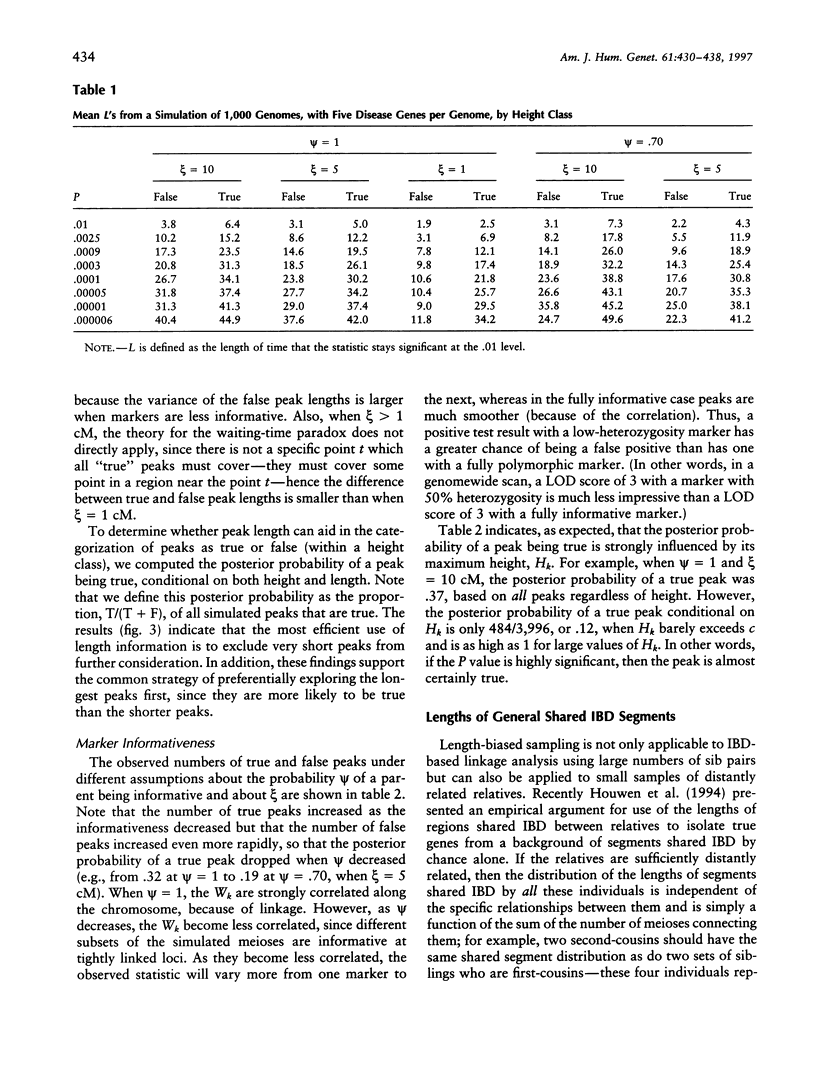
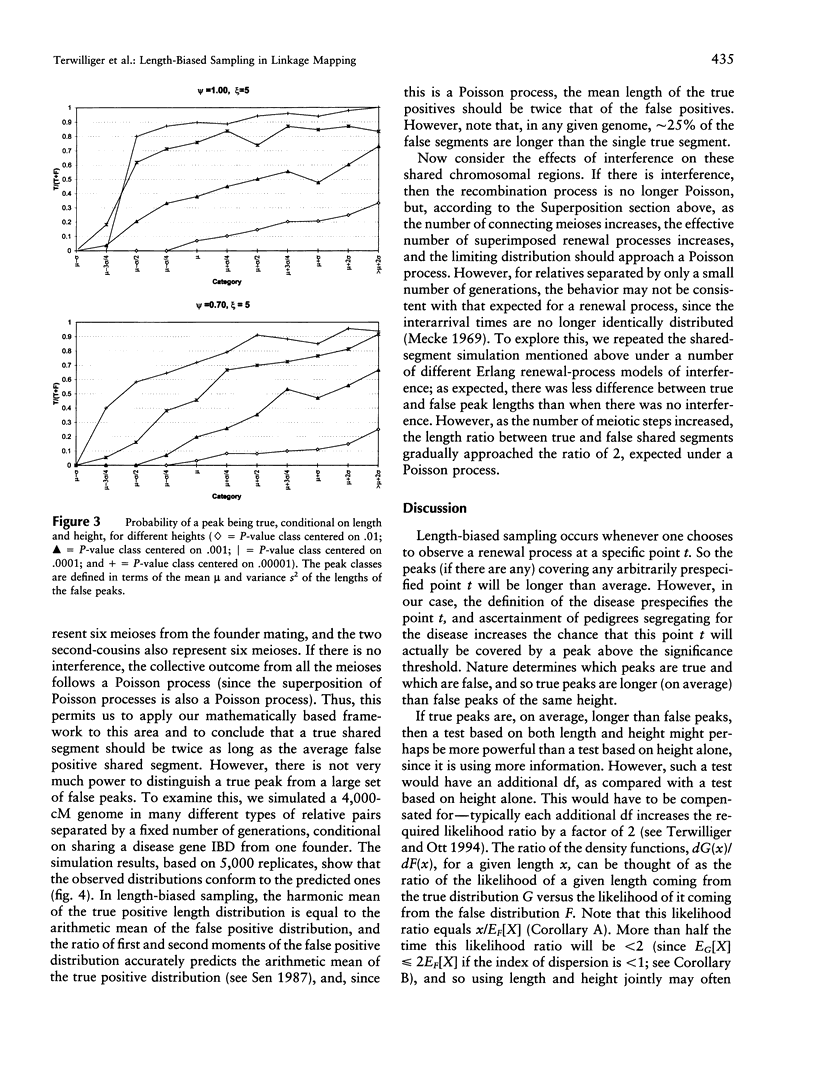
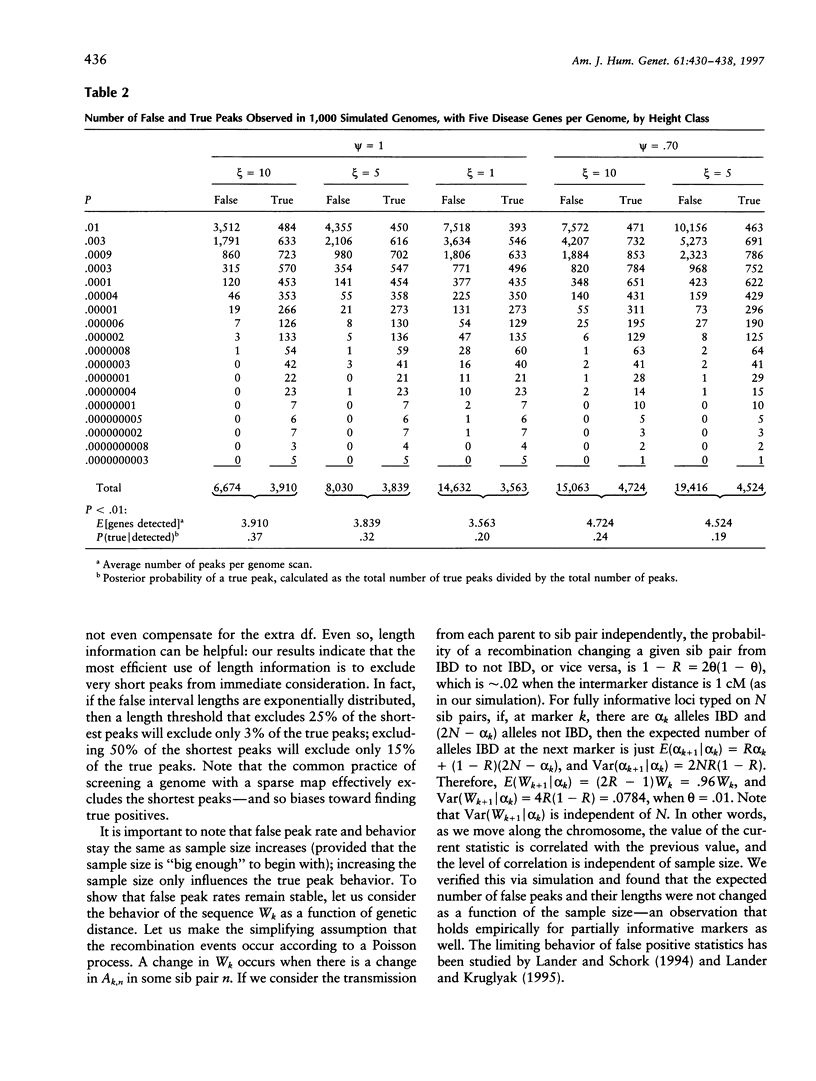
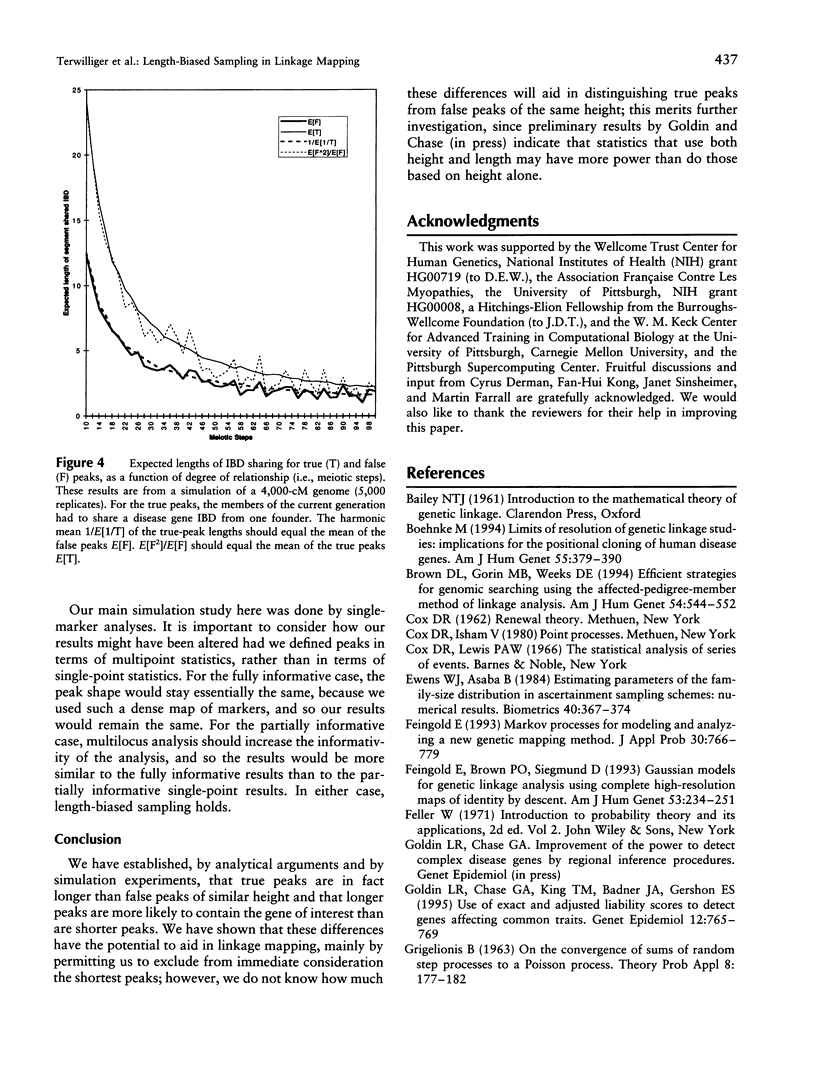
Disease-susceptibility loci are now being mapped via genomewide scans in which a linkage statistic is computed at each of a large number of markers. Such disease-susceptibility loci may be identified via a peak in the test statistic when the latter is plotted against the genetic map. In this paper we establish, by appealing to renewal theory, that true positive peaks are expected to be longer than false positive peaks. These results are verified by a realistic simulation of a genomewide linkage study based on the affected-sib-pair design. Since longer peaks are more likely to contain a gene of interest than are shorter peaks, these differences may aid in linkage mapping, justifying assignment of lower priority to shorter peaks. However, since these differences are generally small, statistics based on both peak length and height may not be much more powerful than those based on height alone. The results presented here also provide a theoretical framework for methods that use the length of shared haplotypes in populations to map disease genes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. L., Gorin M. B., Weeks D. E. Efficient strategies for genomic searching using the affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;54(3):544–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold E., Brown P. O., Siegmund D. Gaussian models for genetic linkage analysis using complete high-resolution maps of identity by descent. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):234–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin L. R., Chase G. A., King T. M., Badner J. A., Gershon E. S. Use of exact and adjusted liability scores to detect genes affecting common traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1995;12(6):765–769. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370120639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S. W. Gametogenesis processes and multilocus gene identity by descent. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Feb;58(2):408–419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwen R. H., Baharloo S., Blankenship K., Raeymaekers P., Juyn J., Sandkuijl L. A., Freimer N. B. Genome screening by searching for shared segments: mapping a gene for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1994 Dec;8(4):380–386. doi: 10.1038/ng1294-380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Kunkel L., Aldridge J., Latt S. A. Accurate and superaccurate gene mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):853–867. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz W. E., Zelen M. Effect of length sampling bias on labeled mitotic index waves. J Theor Biol. 1971 Aug;32(2):383–904. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. Length biased sampling in etiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):444–452. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturt E. A mapping function for human chromosomes. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 Nov;40(2):147–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D., Speer M., Ott J. Chromosome-based method for rapid computer simulation in human genetic linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(4):217–224. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



