Abstract
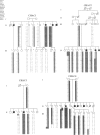
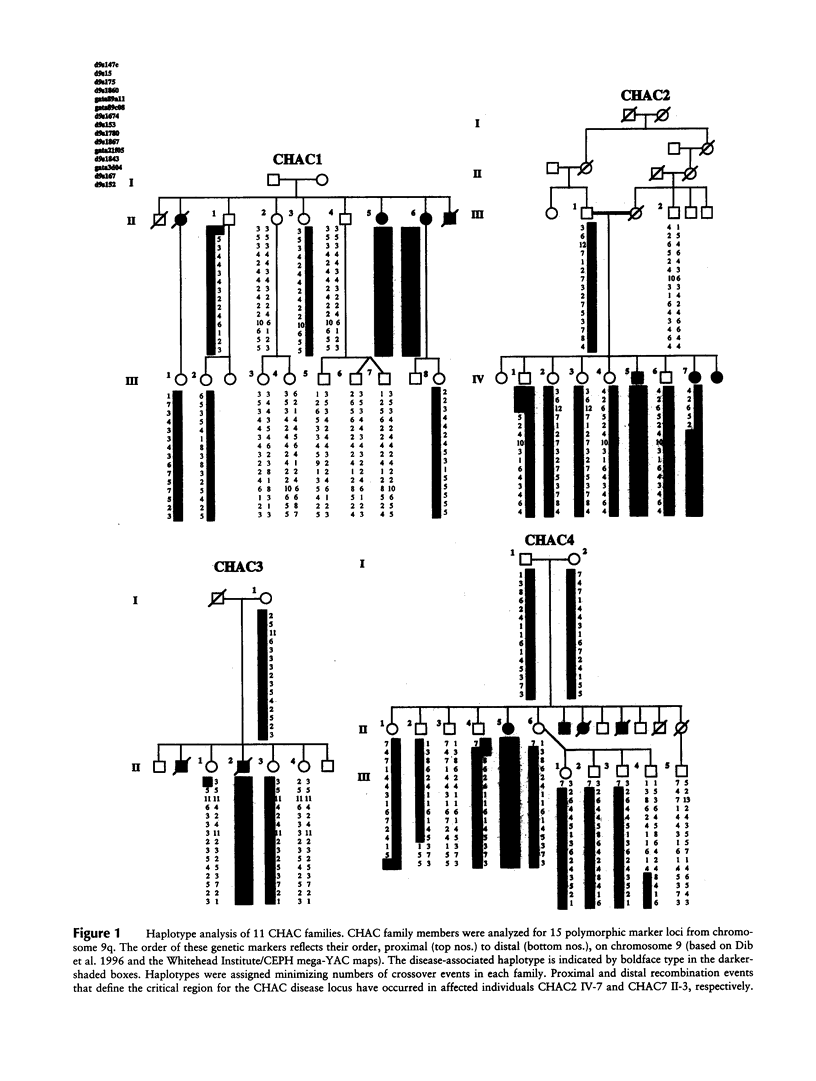
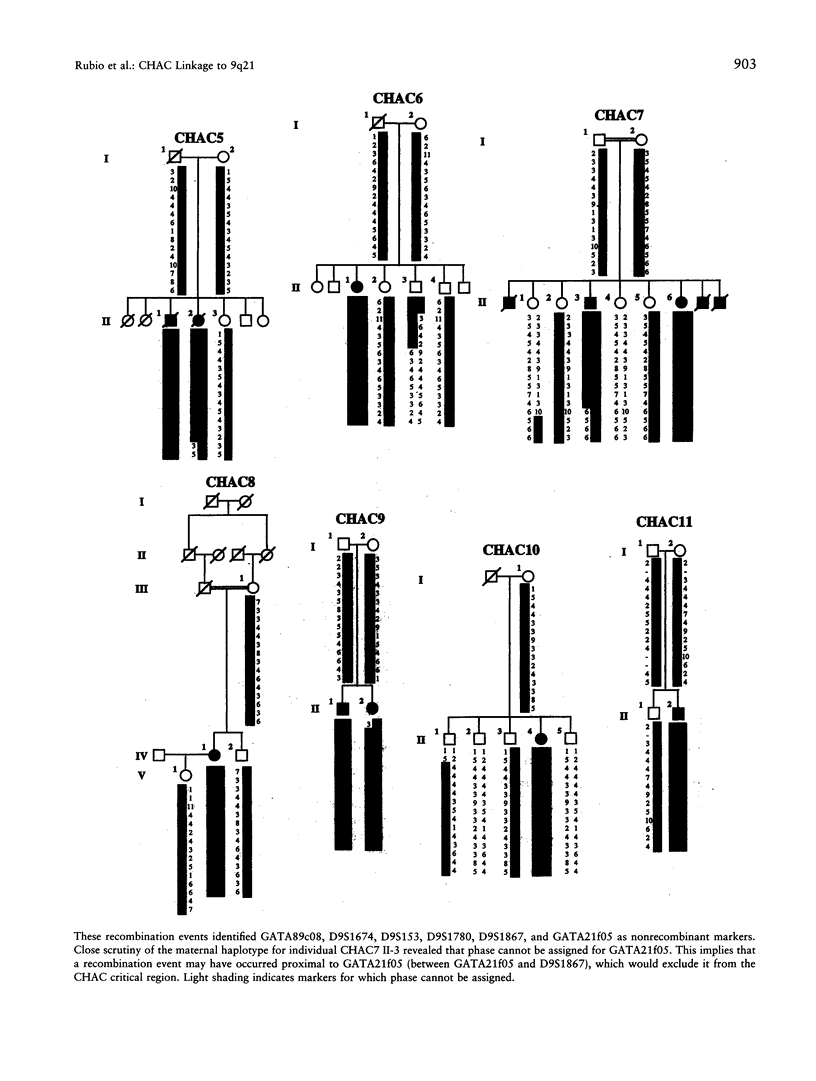
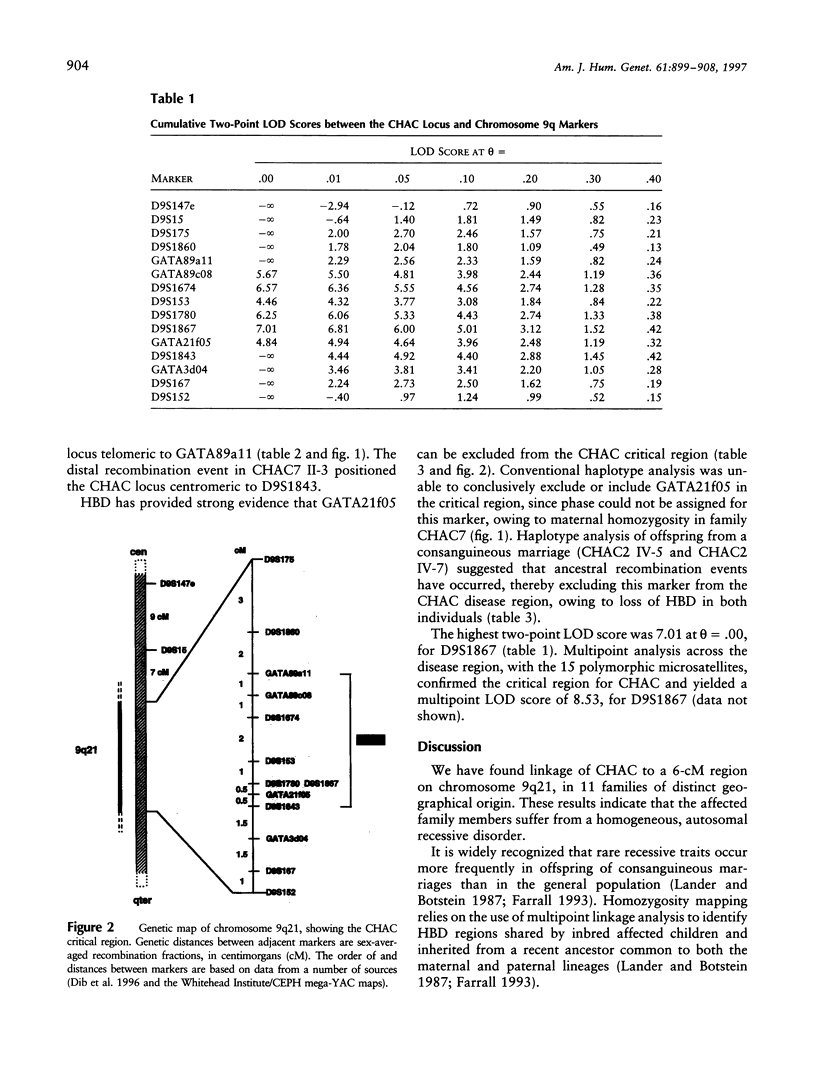
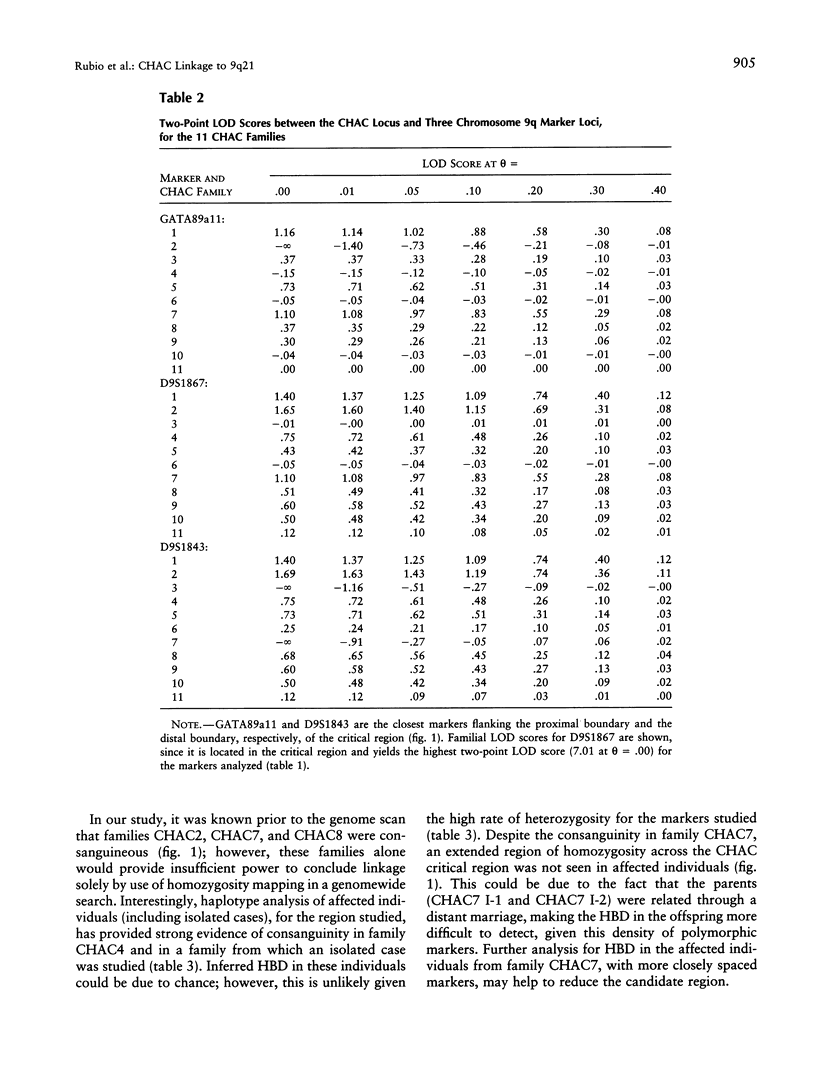
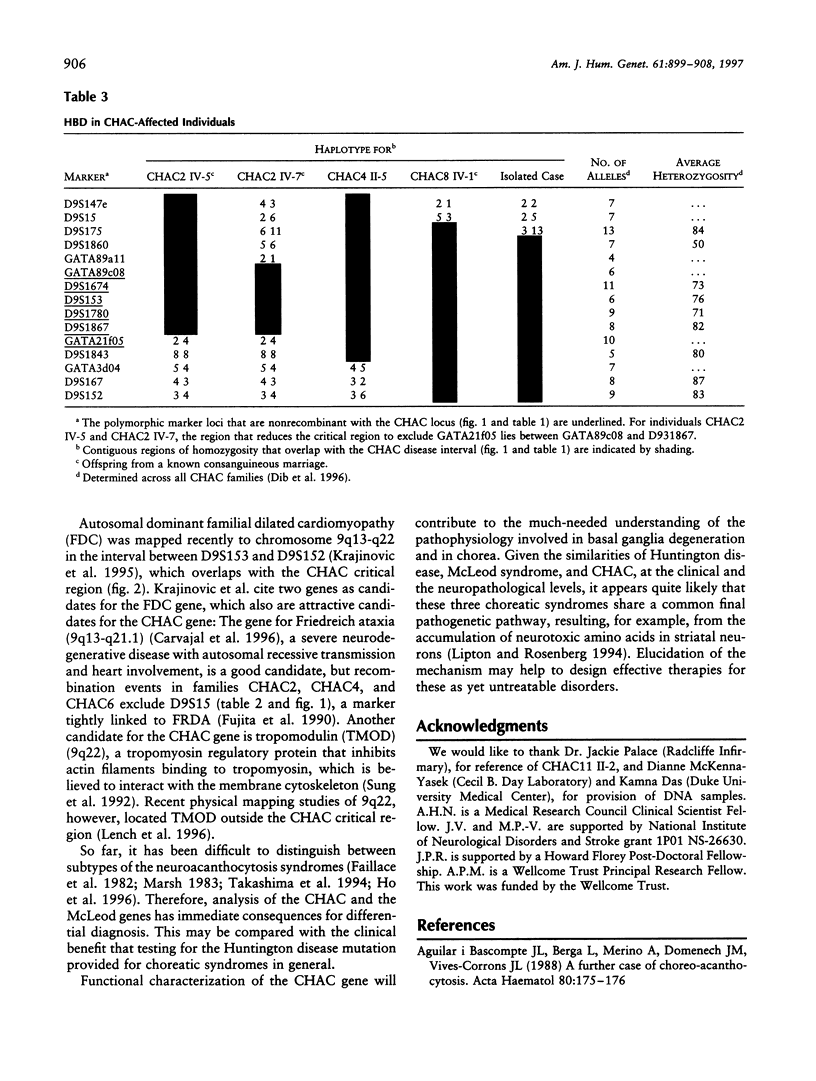
Chorea-acanthocytosis (CHAC) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by progressive neurodegeneration and unusual red-cell morphology (acanthocytosis), with onset in the third to fifth decade of life. Neurological impairment with acanthocytosis (neuroacanthocytosis) also is seen in abetalipoproteinemia and X-linked McLeod syndrome. Whereas the molecular etiology of McLeod syndrome has been defined (Ho et al. 1994), that of CHAC is still unknown. In the absence of cytogenetic rearrangements, we initiated a genomewide scan for linkage in 11 families, segregating for CHAC, who are of diverse geographical origin. We report here that the disease is linked, in all families, to a 6-cM region of chromosome 9q21 that is flanked by the recombinant markers GATA89a11 and D9S1843. A maximum two-point LOD score of 7.1 (theta = .00) for D9S1867 was achieved, and the linked region has been confirmed by homozygosity-by-descent, in offspring from inbred families. These findings provide strong evidence for the involvement of a single locus for CHAC and are the first step in positional cloning of the disease gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar i Bascompte J. L., Berga L., Merino A., Martí Domènech M. J., Vives-Corrons J. L. A further case of choreo-acanthocytosis. Acta Haematol. 1988;80(3):175–176. doi: 10.1159/000205628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso M. E., Teixeira F., Jimenez G., Escobar A. Chorea-acanthocytosis: report of a family and neuropathological study of two cases. Can J Neurol Sci. 1989 Nov;16(4):426–431. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100029516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASSEN F. A., KORNZWEIG A. L. Malformation of the erythrocytes in a case of atypical retinitis pigmentosa. Blood. 1950 Apr;5(4):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. D., Cederbaum S., Valey R. W., Stahl W. L. Familial degeneration of the basal ganglia with acanthocytosis: a clinical, neuropathological, and neurochemical study. Ann Neurol. 1978 Mar;3(3):253–258. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura I., Matias-Guiu J., Cervera C., Codina Puiggros A. Neuroacanthocytosis syndrome, apraxia of eyelid opening, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1276–1276. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1276-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal J. J., Pook M. A., dos Santos M., Doudney K., Hillermann R., Minogue S., Williamson R., Hsuan J. J., Chamberlain S. The Friedreich's ataxia gene encodes a novel phosphatidylinositol-4- phosphate 5-kinase. Nat Genet. 1996 Oct;14(2):157–162. doi: 10.1038/ng1096-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faillace R. T., Kingston W. J., Nanda N. C., Griggs R. C. Cardiomyopathy associated with the syndrome of amyotrophic chorea and acanthocytosis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 May;96(5):616–617. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-5-616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrall M. Homozygosity mapping: familiarity breeds debility. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):107–108. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer X., Julien J., Vital C., Lagueny A., Tison F. La chorée-acanthocytose. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1990;146(12):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita R., Hanauer A., Sirugo G., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Additional polymorphisms at marker loci D9S5 and D9S15 generate extended haplotypes in linkage disequilibrium with Friedreich ataxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. J. Acanthocytosis and neurological impairment--a review. Q J Med. 1989 Apr;71(264):291–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. J., Pullon H. W., Harding A. E., Owen J. S., Pires M., Daniels G. L., Imai Y., Misra V. P., King R. H., Jacobs J. M. Neuroacanthocytosis. A clinical, haematological and pathological study of 19 cases. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1A):13–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. F., Chalmers R. M., Davis M. B., Harding A. E., Monaco A. P. A novel point mutation in the McLeod syndrome gene in neuroacanthocytosis. Ann Neurol. 1996 May;39(5):672–675. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Chelly J., Carter N., Danek A., Crocker P., Monaco A. P. Isolation of the gene for McLeod syndrome that encodes a novel membrane transport protein. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. W., Erwin C. W., Bowman M. H., Massey E. W. Evoked potentials in choreoacanthocytosis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;63(4):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(86)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartsounis L. D., Hardie R. J. The pattern of cognitive impairments in neuroacanthocytosis. A frontosubcortical dementia. Arch Neurol. 1996 Jan;53(1):77–80. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1996.00550010095022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kito S., Itoga E., Hiroshige Y., Matsumoto N., Miwa S. A pedigree of amyotrophic chorea with acanthocytosis. Arch Neurol. 1980 Aug;37(8):514–517. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500570062010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajinovic M., Pinamonti B., Sinagra G., Vatta M., Severini G. M., Milasin J., Falaschi A., Camerini F., Giacca M., Mestroni L. Linkage of familial dilated cardiomyopathy to chromosome 9. Heart Muscle Disease Study Group. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Oct;57(4):846–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2884728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange H., Thörner G., Hopf A., Schröder K. F. Morphometric studies of the neuropathological changes in choreatic diseases. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Aug;28(4):401–425. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lench N. J., Telford E. A., Andersen S. E., Moynihan T. P., Robinson P. A., Markham A. F. An EST and STS-based YAC contig map of human chromosome 9q22.3. Genomics. 1996 Dec 1;38(2):199–205. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine I. M., Estes J. W., Looney J. M. Hereditary neurological disease with acanthocytosis. A new syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1968 Oct;19(4):403–409. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480040069007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Rosenberg P. A. Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994 Mar 3;330(9):613–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199403033300907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malandrini A., Fabrizi G. M., Palmeri S., Ciacci G., Salvadori C., Berti G., Bucalossi A., Federico A., Guazzi G. C. Choreo-acanthocytosis like phenotype without acanthocytes: clinicopathological case report. A contribution to the knowledge of the functional pathology of the caudate nucleus. Acta Neuropathol. 1993;86(6):651–658. doi: 10.1007/BF00294306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narcisi T. M., Shoulders C. C., Chester S. A., Read J., Brett D. J., Harrison G. B., Grantham T. T., Fox M. F., Povey S., de Bruin T. W. Mutations of the microsomal triglyceride-transfer-protein gene in abetalipoproteinemia. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1298–1310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard R. F., Lu C. S., Chu N. S., Teal P., Martin W. R., Calne D. B. Parkinsonism with neuroacanthocytosis. Can J Neurol Sci. 1990 Aug;17(3):298–301. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100030602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Marsh W. L. The Kell blood group system and the McLeod phenotype. Semin Hematol. 1993 Jul;30(3):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Davies J. L., Copeman J. B., Bennett S. T., Palmer S. M., Pritchard L. E., Gough S. C., Kawaguchi Y., Cordell H. J., Balfour K. M. Chromosome-specific microsatellite sets for fluorescence-based, semi-automated genome mapping. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):390–395. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Antoku Y., Iwashita H., Goto I., Nagamatsu K., Shii H. Chorea-acanthocytosis: abnormal composition of covalently bound fatty acids of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):664–669. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Iwashita H., Kakugawa M. Neuroacanthocytosis syndrome and choreoacanthocytosis (Levine-Critchley syndrome) Neurology. 1985 Nov;35(11):1679–1679. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.11.1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra S., Arena A., Xerra A., Gugliotta A. M., Galatioto S. Amyotrophic choreoacanthocytosis: is it really a very rare disease? Ital J Neurol Sci. 1986 Oct;7(5):521–524. doi: 10.1007/BF02342031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Weber J. L., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C., Even D. A., Wiles K., Gastier J. M., Pulido J. C., Yandava C., Sunden S. L. A collection of tri- and tetranucleotide repeat markers used to generate high quality, high resolution human genome-wide linkage maps. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Oct;4(10):1837–1844. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.10.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel E., Lange K. Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker-sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1323–1337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. A., Fowler V. M., Lambert K., Sussman M. A., Karr D., Chien S. Molecular cloning and characterization of human fetal liver tropomodulin. A tropomyosin-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2616–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima H., Sakai T., Iwashita H., Matsuda Y., Tanaka K., Oda K., Okubo Y., Reid M. E. A family of McLeod syndrome, masquerading as chorea-acanthocytosis. J Neurol Sci. 1994 Jun;124(1):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. M., Pericak-Vance M. A., Bowman M. H., Payne C. S., Fredane L., Siddique T., Roses A. D., Massey E. W. Chorea-acanthocytosis: a report of three new families and implications for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):403–410. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt T. N., Danek A., Reiter M., Heim M. U., Dirschinger J., Olsen E. G. McLeod syndrome: a distinct form of neuroacanthocytosis. Report of two cases and literature review with emphasis on neuromuscular manifestations. J Neurol. 1992 Jul;239(6):302–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00867584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]