Abstract
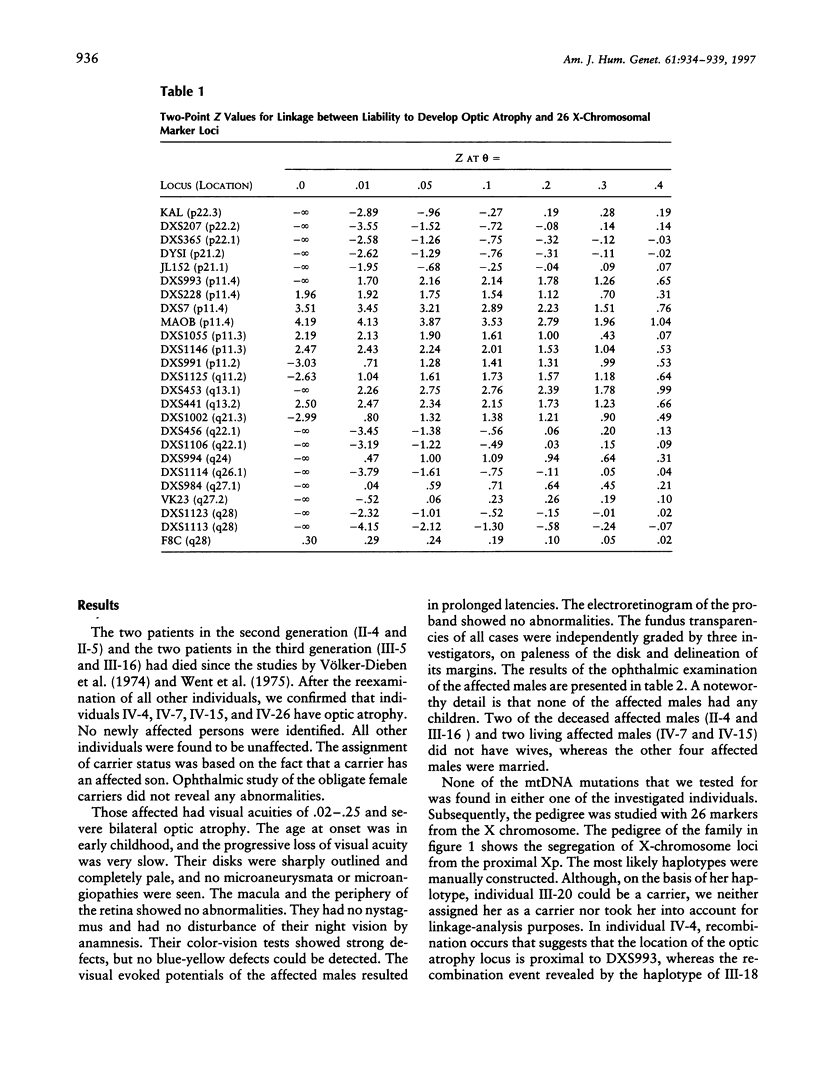
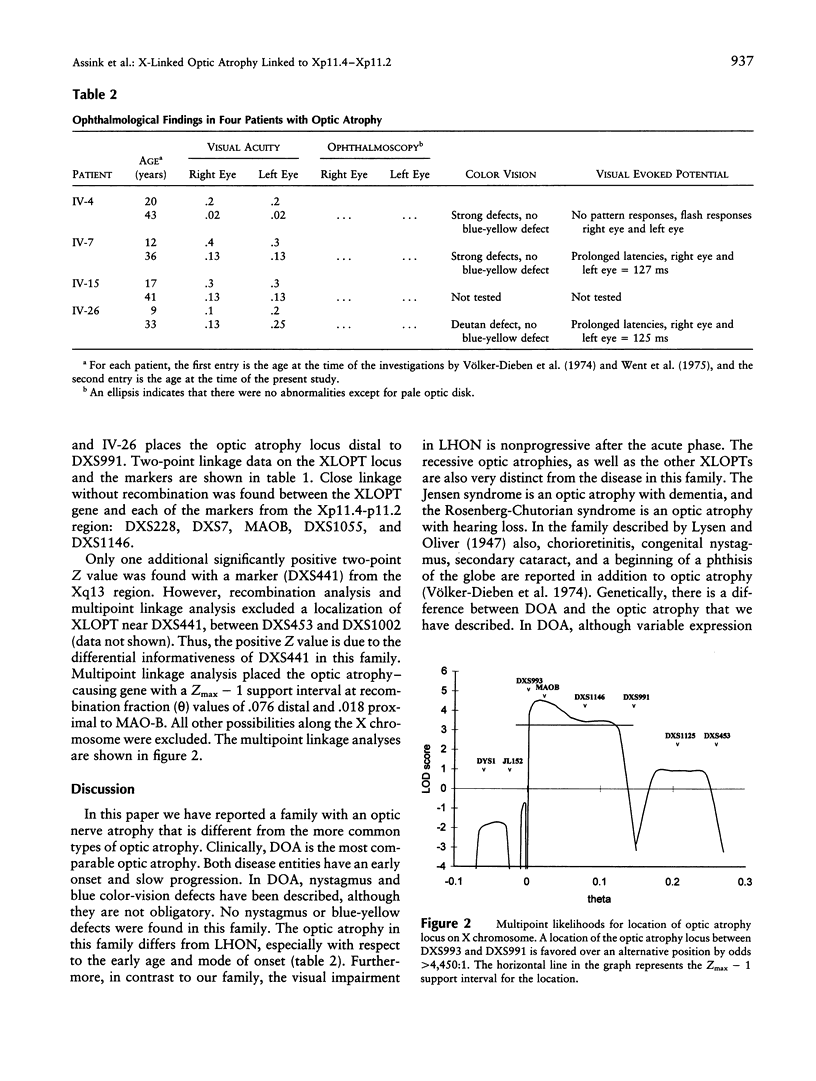
The aim of this study was to identify the chromosomal location of the disease-causing gene in a family apparently segregating X-linked optic atrophy. A large family of 45 individuals with a four-generation history of X-linked optic atrophy was reexamined in a full ophthalmic as well as electrophysiological examination. A DNA linkage analysis of the family was undertaken in order to identify the chromosomal location of the disease-causing gene. Linkage analysis was performed with 26 markers that spanned the entire X chromosome. The affected males showed very early onset and slow progression of the disease. Ophthalmic study of the female carriers did not reveal any abnormalities. Close linkage without recombination was found at the MAOB locus (maximum LOD score [Zmax] 4.19). The Zmax - 1 support interval was found at a recombination fraction of .076 distal and .018 proximal to MAOB. Multipoint linkage analysis placed the optic atrophy-causing gene in the Xp11.4-p11.21 interval between markers DXS993 and DXS991, whereas any other localization along the X chromosome could be excluded.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergen A. A., Samanns C., Schuurman E. J., van Osch L., van Dorp D. B., Pinckers A. J., Bakker E., Gal A., van Ommen G. J., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M. Multipoint linkage analysis in X-linked ocular albinism of the Nettleship-Falls type. Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;88(2):162–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00206065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black G. C., Craig I. W., Oostra R. J., Norby S., Rosenberg T., Morten K., Laborde A., Poulton J. Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: implications of the sex ratio for linkage studies in families with the 3460 ND1 mutation. Eye (Lond) 1995;9(Pt 4):513–516. doi: 10.1038/eye.1995.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu X. D., Rotter J. I. X chromosome-linked and mitochondrial gene control of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: evidence from segregation analysis for dependence on X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8198–8202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M. R., Müller B., Rötzer E., Berninger T., Kommerell G., Blankenagel A., Savontaus M. L., Meitinger T., Lorenz B. Leber's hereditary optic neuroretinopathy and the X-chromosomal susceptibility factor: no linkage to DXs7. Hum Hered. 1992;42(5):316–320. doi: 10.1159/000154089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Cox I., Denton M. J. Preliminary exclusion of an X-linked gene in Leber optic atrophy by linkage analysis. Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;82(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00291154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Kjer B., Kjer P., Rosenberg T. Dominant optic atrophy (OPA1) mapped to chromosome 3q region. I. Linkage analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):977–980. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi A. R., González C. H., Pratesi R. GAPO syndrome: report of three affected brothers. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Oct;19(2):217–223. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K., Reske-Nielsen E., Hein-Sørensen O., Warburg M. The syndrome of opticoacoustic nerve atrophy with dementia. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):517–518. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvonen V., Vilkki J., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E., Savontaus M. L. Reevaluation of the linkage of an optic atrophy susceptibility gene to X-chromosomal markers in Finnish families with Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy (LHON) Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):289–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok-van Alphen C. C. Four families with the dominant infantile form of optic nerve atrophy. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1970;48(5):905–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1970.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meire F., De Laey J. J., de Bie S., van Staey M., Matton M. T. Dominant optic nerve atrophy with progressive hearing loss and chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO). Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1985 Feb;5(1-2):91–97. doi: 10.3109/13816818509007861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra R. J., Kemp S., Bolhuis P. A., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M. No evidence for 'skewed' inactivation of the X-chromosome as cause of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy in female carriers. Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;97(4):500–505. doi: 10.1007/BF02267075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. N., Chutorian A. Familial opticoacoustic nerve degeneration and polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1967 Sep;17(9):827–832. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.9.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney M. G., Davis M. B., Lashwood A., Brockington M., Toscano A., Harding A. E. Evidence against an X-linked locus close to DXS7 determining visual loss susceptibility in British and Italian families with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):741–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treft R. L., Sanborn G. E., Carey J., Swartz M., Crisp D., Wester D. C., Creel D. Dominant optic atrophy, deafness, ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, dystaxia, and myopathy. A new syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1984 Aug;91(8):908–915. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(84)34214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANSENUS A. H. LEBER'S DISEASE IN THE NETHERLANDS. Doc Ophthalmol. 1963;17:1–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00573524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkki J., Ott J., Savontaus M. L., Aula P., Nikoskelainen E. K. Optic atrophy in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy is probably determined by an X-chromosomal gene closely linked to DXS7. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):486–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Singh G., Lott M. T., Hodge J. A., Schurr T. G., Lezza A. M., Elsas L. J., 2nd, Nikoskelainen E. K. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.3201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Went L. N., De Vries-De Mol E. C., Völker-Dieben H. J. A family with apparently sex-linked optic atrophy. J Med Genet. 1975 Mar;12(1):94–98. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


