Abstract
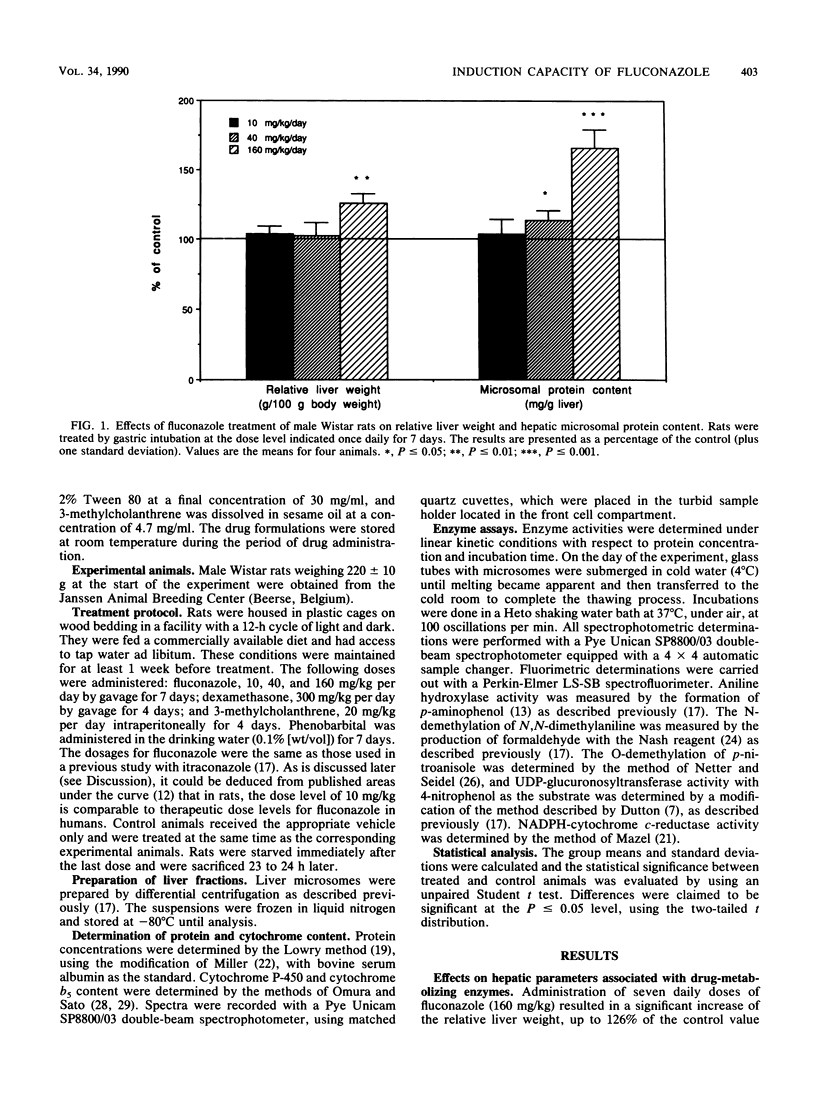
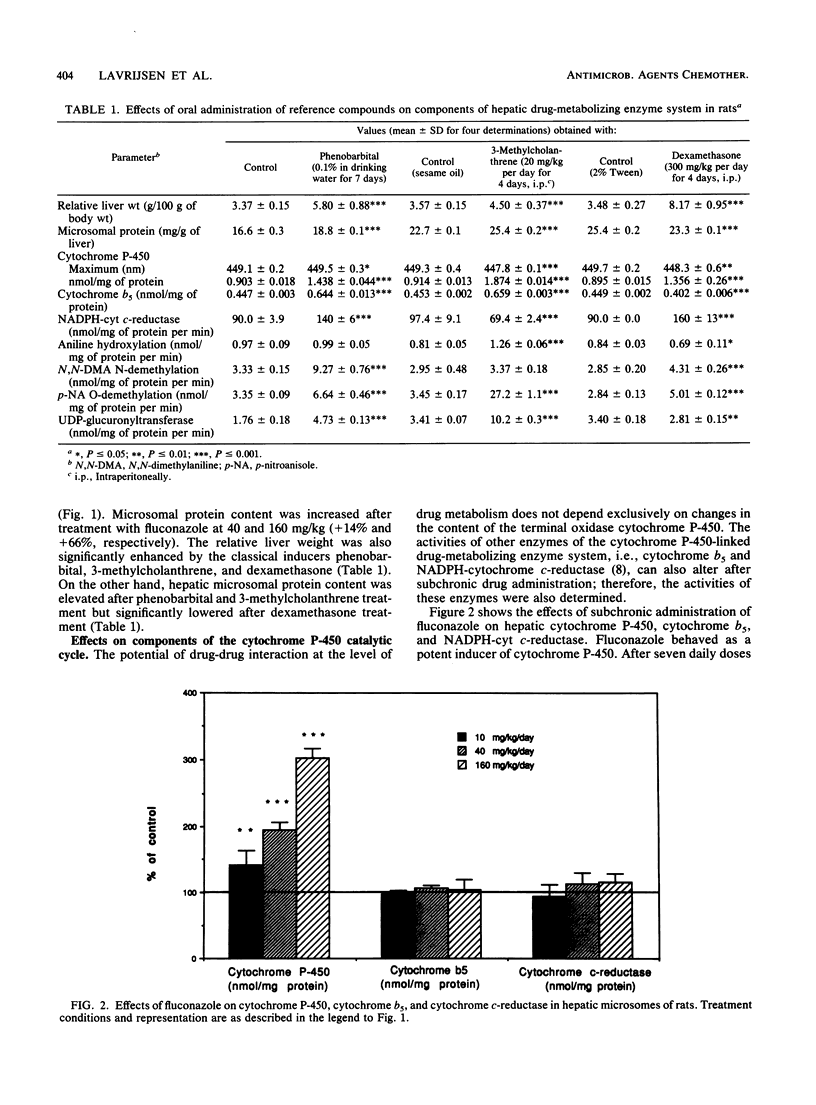
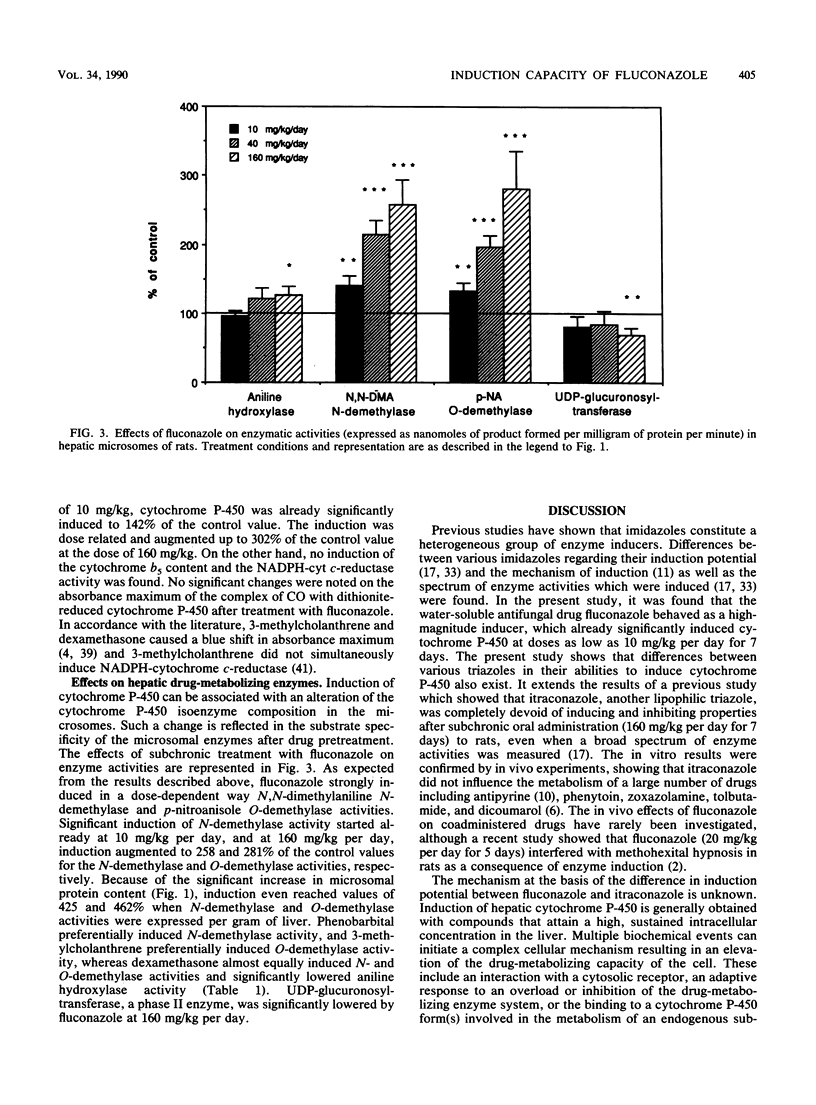
The induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes in rat liver was studied after subchronic administration of the new triazole antifungal agent fluconazole. The administered doses were 10, 40, and 160 mg/kg per day for 7 days. Fluconazole behaved as a high-magnitude inducer and significantly increased cytochrome P-450 concentrations already at 10 mg/kg (+42%). Cytochrome P-450 induction by fluconazole was dose dependent and reached a value of 302% of the control value at the dose of 160 mg/kg. The induction effects on cytochrome P-450 were also reflected in the drug-metabolizing enzyme activities in hepatic microsomes of pretreated rats. Fluconazole (160 mg/kg per day) preferentially induced the demethylase activities of N,N-dimethylaniline and p-nitroanisole to 258 and 281% of the control values, respectively. The detoxification enzyme UDP-glucuronosyltransferase was significantly lowered by fluconazole at the highest dose. A possible link between the induction potential and the pharmacokinetic properties of triazole antifungal agents is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Atchison M. Genes for cytochrome P-450 and their regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(3):247–305. doi: 10.3109/10409238609084657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back D. J., Tjia J. F., Karbwang J., Colbert J. In vitro inhibition studies of tolbutamide hydroxylase activity of human liver microsomes by azoles, sulphonamides and quinolines. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;26(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum L. S., Baird M. B., Massie H. R. Pregnenolone-16alpha-carbonitrile-inducible cytochrome P450 in rat liver. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;15(3):553–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damanhouri Z., Gumbleton M., Nicholls P. J., Shaw M. A. In-vivo effects of itraconazole on hepatic mixed-function oxidase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21(2):187–194. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. A., Wrighton S. A., Molowa D. T., Thomas P. E., Levin W., Guzelian P. S. Coinduction of multiple hepatic cytochrome P-450 proteins and their mRNAs in rats treated with imidazole antimycotic agents. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):279–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey M. J., Jevons S., Tarbit M. H. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of UK-49,858, a metabolically stable triazole antifungal drug, in animals and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):648–653. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., Ito A., Sato R. Evidence for biochemically different types of vesicles in the hepatic microsomal fraction. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):417–428. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Coon M. J. Purification of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 isozymes 3a and 6 from imidazole-treated rabbits. Evidence for the identity of isozyme 3a with the form obtained by ethanol treatment. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):494–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Delfa I., Zhu Q. M., Mo Z., Blaschke T. F. Fluconazole is a potent inhibitor of antipyrine metabolism in vivo in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 1989 Jan-Feb;17(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavrijsen K., Van Houdt J., Thijs D., Meuldermans W., Heykants J. Induction potential of antifungals containing an imidazole or triazole moiety. Miconazole and ketoconazole, but not itraconazole are able to induce hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes of male rats at high doses. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 1;35(11):1867–1878. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavrijsen K., van Houdt J., Thijs D., Meuldermans W., Heykants J. Interaction of miconazole, ketoconazole and itraconazole with rat-liver microsomes. Xenobiotica. 1987 Jan;17(1):45–57. doi: 10.3109/00498258709047174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdalou J., Totis M., Boiteux-Antoine A. F., Fournel-Gigleux S., Siest G., Schladt L., Oesch F. Effect of 1-benzylimidazole on cytochromes P-450 induction and on the activities of epoxide hydrolases and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 1;37(17):3297–3304. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90642-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETTER K. J., SEIDEL G. AN ADAPTIVELY STIMULATED O-DEMETHYLATING SYSTEM IN RAT LIVER MICROSOMES AND ITS KINETIC PROPERTIES. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Oct;146:61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Roberts E. A., Harper P. A., Denison M. S. Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms and consequences. Clin Biochem. 1986 Apr;19(2):132–141. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(86)80060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papac D. I., Franklin M. R. N-benzylimidazole, a high magnitude inducer of rat hepatic cytochrome P-450 exhibiting both polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon- and phenobarbital-type induction of phase I and phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1988 Mar-Apr;16(2):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter J. K., Franklin M. R. High magnitude hepatic cytochrome P-450 induction by an N-substituted imidazole antimycotic, clotrimazole. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 1;36(17):2783–2787. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter J. K., Franklin M. R. Induction and inhibition of rat hepatic drug metabolism by N-substituted imidazole drugs. Drug Metab Dispos. 1987 May-Jun;15(3):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues A. D., Waddell P. R., Ah-Sing E., Morris B. A., Wolf C. R., Ioannides C. Induction of the rat hepatic microsomal mixed-function oxidases by 3 imidazole-containing antifungal agents: selectivity for the cytochrome P-450IIB and P-450III families of cytochromes P-450. Toxicology. 1988 Aug;50(3):283–301. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(88)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Guzelian P. S. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by glucocorticoids in rat liver. II. Evidence that glucocorticoids regulate induction of cytochrome P-450 by a nonclassical receptor mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2007–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick J. L., Stoler B. S., Katz D. B., Anderson W. H. Rifampin, oral contraceptives, and pregnancy. JAMA. 1976 Sep 20;236(12):1382–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R., Remmer H. Classes of hepatic microsomal mixed function oxidase inducers. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;7(2):203–244. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira Y., Greenspan P., Kapke G. F., Redick J. A., Baron J. Effects of phenobarbital, pregnenolone-16 alpha-carbonitrile, and 3-methylcholanthrene pretreatments on the distribution of NADPH-cytochrome c (P-450) reductase within the liver lobule. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):304–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cauteren H., Heykants J., De Coster R., Cauwenbergh G. Itraconazole: pharmacologic studies in animals and humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9 (Suppl 1):S43–S46. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_1.s43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tyle J. H. Ketoconazole. Mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, adverse reactions and therapeutic use. Pharmacotherapy. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):343–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1984.tb03398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Bossche H. Biochemical targets for antifungal azole derivatives: hypothesis on the mode of action. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1985;1:313–351. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9547-8_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


