Abstract
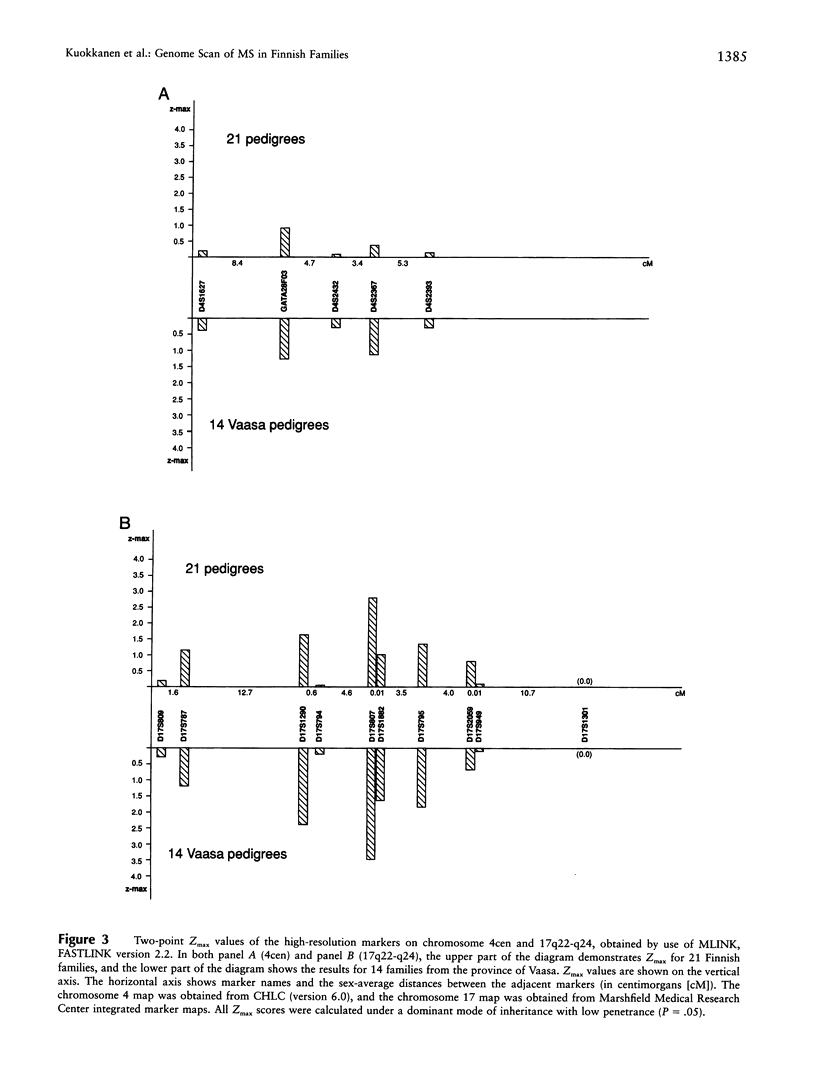
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological, demyelinating disorder with a putative autoimmune etiology. It is thought to be a multifactorial disease with a complex mode of inheritance. Here we report the results of a two-stage genomewide scan for loci predisposing to MS. The first stage of the screen, with a low-resolution map, was performed in a selection of 16 pedigrees collected from an isolated Finnish population. Multipoint, non-parametric linkage analysis of the 328 markers did not reveal statistically significant results. However, 10 slightly interesting regions (P = .1-.15) emerged, including our previous findings of the HLA complex on 6p21 and a putative locus on 5p14-p12. Eight of these novel regions were further analyzed by use of denser marker maps, in the second stage of the scan. For the chromosomal regions 4cen, 11tel, and 17q, the statistical significance increased, but not conclusively; for 2q32 and 10q21, the statistical significance did not change. Accordingly, genotyping of the high-density markers in these regions was performed, and the data were analyzed by use of two-point, parametric linkage analysis using the complete pedigree information of the 21 Finnish multiplex families. We detected suggestive evidence for a predisposing locus on chromosomal region 17q22-q24. Several markers on 17q22-q24 yielded positive LOD scores, with the maximum LOD score (Zmax) occurring with D17S807 (Zmax = 2.8, theta = .04; dominant model). Interestingly, a suggestive linkage between MS and the markers on 17q22-q24 was also revealed by a recent genomewide scan in MS families from the United Kingdom.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall S. S., Concannon P., Charmley P., McFarland H. F., Gatti R. A., Hood L. E., McFarlin D. E., Biddison W. E. The germline repertoire of T cell receptor beta-chain genes in patients with chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jan;21(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dib C., Fauré S., Fizames C., Samson D., Drouot N., Vignal A., Millasseau P., Marc S., Hazan J., Seboun E. A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature. 1996 Mar 14;380(6570):152–154. doi: 10.1038/380152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Paty D. W., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J., Seland T. P., Duquette P., Grey T. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Cousin H. K., Feasby T. E., Paty D. W. Optic neuritis in familial MS. Neurology. 1981 Sep;31(9):1138–1142. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.9.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Kukay K., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Rice G., Anderson C., Armstrong H., Cousin K., Bell R. B., Hader W. A full genome search in multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):472–476. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Sadovnick A. D., Risch N. J. A genetic basis for familial aggregation in multiple sclerosis. Canadian Collaborative Study Group. Nature. 1995 Sep 14;377(6545):150–151. doi: 10.1038/377150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eoli M., Pandolfo M., Milanese C., Gasparini P., Salmaggi A., Zeviani M. The myelin basic protein gene is not a major susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis in Italian patients. J Neurol. 1994 Oct;241(10):615–619. doi: 10.1007/BF00920626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillert J., Leng C., Olerup O. No association with germline T cell receptor beta-chain gene alleles or haplotypes in Swedish patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 May;32(2):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90006-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen E., Wikström J., Porras J., Palo J. The epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in Finland: increase of prevalence and stability of foci in high-risk areas. Acta Neurol Scand. 1983 May;67(5):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb04574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M., Seuchter S. A., Baur M. P. Linkage analysis in nuclear families. 2: Relationship between affected sib-pair tests and lod score analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jan-Feb;44(1):44–51. doi: 10.1159/000154188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Reeve-Daly M. P., Lander E. S. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1347–1363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuokkanen S., Sundvall M., Terwilliger J. D., Tienari P. J., Wikström J., Holmdahl R., Pettersson U., Peltonen L. A putative vulnerability locus to multiple sclerosis maps to 5p14-p12 in a region syntenic to the murine locus Eae2. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):477–480. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. G., Rose J. W., Petajan J. H., Stauffer D., Kamerath C., Leppert M. Discordance of T-cell receptor beta-chain genes in familial multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1991 Sep;30(3):402–410. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Manion F., Quillen J., Sheffield V. C., Sunden S., Duyk G. M. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Cooperative Human Linkage Center (CHLC). Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2049–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8091227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Hillert J. HLA class II-associated genetic susceptibility in multiple sclerosis: a critical evaluation. Tissue Antigens. 1991 Jul;38(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1991.tb02029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J., Gerken S., Lynch S., Pisani P., Varvil T., Otterud B., Leppert M. Genetic susceptibility in familial multiple sclerosis not linked to the myelin basic protein gene. Lancet. 1993 May 8;341(8854):1179–1181. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadovnick A. D., Baird P. A., Ward R. H. Multiple sclerosis: updated risks for relatives. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;29(3):533–541. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadovnick A. D., Ebers G. C., Dyment D. A., Risch N. J. Evidence for genetic basis of multiple sclerosis. The Canadian Collaborative Study Group. Lancet. 1996 Jun 22;347(9017):1728–1730. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90807-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawcer S., Jones H. B., Feakes R., Gray J., Smaldon N., Chataway J., Robertson N., Clayton D., Goodfellow P. N., Compston A. A genome screen in multiple sclerosis reveals susceptibility loci on chromosome 6p21 and 17q22. Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):464–468. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer A. A., Gupta S. K., Shriram K., Cottingham R. W., Jr Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum Hered. 1994 Jul-Aug;44(4):225–237. doi: 10.1159/000154222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seboun E., Robinson M. A., Doolittle T. H., Ciulla T. A., Kindt T. J., Hauser S. L. A susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis is linked to the T cell receptor beta chain complex. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1095–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundvall M., Jirholt J., Yang H. T., Jansson L., Engström A., Pettersson U., Holmdahl R. Identification of murine loci associated with susceptibility to chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat Genet. 1995 Jul;10(3):313–317. doi: 10.1038/ng0795-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienari P. J., Salonen O., Wikström J., Valanne L., Palo J. Familial multiple sclerosis: MRI findings in clinically affected and unaffected siblings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Oct;55(10):883–886. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.10.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienari P. J., Wikström J., Koskimies S., Partanen J., Palo J., Peltonen L. Reappraisal of HLA in multiple sclerosis: close linkage in multiplex families. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(4):257–268. doi: 10.1159/000472423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienari P. J., Wikström J., Sajantila A., Palo J., Peltonen L. Genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis linked to myelin basic protein gene. Lancet. 1992 Oct 24;340(8826):987–991. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93007-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandevyver C., Stinissen P., Cassiman J. J., Raus J. Myelin basic protein gene polymorphism is not associated with chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Jun;52(1):97–99. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström J. Studies on the clustering of multiple sclerosis in Finland II: microepidemiology in one high-risk county with special reference to familial cases. Acta Neurol Scand. 1975 Mar;51(3):173–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1975.tb07598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood N. W., Holmans P., Clayton D., Robertson N., Compston D. A. No linkage or association between multiple sclerosis and the myelin basic protein gene in affected sibling pairs. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Oct;57(10):1191–1194. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.10.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]