Abstract
A number of recent linkage studies have suggested the presence of a schizophrenia susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p. We evaluated 28 genetic markers, spanning chromosome 6, for linkage to schizophrenia in 10 moderately large Canadian families of Celtic ancestry. Parametric analyses of these families under autosomal dominant and recessive models, using broad and narrow definitions of schizophrenia, produced no significant evidence for linkage. A sib-pair analysis using categorical disease definitions also failed to produce significant evidence for linkage. We then conducted a separate sibpair analysis using scores on positive-symptom (psychotic), negative-symptom (deficit), and general psychopathology-symptom scales as quantitative traits. With the positive symptom-scale scores, the marker D6S1960 produced P = 1.2 x 10(-5) under two-point and P = 5.4 x 10(-6) under multipoint analyses. Using simulation studies, we determined that these nominal P values correspond to empirical P values of .034 and .0085, respectively. These results suggest that a schizophrenia susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p may be related to the severity of psychotic symptoms. Assessment of behavioral quantitative traits may provide increased power over categorical phenotype assignment for detection of linkage in complex psychiatric disorders.
Full text
PDF

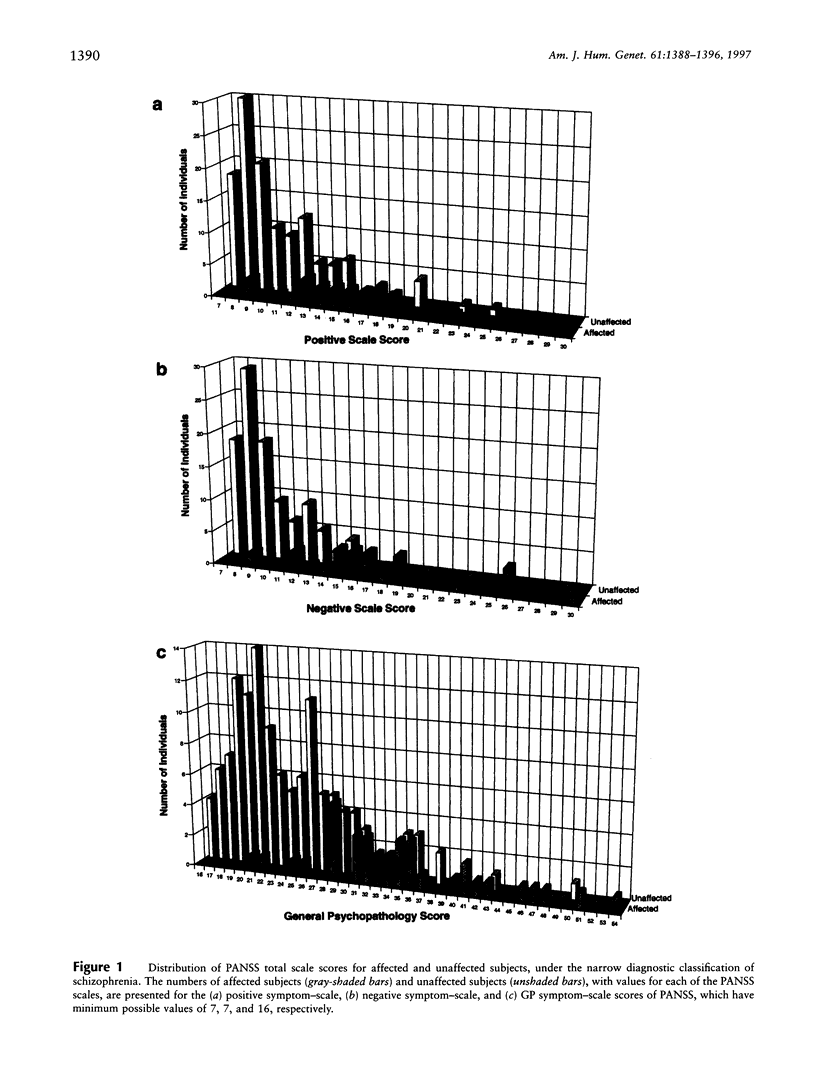

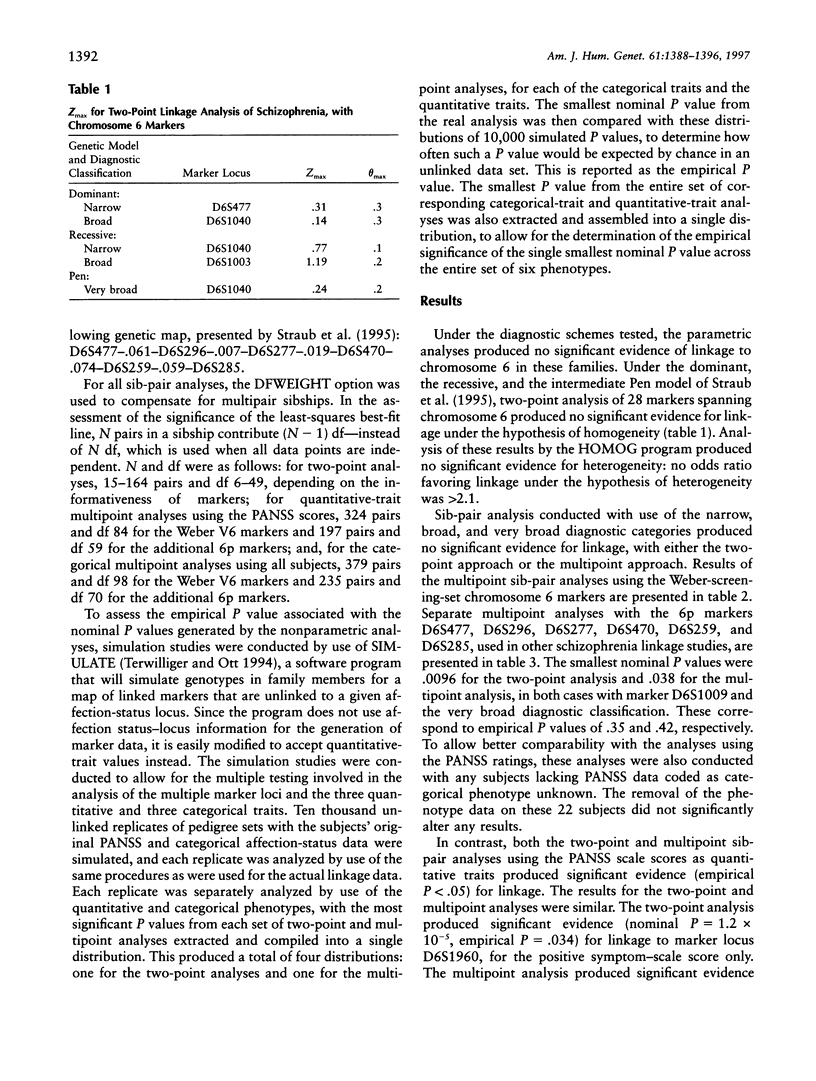
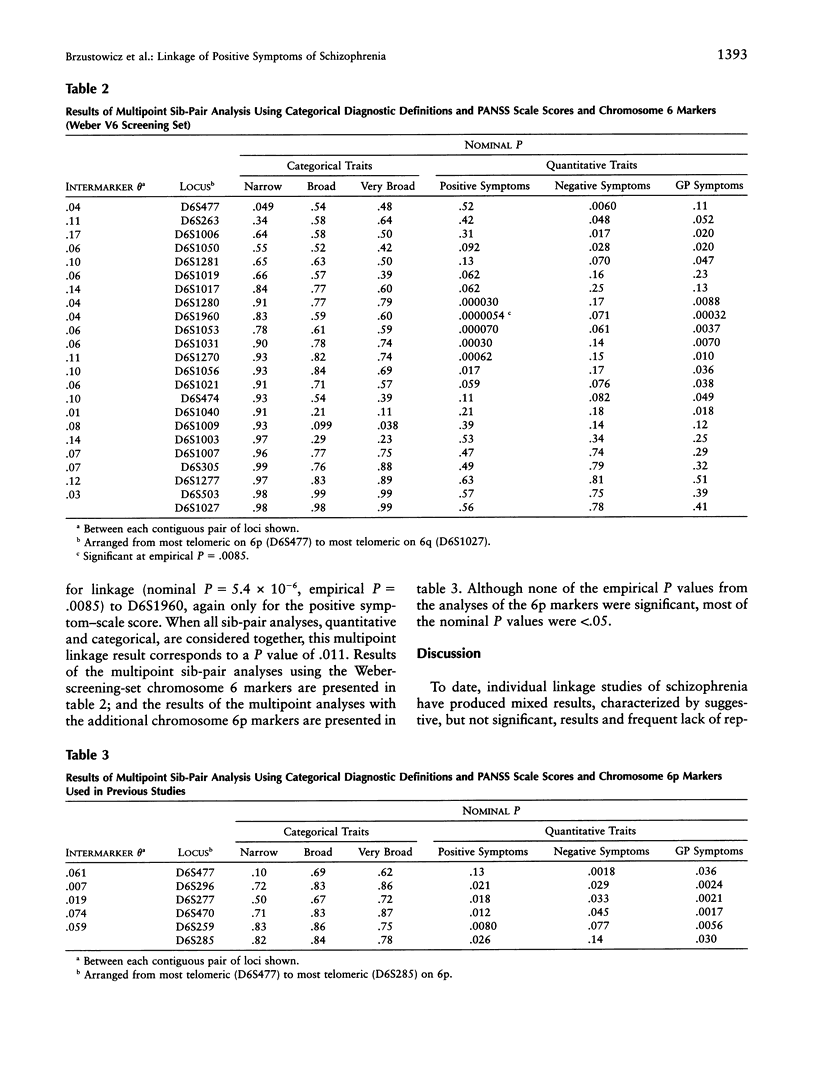



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen N. C., Nopoulos P., Schultz S., Miller D., Gupta S., Swayze V., Flaum M. Positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia: past, present, and future. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1994;384:51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb05891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Blouin J. L., Pulver A. E., Wolyniec P., Lasseter V. K., Nestadt G., Kasch L., Babb R., Kazazian H. H., Dombroski B. Schizophrenia susceptibility and chromosome 6p24-22. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):235–236. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt S., Andreasen N. C., Flaum M., Miller D., Nopoulos P. A longitudinal study of symptom dimensions in schizophrenia. Prediction and patterns of change. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 May;52(5):352–360. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950170026004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett A. S., Collins E. J., Nuttall S. E., Honer W. G. Positive and negative symptoms in families with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 1993 Dec;11(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(93)90033-f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett A. S., Honer W. G. Evidence for anticipation in schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):864–870. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R. H., Bernstein G., Kaplansky L. M., Lipsitz J. D., Rinaldi A., Slater S. L., Cornblatt B. A., Erlenmeyer-Kimling L. Social competence and positive and negative symptoms: a longitudinal study of children and adolescents at risk for schizophrenia and affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Sep;148(9):1182–1188. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.9.1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. W., Thara R., Federman B., Melton B., Liang K. Y. Structure and course of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 Feb;52(2):127–134. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950140045005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraone S. V., Kremen W. S., Lyons M. J., Pepple J. R., Seidman L. J., Tsuang M. T. Diagnostic accuracy and linkage analysis: how useful are schizophrenia spectrum phenotypes? Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;152(9):1286–1290. doi: 10.1176/ajp.152.9.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer A. E., Williams J., Jones I. Phenotypic definitions of psychotic illness for molecular genetic research. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Dec 15;54(4):365–371. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320540416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurling H., Kalsi G., Chen A. C., Green M., Butler R., Read T., Murphy P., Curtis D., Sharma T., Chen A. H. Schizophrenia susceptibility and chromosome 6p24-22. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):234–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseman J. K., Elston R. C. The investigation of linkage between a quantitative trait and a marker locus. Behav Genet. 1972 Mar;2(1):3–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01066731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. R., Fiszbein A., Opler L. A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(2):261–276. doi: 10.1093/schbul/13.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., Diehl S. R. The genetics of schizophrenia: a current, genetic-epidemiologic perspective. Schizophr Bull. 1993;19(2):261–285. doi: 10.1093/schbul/19.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malla A. K., Norman R. M., Williamson P. Stability of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Can J Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;38(9):617–621. doi: 10.1177/070674379303800910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse S., Levy D. L., Kinney D., Deutsch C., Lajonchere C., Yurgelun-Todd D., Woods B., Holzman P. S. Gene expression in mental illness: a navigation chart to future progress. J Psychiatr Res. 1992 Oct;26(4):461–473. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(92)90046-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin P., Asherson P., Owen M., Farmer A. The strength of the genetic effect. Is there room for an environmental influence in the aetiology of schizophrenia? Br J Psychiatry. 1994 May;164(5):593–599. doi: 10.1192/bjp.164.5.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moises H. W., Yang L., Kristbjarnarson H., Wiese C., Byerley W., Macciardi F., Arolt V., Blackwood D., Liu X., Sjögren B. An international two-stage genome-wide search for schizophrenia susceptibility genes. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):321–324. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry B. J., Nancarrow D. J., Lennon D. P., Sandkuijl L. A., Crowe R. R., Silverman J. M., Mohs R. C., Siever L. J., Endicott J., Sharpe L. Schizophrenia susceptibility and chromosome 6p24-22. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):233–234. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey E. R., Bailer J., Bräuer W., Händel M., Laubenstein D., Stein A. Stability trends and longitudinal correlations of negative and positive syndromes within a three-year follow-up of initially hospitalized schizophrenics. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1994 Dec;90(6):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb01615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits. II. The power of affected relative pairs. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):229–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M. Psychiatric genetics: research challenges and pathways forward. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Sep 15;54(3):185–198. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320540305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab S. G., Albus M., Hallmayer J., Hönig S., Borrmann M., Lichtermann D., Ebstein R. P., Ackenheil M., Lerer B., Risch N. Evaluation of a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p by multipoint affected sib-pair linkage analysis. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., MacLean C. J., O'Neill F. A., Burke J., Murphy B., Duke F., Shinkwin R., Webb B. T., Zhang J., Walsh D. A potential vulnerability locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p24-22: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):287–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuang M. T. Genotypes, phenotypes, and the brain. A search for connections in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;163:299–307. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.3.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Detera-Wadleigh S. D., Coon H., Sun C. E., Goldin L. R., Duffy D. L., Byerley W. F., Gershon E. S., Diehl S. R. Evidence of linkage disequilibrium between schizophrenia and the SCa1 CAG repeat on chromosome 6p23. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Sep;59(3):731–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Sun C. E., Walczak C. A., Ziegle J. S., Kipps B. R., Goldin L. R., Diehl S. R. Evidence for a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6pter-p22. Nat Genet. 1995 May;10(1):41–46. doi: 10.1038/ng0595-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


