Abstract
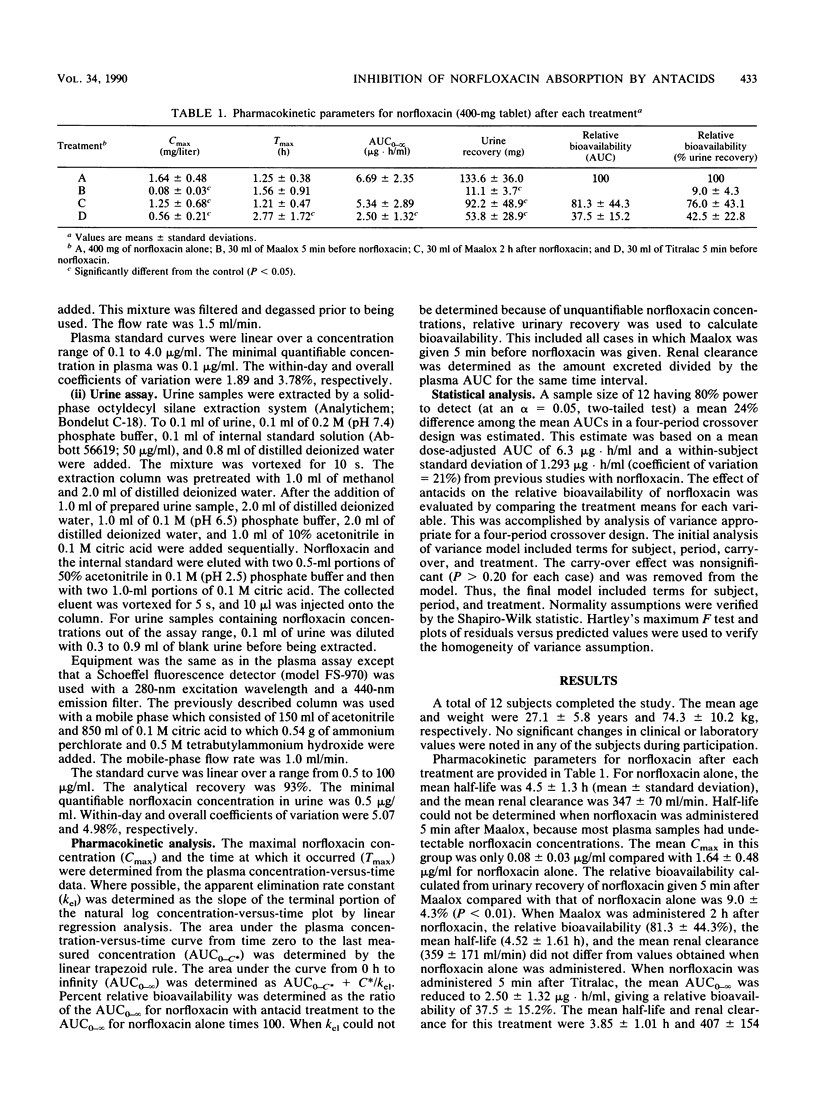
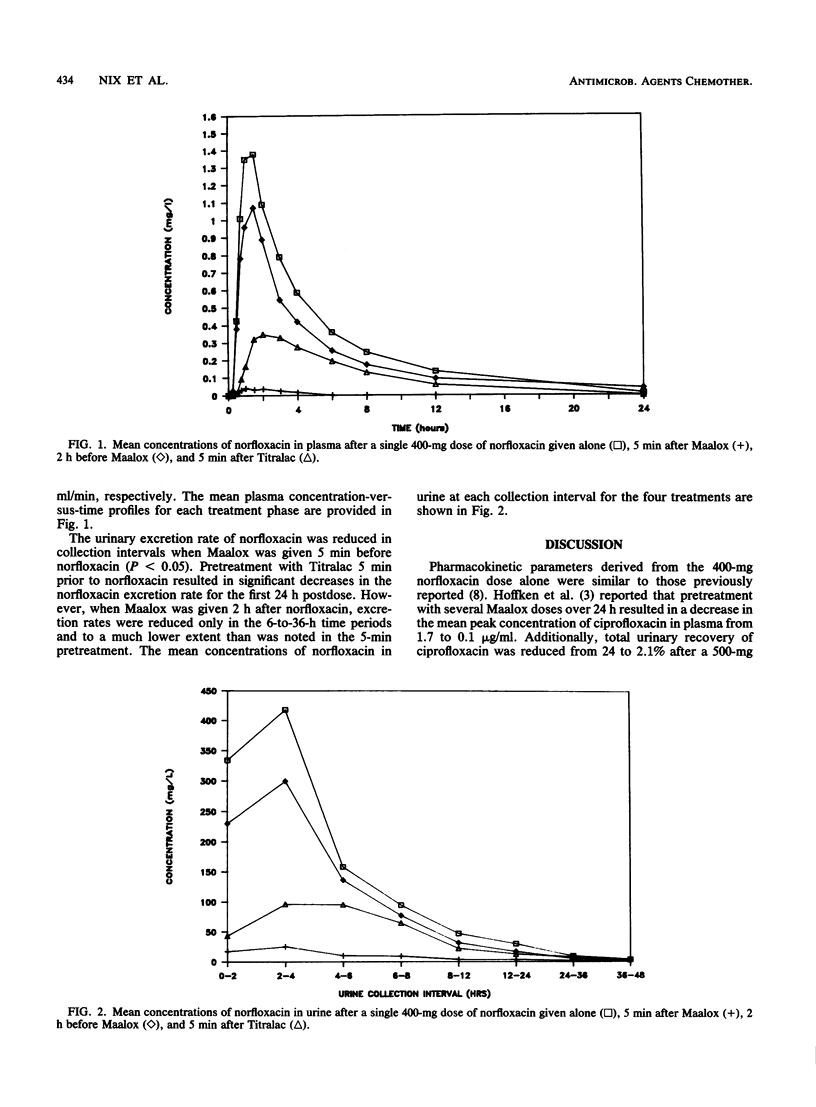
The effect of antacids on the systemic absorption of oral norfloxacin was evaluated in 12 healthy volunteers. Subjects were given each treatment in a balanced sequence at 7-day intervals. Treatments included 400 mg of norfloxacin alone, 400 mg of norfloxacin 5 min after aluminum-magnesium hydroxide (Maalox), Maalox 2 h after 400 mg of norfloxacin, and 400 mg of norfloxacin 5 min after calcium carbonate (Titralac). Blood and urine samples were collected at predetermined time intervals for 24 and 48 h, respectively. Norfloxacin concentrations in plasma and urine were determined by high-pressure liquid chromatography. The area under the plasma concentration-versus-time curve from time zero to infinity and urinary recovery were used to compare the relative bioavailability of norfloxacin with antacids with that of norfloxacin alone. Norfloxacin bioavailability was markedly reduced when subjects received antacid pretreatment. When norfloxacin was given 5 min after Maalox and Titralac, the bioavailabilities were 9.02 and 37.5%, respectively, relative to that for 400 mg of norfloxacin alone. When Maalox was given 2 h after norfloxacin, maximal concentrations of norfloxacin in plasma occurred between 1 and 1.5 h postdose, and absorption was reduced to a lesser extent, with a relative bioavailability of 81.31%. Norfloxacin concentrations in urine were also reduced as a result of antacid administration. Antacids containing aluminum and magnesium salts and calcium carbonate should be avoided by patients taking norfloxacin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gesu G. P., Eftimiadi C., Debbia E., Schito G. C. Effects of changes in pH, medium and inoculum size on the in vitro activity of different quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics against urinary pathogens. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1987;13(2):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Borner K., Glatzel P. D., Koeppe P., Lode H. Reduced enteral absorption of ciprofloxacin in the presence of antacids. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02013667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Yamamoto M., Arita T. Interactions of aluminum, magnesium, and calcium ions with nalidixic acid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1978 May;26(5):1505–1510. doi: 10.1248/cpb.26.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., DeVito J. M. Ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin, two fluoroquinolone antimicrobials. Clin Pharm. 1987 Feb;6(2):105–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L. C., Cuevas T. A., Roccaforte J. S., Mellencamp M. A., Bittner M. J. Ciprofloxacin and antacids. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):48–48. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92596-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAMEY T. A., GOVAN D. E., PALMER J. M. THE LOCALIZATION AND TREATMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: THE ROLE OF BACTERICIDAL URINE LEVELS AS OPPOSED TO SERUM LEVELS. Medicine (Baltimore) 1965 Jan;44:1–36. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196501000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson B. N., Boppana V. K., Vlasses P. H., Rotmensch H. H., Ferguson R. K. Norfloxacin disposition after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):284–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J. Influence of pH and human urine on the antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(5):335–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sharkawi A. M., Morgan W. D., Cobbold S., Jaib M. B., Evans C. J., Somervaille L. J., Chettle D. R., Scott M. C. Unexpected mobilisation of lead during cisplatin chemotherapy. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):249–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


