Abstract
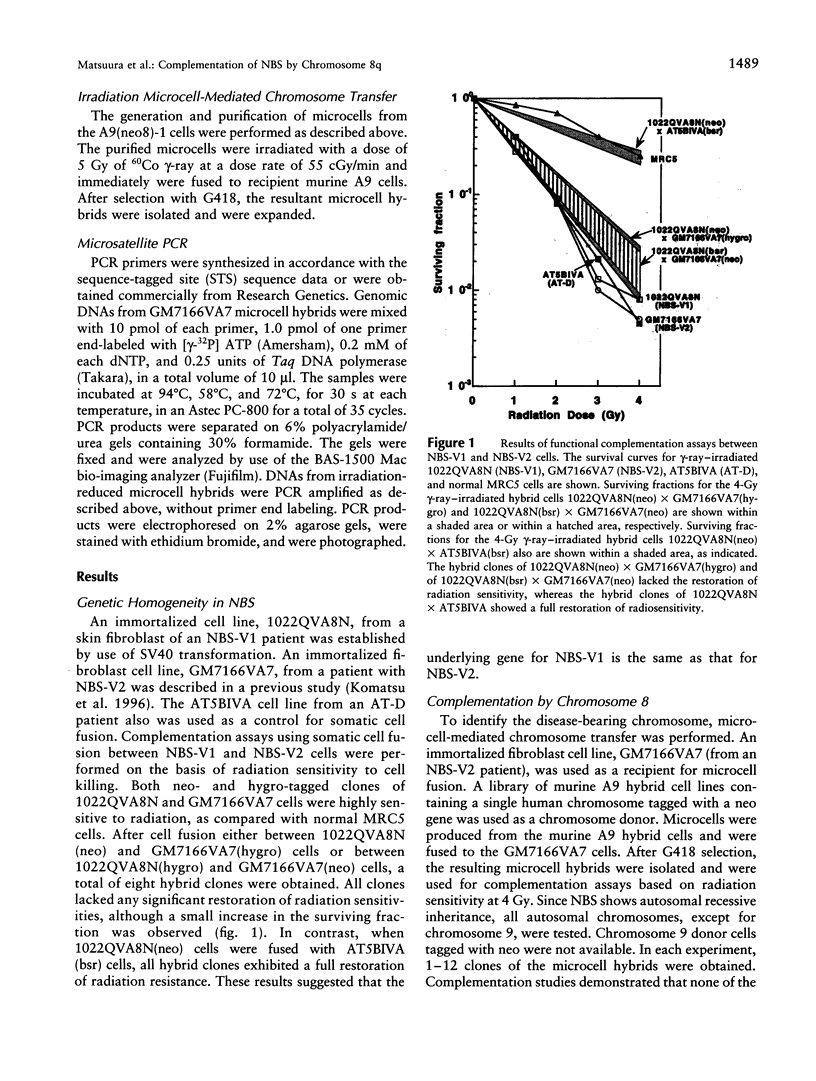
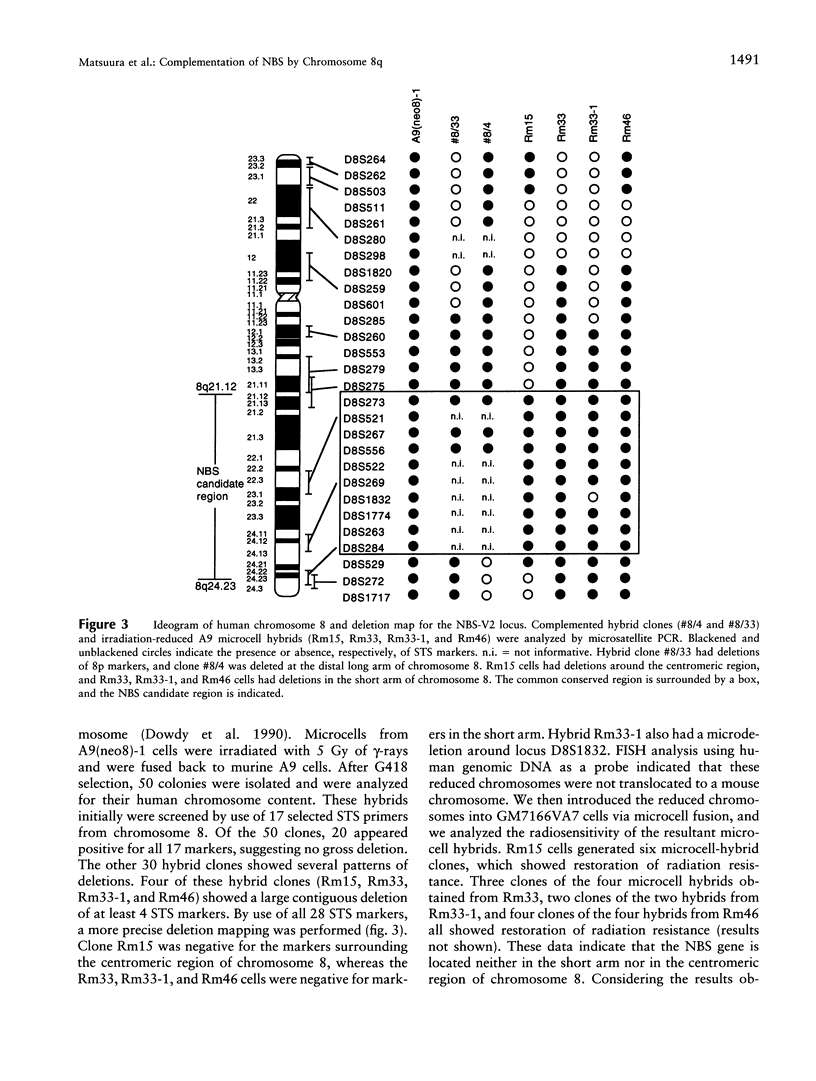
Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by microcephaly, short stature, immunodeficiency, and a high incidence of cancer. Cultured cells from NBS show chromosome instability, an increased sensitivity to radiation-induced cell killing, and an abnormal cell-cycle regulation after irradiation. Hitherto, patients with NBS have been divided into the two complementation groups V1 and V2, on the basis of restoration of radioresistant DNA synthesis, suggesting that each group arises from a different gene. However, the presence of genetic heterogeneity in NBS has been considered to be controversial. To localize the NBS gene, we have performed functional complementation assays using somatic cell fusion between NBS-V1 and NBS-V2 cells, on the basis of hyper-radiosensitivity, and then have performed a genomewide search for the NBS locus, using microcell-mediated chromosome transfer followed by complementation assays based on radiosensitivity. We found that radiation resistance was not restored in the fused NBS-V1 and NBS-V2 cells and that only human chromosome 8 complements the sensitivity to ionizing radiation, in NBS cell lines. In complementation assays performed after the transfer of a reduced chromosome, merely the long arm of chromosome 8 was sufficient for restoring the defect. Our results strongly suggest that NBS is a homogeneous disorder and that the gene for NBS is located at 8q21-24.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blunt T., Finnie N. J., Taccioli G. E., Smith G. C., Demengeot J., Gottlieb T. M., Mizuta R., Varghese A. J., Alt F. W., Jeggo P. A. Defective DNA-dependent protein kinase activity is linked to V(D)J recombination and DNA repair defects associated with the murine scid mutation. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):813–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90360-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Bollum F. J., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Cheung L. C., Xu X., Hecht B. K., Hecht F., Chang L. M. Chromosome sublocalization of a cDNA for human DNA polymerase-beta to 8p11----p12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;47(3):121–124. doi: 10.1159/000132527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimprich K. A., Shin T. B., Keith C. T., Schreiber S. L. cDNA cloning and gene mapping of a candidate human cell cycle checkpoint protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):2850–2855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.7.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Spinner N. B., Emanuel B. S., Nowell P. C., Nichols W. W. A chromosomal breakage syndrome with profound immunodeficiency. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Scanlon D. J., Fasching C. L., Casey G., Stanbridge E. J. Irradiation microcell-mediated chromosome transfer (XMMCT): the generation of specific chromosomal arm deletions. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Nov;2(4):318–327. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti R. A., Berkel I., Boder E., Braedt G., Charmley P., Concannon P., Ersoy F., Foroud T., Jaspers N. G., Lange K. Localization of an ataxia-telangiectasia gene to chromosome 11q22-23. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):577–580. doi: 10.1038/336577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. J., Yates J. R., Taylor A. M., Biggs P., McGuire G. M., McConville C. M., Billing C. J., Barnes N. D. Severe microcephaly with normal intellectual development: the Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Nov;73(5):431–434. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers N. G., Bootsma D. Genetic heterogeneity in ataxia-telangiectasia studied by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2641–2644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers N. G., Taalman R. D., Baan C. Patients with an inherited syndrome characterized by immunodeficiency, microcephaly, and chromosomal instability: genetic relationship to ataxia telangiectasia. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):66–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongmans W., Verhaegh G. W., Jaspers N. G., Oshimura M., Stanbridge E. J., Lohman P. H., Zdzienicka M. Z. Studies on phenotypic complementation of ataxia-telangiectasia cells by chromosome transfer. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;56(2):438–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung M., Zhang Y., Lee S., Dritschilo A. Correction of radiation sensitivity in ataxia telangiectasia cells by a truncated I kappa B-alpha. Science. 1995 Jun 16;268(5217):1619–1621. doi: 10.1126/science.7777860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C. T., Schreiber S. L. PIK-related kinases: DNA repair, recombination, and cell cycle checkpoints. Science. 1995 Oct 6;270(5233):50–51. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5233.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K., Kodama S., Okumura Y., Koi M., Oshimura M. Restoration of radiation resistance in ataxia telangiectasia cells by the introduction of normal human chromosome 11. Mutat Res. 1990 Mar;235(2):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90058-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K., Matsuura S., Tauchi H., Endo S., Kodama S., Smeets D., Weemaes C., Oshimura M. The gene for Nijmegen breakage syndrome (V2) is not located on chromosome 11. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Apr;58(4):885–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Okumura Y. Functional complementation in mouse-human radiation hybrids assigns the putative murine scid gene to the pericentric region of human chromosome 8. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):1031–1034. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K., Okumura Y., Kodama S., Yoshida M., Miller R. C. Lack of correlation between radiosensitivity and inhibition of DNA synthesis in hybrids (A-T x HeLa). Int J Radiat Biol. 1989 Dec;56(6):863–867. doi: 10.1080/09553008914552331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavin M. F., Khanna K. K., Beamish H., Spring K., Watters D., Shiloh Y. Relationship of the ataxia-telangiectasia protein ATM to phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Oct;20(10):382–383. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. J., Thayer M. J., Schafer A. J., Fournier R. E. Physical mapping of human chromosome 17 using fragment-containing microcell hybrids. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Liu P., Li L., Peterson C. A., Zhao Y., Leach R. J., Naylor S. L., Siciliano M. J. Assignment of xeroderma pigmentosum group C (XPC) gene to chromosome 3p25. Genomics. 1994 May 1;21(1):266–269. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville C. M., Stankovic T., Byrd P. J., McGuire G. M., Yao Q. Y., Lennox G. G., Taylor M. R. Mutations associated with variant phenotypes in ataxia-telangiectasia. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Aug;59(2):320–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn M. S., Lu-Kuo J. M., Herzing L. B. Expression cloning of multiple human cDNAs that complement the phenotypic defects of ataxia-telangiectasia group D fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Dec;53(6):1206–1216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitsky K., Bar-Shira A., Gilad S., Rotman G., Ziv Y., Vanagaite L., Tagle D. A., Smith S., Uziel T., Sfez S. A single ataxia telangiectasia gene with a product similar to PI-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1749–1753. doi: 10.1126/science.7792600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola B., Avner P., Sultan Y., Jeanneau C., Maisonneuve P. Monoclonal antibodies against human factor VIII molecular neutralize antihemophilic factor and ristocetin cofactor activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):183–187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumm M., Gatti R. A., Reis A., Udar N., Chrzanowska K., Seemanova E., Sperling K., Wegner R. D. The ataxia-telangiectasia-variant genes 1 and 2 are distinct from the ataxia-telangiectasia gene on chromosome 11q23.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Oct;57(4):960–962. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weemaes C. M., Hustinx T. W., Scheres J. M., van Munster P. J., Bakkeren J. A., Taalman R. D. A new chromosomal instability disorder: the Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Jul;70(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney M., Thayer M., Reifsteck C., Olson S., Smith L., Jakobs P. M., Leach R., Naylor S., Joenje H., Grompe M. Microcell mediated chromosome transfer maps the Fanconi anaemia group D gene to chromosome 3p. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):341–343. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Oshima J., Fu Y. H., Wijsman E. M., Hisama F., Alisch R., Matthews S., Nakura J., Miki T., Ouais S. Positional cloning of the Werner's syndrome gene. Science. 1996 Apr 12;272(5259):258–262. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5259.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. ATM-related genes: what do they tell us about functions of the human gene? Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):685–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Verhaegh G. W., Jongmans W., Morolli B., Jaspers N. G., Oshimura M. Functional complementation studies with X-ray-sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster cells closely resembling ataxia-telangiectasia cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Dec;66(6 Suppl):S189–S195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Burgt I., Chrzanowska K. H., Smeets D., Weemaes C. Nijmegen breakage syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):153–156. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


