Abstract
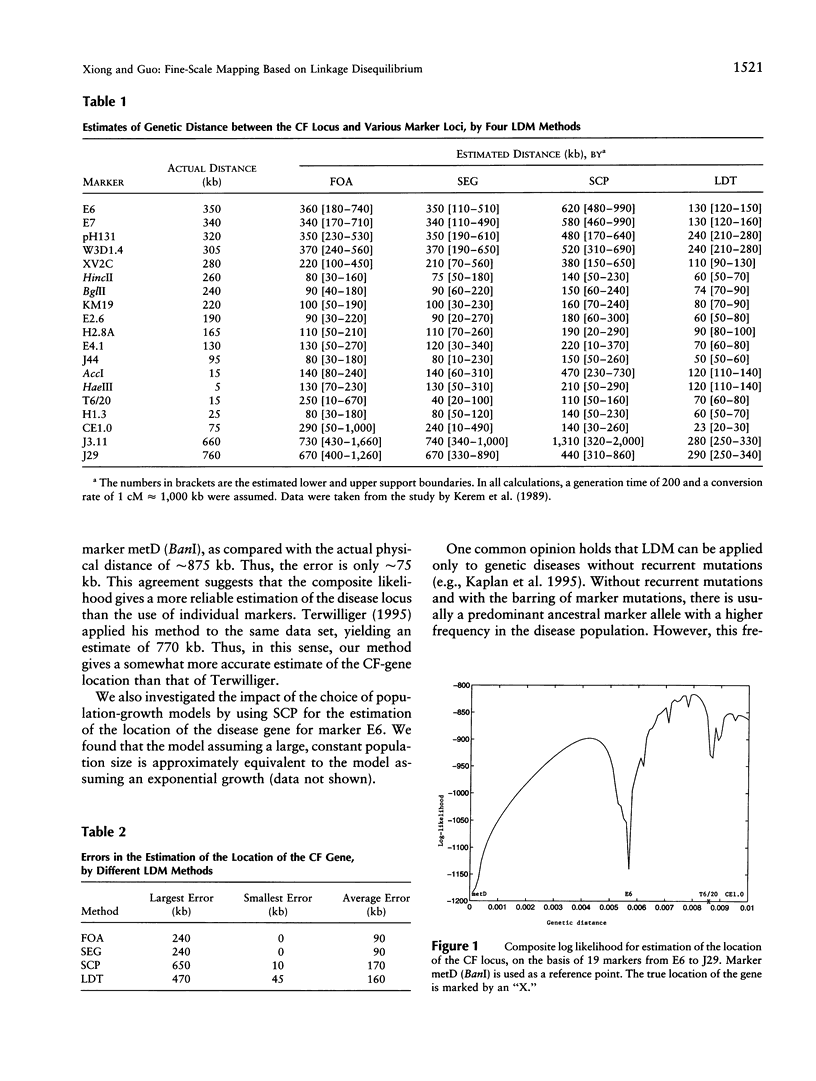
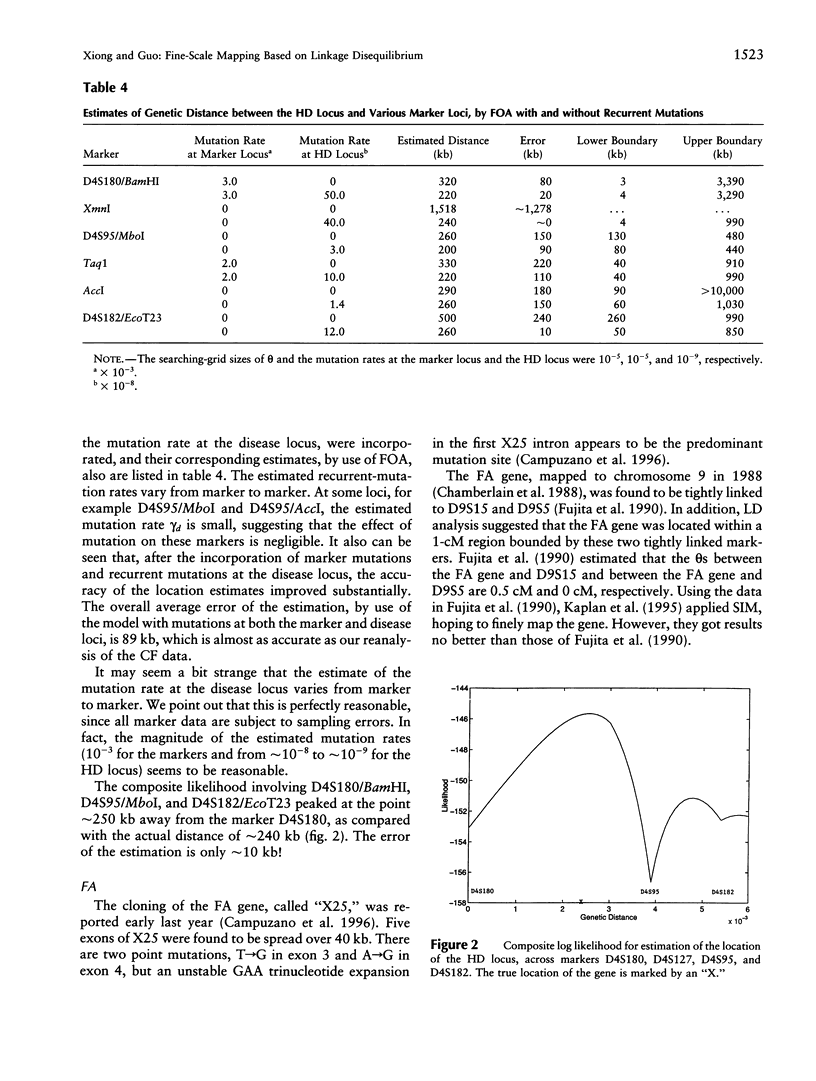
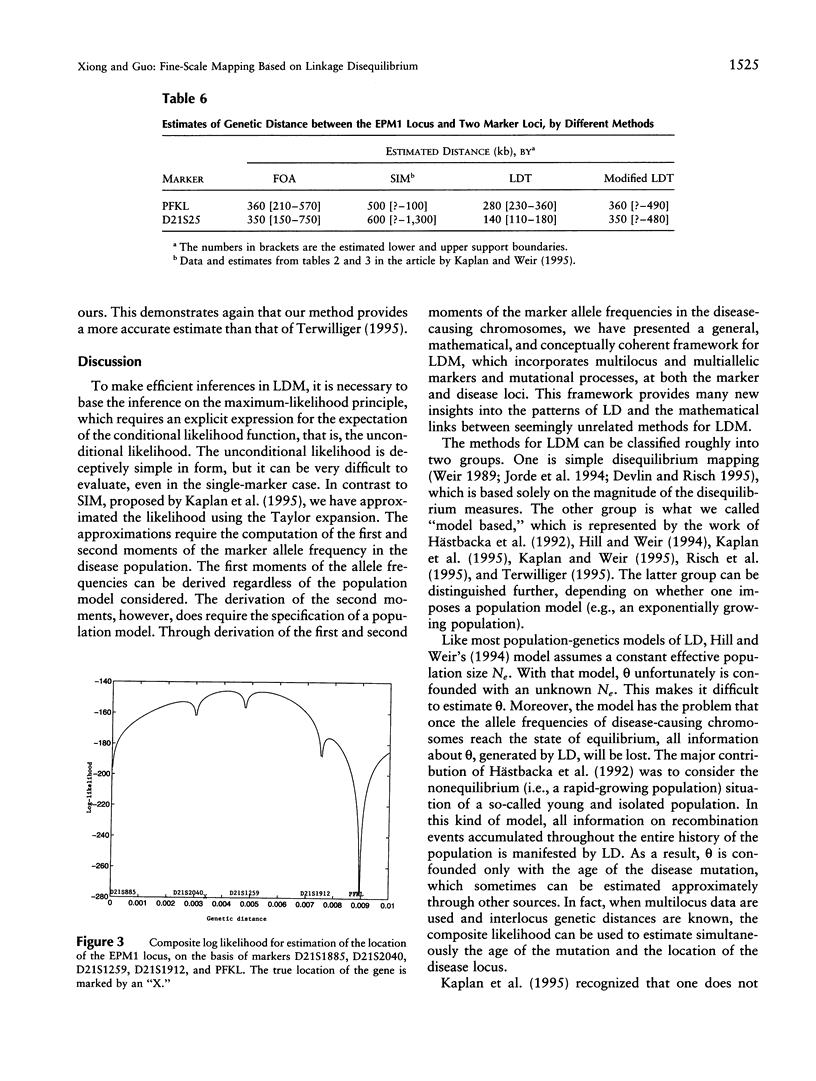
Linkage-disequilibrium mapping (LDM) recently has been hailed as a powerful statistical method for fine-scale mapping of disease genes. After reviewing its historical background and methodological development, we present a general, mathematical, and conceptually coherent framework for LDM that incorporates multilocus and multiallelic markers and mutational processes at the marker and disease loci. With this framework, we address several issues relevant to fine-scale mapping and propose some efficient computational methods for LDM. We implement various LDM methods that incorporate population growth, recurrent mutation, and marker mutations, on the basis of a general framework. We demonstrate these methods by applying them to published data on cystic fibrosis, Huntington disease, Friedreich ataxia, and progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Since the genes responsible for these diseases all have been cloned, we can evaluate the performance of our methods and can compare ours with that of other methods. Using the proposed methods, we successfully and accurately predicted the locations of genes responsible for these diseases, on the basis of published data only.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodmer W. F. Human genetics: the molecular challenge. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehnke M. Limits of resolution of genetic linkage studies: implications for the positional cloning of human disease genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):379–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano V., Montermini L., Moltò M. D., Pianese L., Cossée M., Cavalcanti F., Monros E., Rodius F., Duclos F., Monticelli A. Friedreich's ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science. 1996 Mar 8;271(5254):1423–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5254.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain S., Shaw J., Rowland A., Wallis J., South S., Nakamura Y., von Gabain A., Farrall M., Williamson R. Mapping of mutation causing Friedreich's ataxia to human chromosome 9. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):248–250. doi: 10.1038/334248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Positional cloning: let's not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita R., Hanauer A., Sirugo G., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Additional polymorphisms at marker loci D9S5 and D9S15 generate extended haplotypes in linkage disequilibrium with Friedreich ataxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick P. W. Hitchhiking: a comparison of linkage and partial selfing. Genetics. 1980 Mar;94(3):791–808. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Maximum-likelihood estimation of gene location by linkage disequilibrium. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):705–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Mahtani M. M., Clines G., Reeve-Daly M. P., Daly M., Hamilton B. A., Kusumi K., Trivedi B., Weaver A. The diastrophic dysplasia gene encodes a novel sulfate transporter: positional cloning by fine-structure linkage disequilibrium mapping. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H S. The Numerical Results of Diverse Systems of Breeding, with Respect to Two Pairs of Characters, Linked or Independent, with Special Relation to the Effects of Linkage. Genetics. 1917 Mar;2(2):97–154. doi: 10.1093/genetics/2.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B. Linkage disequilibrium as a gene-mapping tool. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):11–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B., Watkins W. S., Carlson M., Groden J., Albertsen H., Thliveris A., Leppert M. Linkage disequilibrium predicts physical distance in the adenomatous polyposis coli region. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):884–898. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Likelihood methods for locating disease genes in nonequilibrium populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):18–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Weir B. S. Are moment bounds on the recombination fraction between a marker and a disease locus too good to be true? Allelic association mapping revisited for simple genetic diseases in the Finnish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1486–1498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping complex genetic traits in humans: new methods using a complete RFLP linkage map. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):49–62. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Kunkel L., Aldridge J., Latt S. A. Accurate and superaccurate gene mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):853–867. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Norio R., Tirrito S., Sistonen P., Lander E., de la Chapelle A. Localization of the EPM1 gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy on chromosome 21: linkage disequilibrium allows high resolution mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Novelletto A., Lin C., Tagle D., Barnes G., Bates G., Taylor S., Allitto B., Altherr M., Myers R. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):99–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Linkage disequilibrium in subdivided populations. Genetics. 1973 Sep;75(1):213–219. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo M., Sirugo G., Antonelli A., Weitnauer L., Ferretti L., Leone M., Dones I., Cerino A., Fujita R., Hanauer A. Friedreich ataxia in Italian families: genetic homogeneity and linkage disequilibrium with the marker loci D9S5 and D9S15. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):228–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennacchio L. A., Lehesjoki A. E., Stone N. E., Willour V. L., Virtaneva K., Miao J., D'Amato E., Ramirez L., Faham M., Koskiniemi M. Mutations in the gene encoding cystatin B in progressive myoclonus epilepsy (EPM1) Science. 1996 Mar 22;271(5256):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5256.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Kramer P., Almasy L., Singer B., Fahn S., Breakefield X., Bressman S. Genetic analysis of idiopathic torsion dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews and their recent descent from a small founder population. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):152–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R B. Some Applications of Mathematics to Breeding Problems III. Genetics. 1918 Jul;3(4):375–389. doi: 10.1093/genetics/3.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriver M. D., Jin L., Chakraborty R., Boerwinkle E. VNTR allele frequency distributions under the stepwise mutation model: a computer simulation approach. Genetics. 1993 Jul;134(3):983–993. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnock P., Sing C. F. Analysis of multilocus genetic systems in Tecumseh, Michigan. II. Consideration of the correlation between nonalleles in gametes. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Jul;24(4):393–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin M. Linkage disequilibrium in growing and stable populations. Genetics. 1994 May;137(1):331–336. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smouse P. E., Neel J. V. Multivariate analysis of gametic disequilibrium in the Yanomama. Genetics. 1977 Apr;85(4):733–752. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone N. E., Fan J. B., Willour V., Pennacchio L. A., Warrington J. A., Hu A., de la Chapelle A., Lehesjoki A. E., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Construction of a 750-kb bacterial clone contig and restriction map in the region of human chromosome 21 containing the progressive myoclonus epilepsy gene. Genome Res. 1996 Mar;6(3):218–225. doi: 10.1101/gr.6.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger J. D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):777–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. The effect of a selected locus on linked neutral loci. Genetics. 1977 Apr;85(4):753–788. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes A. M., Slatkin M., Freimer N. B. Allele frequencies at microsatellite loci: the stepwise mutation model revisited. Genetics. 1993 Mar;133(3):737–749. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtaneva K., Miao J., Träskelin A. L., Stone N., Warrington J. A., Weissenbach J., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Sistonen P., de la Chapelle A. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy EPM1 locus maps to a 175-kb interval in distal 21q. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1247–1253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Wong C. Mutation of human short tandem repeats. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1123–1128. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S., Allard R. W., Kahler A. L. Analysis of complex allozyme polymorphisms in a barley population. Genetics. 1972 Nov;72(3):505–523. doi: 10.1093/genetics/72.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


