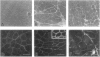
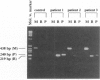
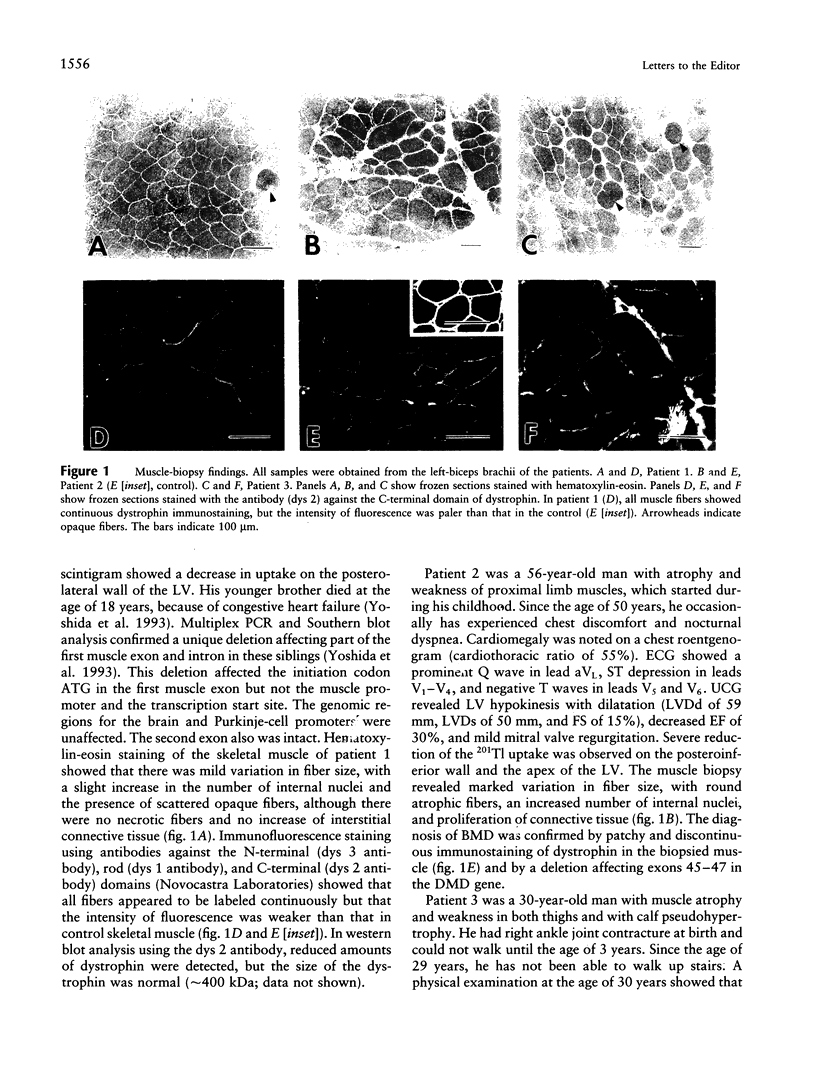
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berko B. A., Swift M. X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 7;316(19):1186–1191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705073161904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz W. M., Cremer M., Herrmann R., Grünig E., Fogel W., Scheffold T., Goebel H. H., Kircheisen R., Kübler W., Voit T. X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Novel mutation of the dystrophin gene. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Mar 27;752:470–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb17457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klamut H. J., Bosnoyan-Collins L. O., Worton R. G., Ray P. N., Davis H. L. Identification of a transcriptional enhancer within muscle intron 1 of the human dystrophin gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Oct;5(10):1599–1606. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.10.1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milasin J., Muntoni F., Severini G. M., Bartoloni L., Vatta M., Krajinovic M., Mateddu A., Angelini C., Camerini F., Falaschi A. A point mutation in the 5' splice site of the dystrophin gene first intron responsible for X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Jan;5(1):73–79. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntoni F., Cau M., Ganau A., Congiu R., Arvedi G., Mateddu A., Marrosu M. G., Cianchetti C., Realdi G., Cao A. Brief report: deletion of the dystrophin muscle-promoter region associated with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 23;329(13):921–925. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309233291304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntoni F., Melis M. A., Ganau A., Dubowitz V. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in normal tissues and in skeletal muscle of a family with X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):151–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfors A., Eriksson B. O., Kyllerman M., Martinsson T., Wahlström J. Dilated cardiomyopathy and the dystrophin gene: an illustrated review. Br Heart J. 1994 Oct;72(4):344–348. doi: 10.1136/hrt.72.4.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba H., Ishii K., Shimmoto M., Yamada H., Suzuki Y. A screening for dystrophin gene deletions in Japanese patients with Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy by the multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Brain Dev. 1991 Sep;13(5):339–342. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(12)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin J. A., Hejtmancik J. F., Brink P., Gelb B., Zhu X. M., Chamberlain J. S., McCabe E. R., Swift M. X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Molecular genetic evidence of linkage to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (dystrophin) gene at the Xp21 locus. Circulation. 1993 Jun;87(6):1854–1865. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.6.1854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ikeda S., Nakamura A., Kagoshima M., Takeda S., Shoji S., Yanagisawa N. Molecular analysis of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in patients with Becker muscular dystrophy presenting with dilated cardiomyopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1993 Nov;16(11):1161–1166. doi: 10.1002/mus.880161104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]