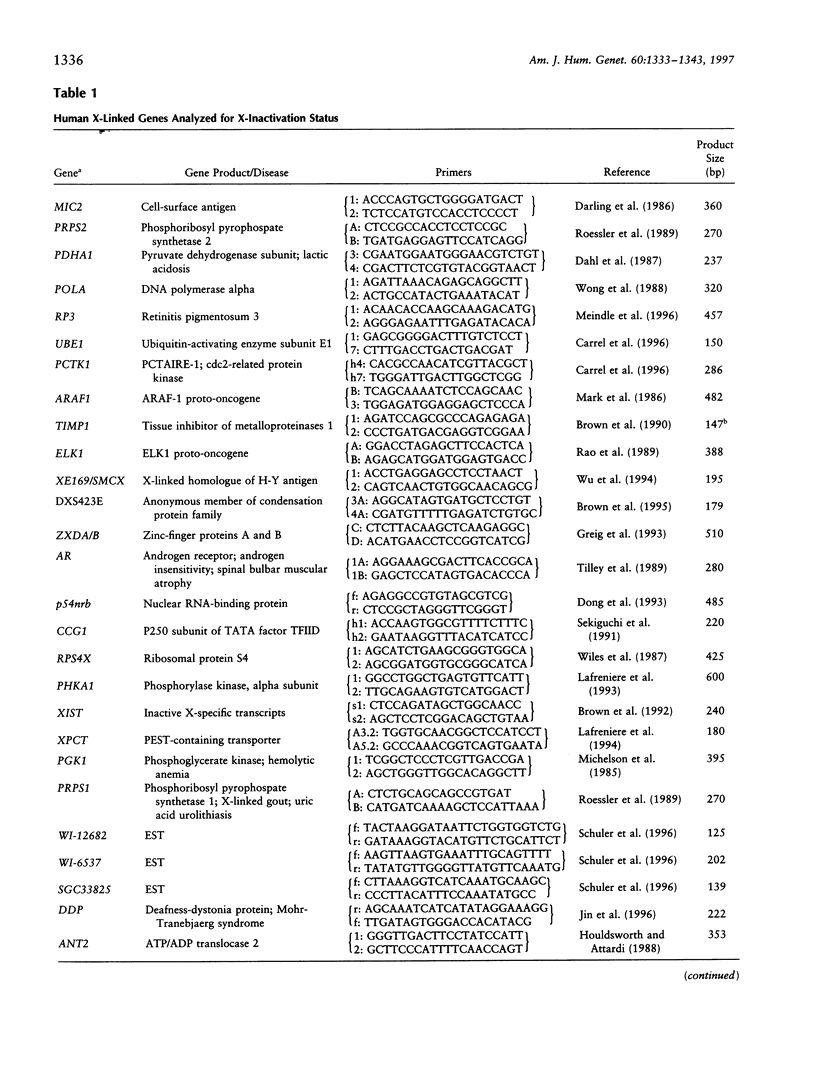
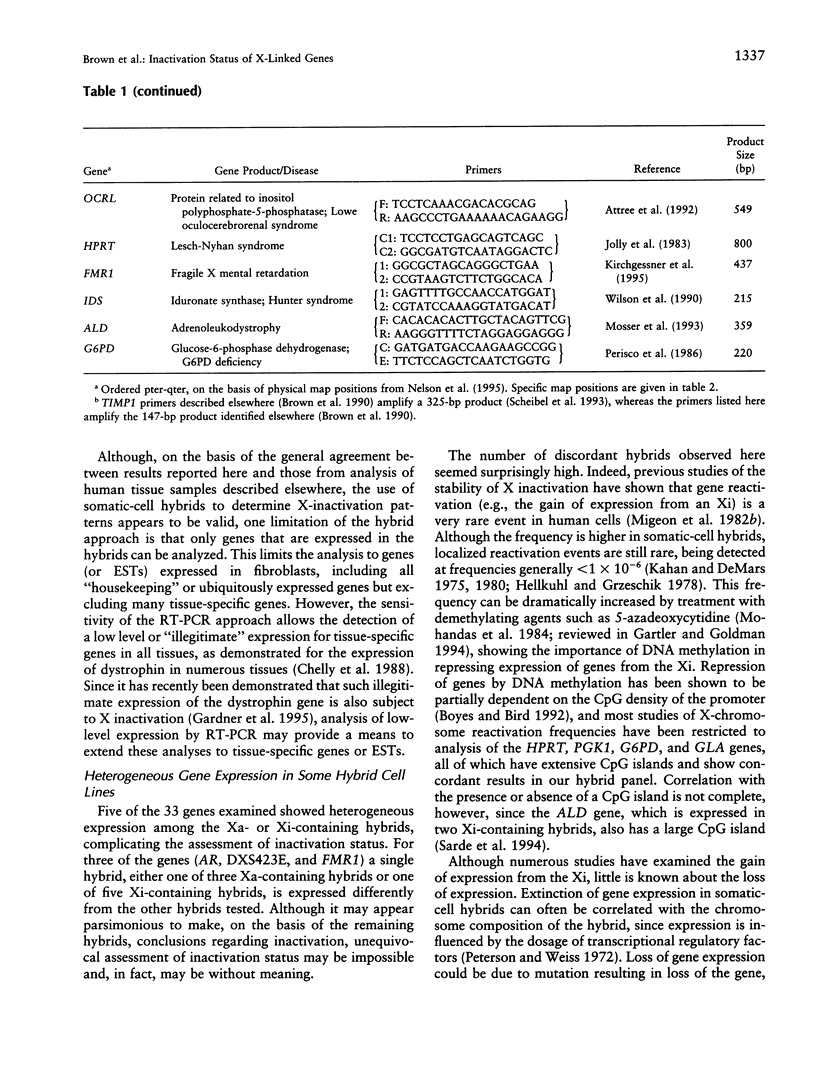
Abstract
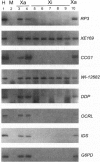
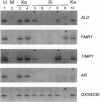
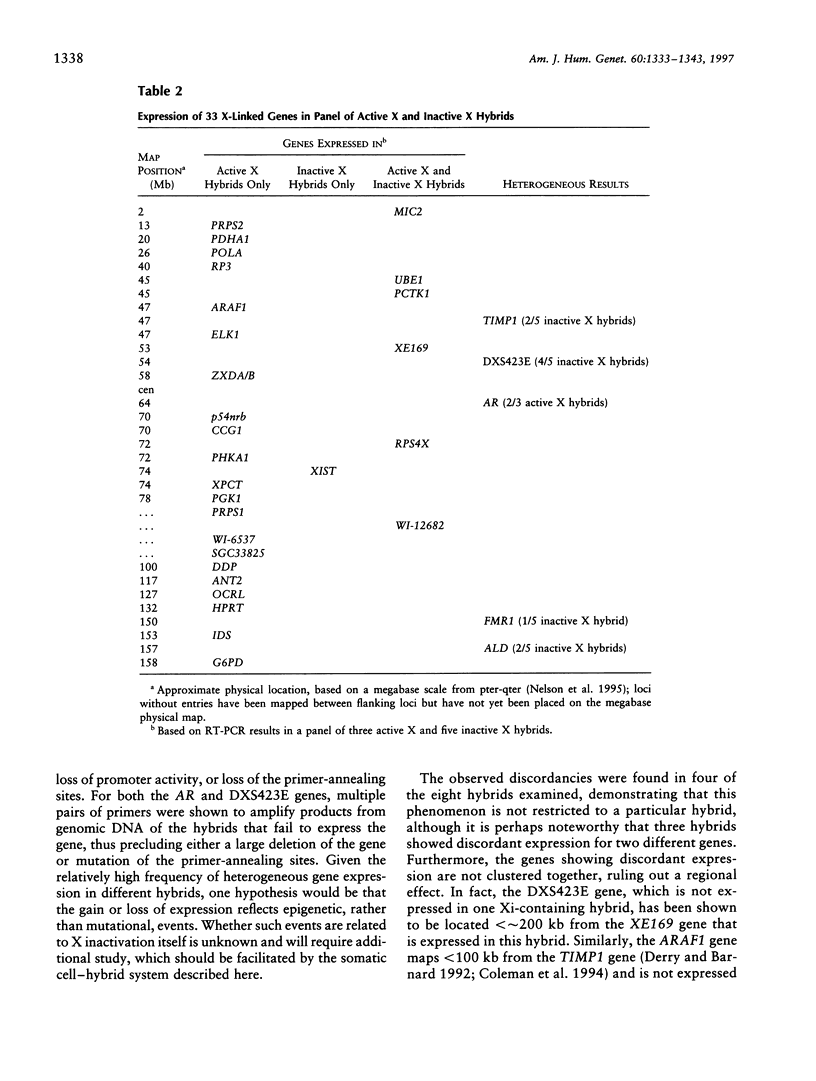
X-chromosome inactivation results in the cis-limited inactivation of many, but not all, of the genes on one of the pair of X chromosomes in mammalian females. In addition to the genes from the pseudoautosomal region, which have long been anticipated to escape inactivation, genes from several other regions of the human X chromosome have now been shown to escape inactivation and to be expressed from both the active and inactive X chromosomes. The growing number of genes escaping inactivation emphasizes the need for a reliable system for assessing the inactivation status of X-linked genes. Since many features of the active or inactive X chromosome, including transcriptional activity, are maintained in rodent/human somatic-cell hybrids, such hybrids have been used to study the inactivation process and to determine the inactivation status of human X-linked genes. In order to assess the fidelity of inactivation status in such hybrids, we have examined the expression of 33 X-linked genes in eight mouse/human somatic-cell hybrids that contain either the human active (three hybrids) or inactive X (five hybrids) chromosome. Inactivation of nine of these genes had previously been demonstrated biochemically in human cells, and the expression of these genes only in hybrids retaining an active X, but not in those retaining an inactive X, confirms that expression in hybrids reflects expression in human cells. Although the majority of genes tested showed consistent patterns of expression among the active X hybrids or inactive X hybrids, surprisingly, 5 of the 33 genes showed heterogeneous expression among the hybrids, demonstrating a significantly higher rate of variability than previously reported for other genes in either human somatic cells or mouse/human somatic-cell hybrids. These data suggest that at least some X-linked genes may be under additional levels of epigenetic regulation not previously recognized and that somatic-cell hybrids may provide a useful approach for studying these chromosomal phenomena.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agulnik A. I., Mitchell M. J., Mattei M. G., Borsani G., Avner P. A., Lerner J. L., Bishop C. E. A novel X gene with a widely transcribed Y-linked homologue escapes X-inactivation in mouse and human. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):879–884. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attree O., Olivos I. M., Okabe I., Bailey L. C., Nelson D. L., Lewis R. A., McInnes R. R., Nussbaum R. L. The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):239–242. doi: 10.1038/358239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., YEH M., FAIRBANKS V. F. The normal human female as a mosaic of X-chromosome activity: studies using the gene for C-6-PD-deficiency as a marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. Repression of genes by DNA methylation depends on CpG density and promoter strength: evidence for involvement of a methyl-CpG binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):327–333. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Flenniken A. M., Williams B. R., Willard H. F. X chromosome inactivation of the human TIMP gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4191–4195. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Hendrich B. D., Rupert J. L., Lafrenière R. G., Xing Y., Lawrence J., Willard H. F. The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):527–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90520-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Miller A. P., Carrel L., Rupert J. L., Davies K. E., Willard H. F. The DXS423E gene in Xp11.21 escapes X chromosome inactivation. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Feb;4(2):251–255. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Willard H. F. Noninactivation of a selectable human X-linked gene that complements a murine temperature-sensitive cell cycle defect. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):592–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Dahl H. H., Brown G. K. X-chromosome localization of the functional gene for the E1 alpha subunit of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianchi M. R., Romeo G. Mosaicism for sulfoiduronate sulfatase deficiency in carriers of Hunter's syndrome. Experientia. 1976 Apr 15;32(4):459–460. doi: 10.1007/BF01920795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrel L., Clemson C. M., Dunn J. M., Miller A. P., Hunt P. A., Lawrence J. B., Willard H. F. X inactivation analysis and DNA methylation studies of the ubiquitin activating enzyme E1 and PCTAIRE-1 genes in human and mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Mar;5(3):391–401. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrel L., Willard H. F. An assay for X inactivation based on differential methylation at the fragile X locus, FMR1. Am J Med Genet. 1996 Jul 12;64(1):27–30. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<27::AID-AJMG3>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. P., Németh A. H., Campbell L., Raut C. P., Weissenbach J., Davies K. E. A 1.8-Mb YAC contig in Xp11.23: identification of CpG islands and physical mapping of CA repeats in a region of high gene density. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):337–343. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON R. G., NITOWSKY H. M., CHILDS B. DEMONSTRATION OF TWO POPULATIONS OF CELLS IN THE HUMAN FEMALE HETEROZYGOUS FOR GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE VARIANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:481–485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H. H., Hunt S. M., Hutchison W. M., Brown G. K. The human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Isolation of cDNA clones for the E1 alpha subunit, sequence analysis, and characterization of the mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7398–7403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Goodfellow P. J., Pym B., Banting G. S., Pritchard C., Goodfellow P. N. Molecular genetics of MIC2: a gene shared by the human X and Y chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):205–212. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derry J. M., Barnard P. J. Physical linkage of the A-raf-1, properdin, synapsin I, and TIMP genes on the human and mouse X chromosomes. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):632–638. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M. Escape from X inactivation in human and mouse. Trends Genet. 1995 Jan;11(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)88981-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong B., Horowitz D. S., Kobayashi R., Krainer A. R. Purification and cDNA cloning of HeLa cell p54nrb, a nuclear protein with two RNA recognition motifs and extensive homology to human splicing factor PSF and Drosophila NONA/BJ6. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):4085–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Passage M., Yu L. C., Yen P., Mohandas T. K., Shapiro L. Directed isolation of human genes that escape X inactivation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1992 May;18(3):259–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01233862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. M., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Ridley A., McNeil J. A., Lawrence J. B., Willard H. F., Bieber F. R., Page D. C. Homologous ribosomal protein genes on the human X and Y chromosomes: escape from X inactivation and possible implications for Turner syndrome. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1205–1218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90416-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco B., Meroni G., Parenti G., Levilliers J., Bernard L., Gebbia M., Cox L., Maroteaux P., Sheffield L., Rappold G. A. A cluster of sulfatase genes on Xp22.3: mutations in chondrodysplasia punctata (CDPX) and implications for warfarin embryopathy. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. J., Bobrow M., Roberts R. G. The identification of point mutations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients by using reverse-transcription PCR and the protein truncation test. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):311–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Chen S. H., Fialkow P. J., Giblett E. R., Singh S. X chromosome inactivation in cells from an individual heterozygous for two X-linked genes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):149–150. doi: 10.1038/newbio236149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Goldman M. A. Reactivation of inactive X-linked genes. Dev Genet. 1994;15(6):504–514. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020150609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerkens C., Vetter U., Just W., Fedarko N. S., Fisher L. W., Young M. F., Termine J. D., Robey P. G., Wöhrle D., Vogel W. The X-chromosomal human biglycan gene BGN is subject to X inactivation but is transcribed like an X-Y homologous gene. Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;96(1):44–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00214185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Pym B., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. The cell surface antigen locus, MIC2X, escapes X-inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):777–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. A., Gartler S. M. Mammalian X chromosome inactivation: testing the hypothesis of transcriptional control. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 May;12(3):275–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01570786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. A., Watson J. M. Mammalian sex chromosomes: evolution of organization and function. Chromosoma. 1991 Nov;101(2):63–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00357055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig G. M., Sharp C. B., Carrel L., Willard H. F. Duplicated zinc finger protein genes on the proximal short arm of the human X chromosome: isolation, characterization and X-inactivation studies. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1611–1618. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H. Partial reactivation of a human inactive X chromosome in human-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):527–530. doi: 10.1159/000131016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houldsworth J., Attardi G. Two distinct genes for ADP/ATP translocase are expressed at the mRNA level in adult human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):377–381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Okayama H., Berg P., Esty A. C., Filpula D., Bohlen P., Johnson G. G., Shively J. E., Hunkapillar T., Friedmann T. Isolation and characterization of a full-length expressible cDNA for human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):477–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. H., Furlong R. A., Burkin H., Chalmers I. J., Brown G. M., Khwaja O., Affara N. A. The Drosophila developmental gene fat facets has a human homologue in Xp11.4 which escapes X-inactivation and has related sequences on Yq11.2. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Nov;5(11):1695–1701. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.11.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B., DeMars R. Localized Derepression on the Human Inactive X Chromosone in Mouse-Human Cell Hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1510–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner C. U., Warren S. T., Willard H. F. X inactivation of the FMR1 fragile X mental retardation gene. J Med Genet. 1995 Dec;32(12):925–929. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.12.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafrenière R. G., Brown C. J., Rider S., Chelly J., Taillon-Miller P., Chinault A. C., Monaco A. P., Willard H. F. 2.6 Mb YAC contig of the human X inactivation center region in Xq13: physical linkage of the RPS4X, PHKA1, XIST and DXS128E genes. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1105–1115. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafrenière R. G., Carrel L., Willard H. F. A novel transmembrane transporter encoded by the XPCT gene in Xq13.2. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1133–1139. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. E., Seeley T. W., Shows T. B., Mountz J. D. Pks, a raf-related sequence in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6312–6316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl A., Dry K., Herrmann K., Manson F., Ciccodicola A., Edgar A., Carvalho M. R., Achatz H., Hellebrand H., Lennon A. A gene (RPGR) with homology to the RCC1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is mutated in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3). Nat Genet. 1996 May;13(1):35–42. doi: 10.1038/ng0596-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. J., 3rd, Migeon B. R., Migeon C. J. Locus on human X chromosome for dihydrotestosterone receptor and androgen insensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1469–1472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Blake C. C., Evans S. T., Orkin S. H. Structure of the human phosphoglycerate kinase gene and the intron-mediated evolution and dispersal of the nucleotide-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Axelman J., Beggs A. H. Effect of ageing on reactivation of the human X-linked HPRT locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):93–96. doi: 10.1038/335093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Der Kaloustian V. M., Nyhan W. L., Yough W. J., Childs B. X-linked hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency: heterozygote has two clonal populations. Science. 1968 Apr 26;160(3826):425–427. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3826.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Kennedy J. F. Evidence for the inactivation of an X chromosome early in the development of the human female. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Mar;27(2):233–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Norum R. A., Corsaro C. M. Isolation and analysis of somatic hybrids derived from two human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Shapiro L. J., Norum R. A., Mohandas T., Axelman J., Dabora R. L. Differential expression of steroid sulphatase locus on active and inactive human X chromosome. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):838–840. doi: 10.1038/299838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Sprenkle J. A., Liebaers I., Scott J. F., Neufeld E. F. X-linked Hunter syndrome: the heterozygous phenotype in cell culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):448–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R. Studies of skin fibroblasts from 10 families with HGPRT deficiency, with reference in X-chromosomal inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Mar;23(2):199–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Wolf S. F., Mareni C., Axelman J. Derepression with decreased expression of the G6PD locus on the inactive X chromosome in normal human cells. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):595–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. P., Gustashaw K., Wolff D. J., Rider S. H., Monaco A. P., Eble B., Schlessinger D., Gorski J. L., van Ommen G. J., Weissenbach J. Three genes that escape X chromosome inactivation are clustered within a 6 Mb YAC contig and STS map in Xp11.21-p11.22. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):731–739. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J., Shapiro L. J. Frequency of reactivation and variability in expression of X-linked enzyme loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):916–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J., Douar A. M., Sarde C. O., Kioschis P., Feil R., Moser H., Poustka A. M., Mandel J. L., Aubourg P. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):726–730. doi: 10.1038/361726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAYANNOPOULOU T., STAMATOYANNOPOULOS G. PSEUDO-MOSAICISM IN MALES WITH MILD GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY. Lancet. 1964 Dec 5;2(7371):1215–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Weiss M. C. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: induction of mouse albumin production in rat hepatoma-mouse fibroblast hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roessler B. J., Bell G., Heidler S., Seino S., Becker M., Palella T. D. Cloning of two distinct copies of human phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):193–193. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarde C. O., Mosser J., Kioschis P., Kretz C., Vicaire S., Aubourg P., Poustka A., Mandel J. L. Genomic organization of the adrenoleukodystrophy gene. Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):13–20. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel K., Weiss B., Wöhrle D., Rappold G. A human pseudoautosomal gene, ADP/ATP translocase, escapes X-inactivation whereas a homologue on Xq is subject to X-inactivation. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):82–87. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Beer-Romero P., Brown L. G., Nussbaum R., Page D. C. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1247–1258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Boguski M. S., Stewart E. A., Stein L. D., Gyapay G., Rice K., White R. E., Rodriguez-Tomé P., Aggarwal A., Bajorek E. A gene map of the human genome. Science. 1996 Oct 25;274(5287):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi T., Nohiro Y., Nakamura Y., Hisamoto N., Nishimoto T. The human CCG1 gene, essential for progression of the G1 phase, encodes a 210-kilodalton nuclear DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3317–3325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Mohandas T., Weiss R., Romeo G. Non-inactivation of an x-chromosome locus in man. Science. 1979 Jun 15;204(4398):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.156396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slim R., Levilliers J., Lüdecke H. J., Claussen U., Nguyen V. C., Gough N. M., Horsthemke B., Petit C. A human pseudoautosomal gene encodes the ANT3 ADP/ATP translocase and escapes X-inactivation. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):26–33. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Goodfellow P. J., Goodfellow P. N. The genomic organisation of the human pseudoautosomal gene MIC2 and the detection of a related locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., Wilson J. D., McPhaul M. J. Characterization and expression of a cDNA encoding the human androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):327–331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeesch J. R., Petit P., Kermouni A., Renauld J. C., Van Den Berghe H., Marynen P. The IL-9 receptor gene, located in the Xq/Yq pseudoautosomal region, has an autosomal origin, escapes X inactivation and is expressed from the Y. Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Jan;6(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Passage M. B., Ellison J., Becker M. A., Yen P. H., Shapiro L. J., Mohandas T. K. Physical mapping of loci in the distal half of the short arm of the human X chromosome: implications for the spreading of X-chromosome inactivation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1992 Mar;18(2):195–200. doi: 10.1007/BF01233165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Pearson B. E., Suomalainen H. A., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Schröder J., Korn D. Assignment of the gene for human DNA polymerase alpha to the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5270–5274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V., Alexander C. M., Goodfellow P. N. Isolation of an abundantly expressed sequence from the human X chromosome by differential screening. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jan;14(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF01535047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Brown C. J., Carrel L., Hendrich B., Miller A. P. Epigenetic and chromosomal control of gene expression: molecular and genetic analysis of X chromosome inactivation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:315–322. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Morris C. P., Anson D. S., Occhiodoro T., Bielicki J., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8531–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Wahl A. F., Yuan P. M., Arai N., Pearson B. E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M. W., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene expression is cell proliferation dependent and its primary structure is similar to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Ellison J., Salido E., Yen P., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Isolation and characterization of XE169, a novel human gene that escapes X-inactivation. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):153–160. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn A. R., Page D. C., Fisher E. M. Turner syndrome: the case of the missing sex chromosome. Trends Genet. 1993 Mar;9(3):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90230-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]