Abstract
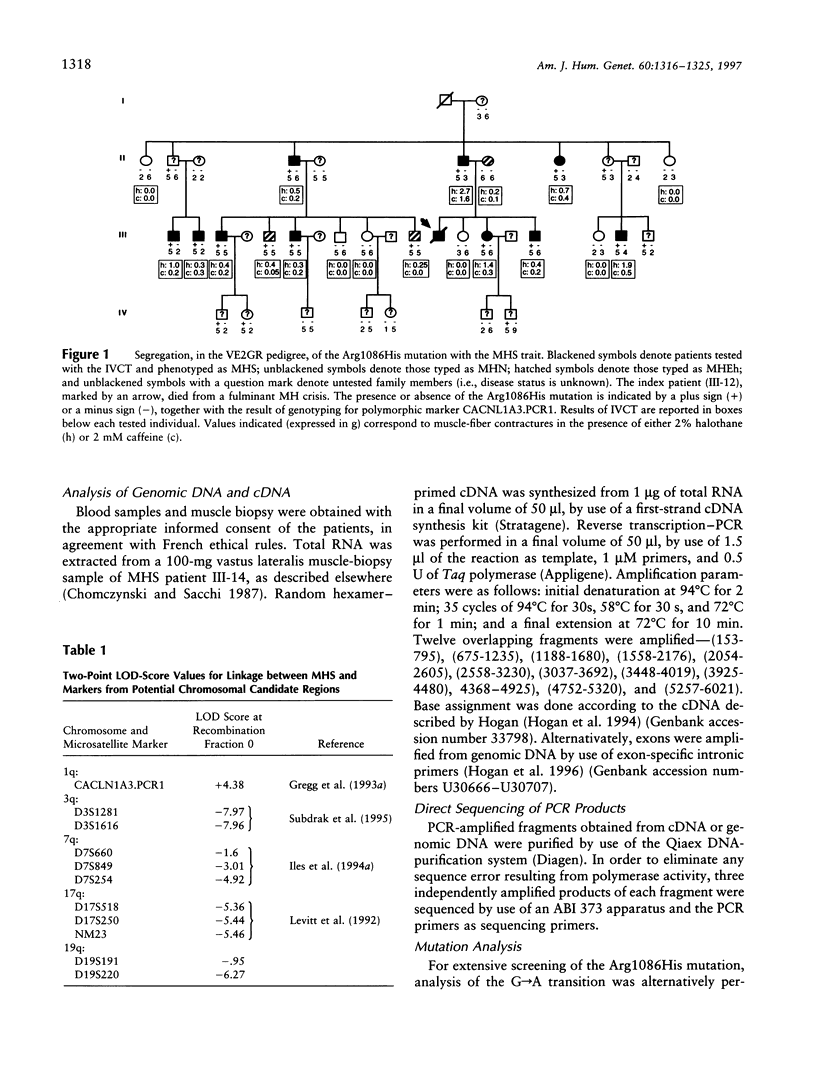
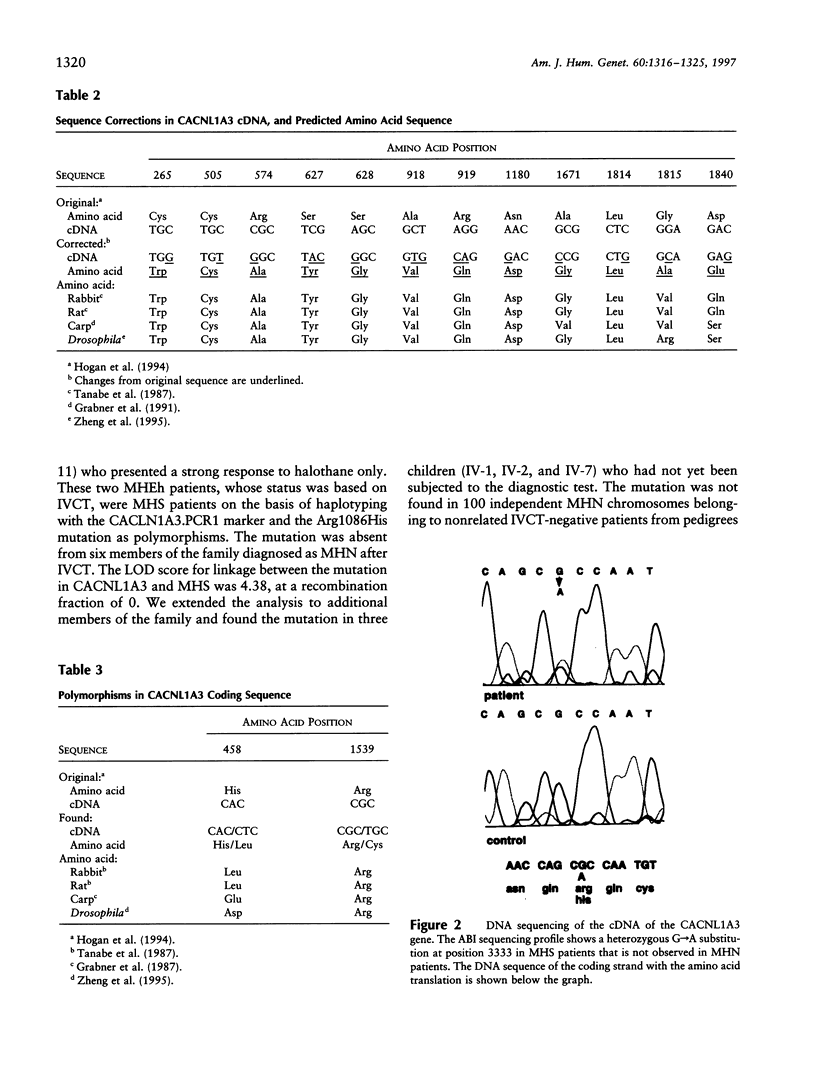
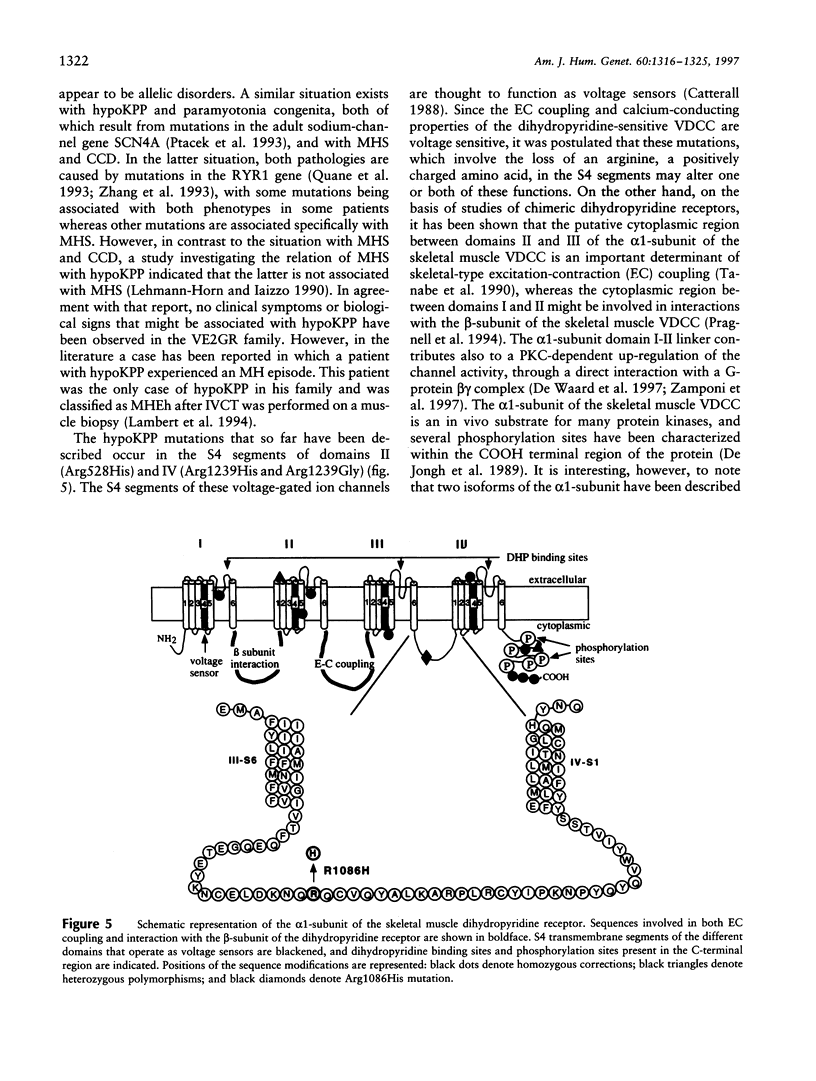
Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility (MHS) is characterized by genetic heterogeneity. However, except for the MHS1 locus, which corresponds to the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor (RYR1) and for which several mutations have been described, no direct molecular evidence for a mutation in another gene has been reported so far. In this study we show that the CACNL1A3 gene encoding the alpha 1-subunit of the human skeletal muscle dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) represents a new MHS locus and is responsible for the disease in a large French family. Linkage analysis performed with an intragenic polymorphic microsatellite marker of the CACLN1A3 gene generated a two-point LOD score of 4.38 at a recombinant fraction of 0. Sequence analysis of the coding region of the CACLN1A3 gene showed the presence of an Arg-His substitution at residue 1086, resulting from the transition of A for G3333, which segregates perfectly with the MHS phenotype in the family. The mutation is localized in a very different part of the alpha 1-subunit of the human skeletal muscle VDCC, compared with previously reported mutations found in patients with hypokalemic periodic paralysis, and these two diseases might be discussed in terms of allelic diseases. This report is the first direct evidence that the skeletal muscle VDCC is involved in MHS, and it suggests a direct interaction between the skeletal muscle VDCC and the ryanodine receptor in the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jongh K. S., Merrick D. K., Catterall W. A. Subunits of purified calcium channels: a 212-kDa form of alpha 1 and partial amino acid sequence of a phosphorylation site of an independent beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8585–8589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jongh K. S., Warner C., Colvin A. A., Catterall W. A. Characterization of the two size forms of the alpha 1 subunit of skeletal muscle L-type calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10778–10782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waard M., Liu H., Walker D., Scott V. E., Gurnett C. A., Campbell K. P. Direct binding of G-protein betagamma complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1997 Jan 30;385(6615):446–450. doi: 10.1038/385446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deufel T., Golla A., Iles D., Meindl A., Meitinger T., Schindelhauer D., DeVries A., Pongratz D., MacLennan D. H., Johnson K. J. Evidence for genetic heterogeneity of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;50(6):1151–1161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Otsu K., Fujii J., Khanna V. K., de Leon S., Derdemezi J., Britt B. A., Duff C. L., Worton R. G., MacLennan D. H. A substitution of cysteine for arginine 614 in the ryanodine receptor is potentially causative of human malignant hyperthermia. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):751–755. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90084-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabner M., Friedrich K., Knaus H. G., Striessnig J., Scheffauer F., Staudinger R., Koch W. J., Schwartz A., Glossmann H. Calcium channels from Cyprinus carpio skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. G., Powers P. A., Hogan K. Assignment of the human gene for the beta subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel (CACNLB1) to chromosome 17 using somatic cell hybrids and linkage mapping. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):185–187. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan K., Gregg R. G., Powers P. A. The structure of the gene encoding the human skeletal muscle alpha 1 subunit of the dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type calcium channel (CACNL1A3). Genomics. 1996 Feb 1;31(3):392–394. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan K., Powers P. A., Gregg R. G. Cloning of the human skeletal muscle alpha 1 subunit of the dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type calcium channel (CACNL1A3). Genomics. 1994 Dec;24(3):608–609. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles D. E., Lehmann-Horn F., Scherer S. W., Tsui L. C., Olde Weghuis D., Suijkerbuijk R. F., Heytens L., Mikala G., Schwartz A., Ellis F. R. Localization of the gene encoding the alpha 2/delta-subunits of the L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel to chromosome 7q and analysis of the segregation of flanking markers in malignant hyperthermia susceptible families. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):969–975. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles D. E., Segers B., Heytens L., Sengers R. C., Wieringa B. High-resolution physical mapping of four microsatellite repeat markers near the RYR1 locus on chromosome 19q13.1 and apparent exclusion of the MHS locus from this region in two malignant hyperthermia susceptible families. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):749–754. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles D. E., Segers B., Olde Weghuis D., Suijkerbuijk R., Mikala G., Schwartz A., Wieringa B. Refined localization of the alpha 1-subunit of the skeletal muscle L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (CACNL1A3) to human chromosome 1q32 by in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1994 Feb;19(3):561–563. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles D. E., Segers B., Sengers R. C., Monsieurs K., Heytens L., Halsall P. J., Hopkins P. M., Ellis F. R., Hall-Curran J. L., Stewart A. D. Genetic mapping of the beta 1- and gamma-subunits of the human skeletal muscle L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel on chromosome 17q and exclusion as candidate genes for malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):863–868. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanpierre M. A rapid method for the purification of DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9611–9611. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalasz H., Watanabe T., Yabana H., Itagaki K., Naito K., Nakayama H., Schwartz A., Vaghy P. L. Identification of 1,4-dihydropyridine binding domains within the primary structure of the alpha 1 subunit of the skeletal muscle L-type calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80321-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert C., Blanloeil Y., Horber R. K., Bérard L., Reyford H., Pinaud M. Malignant hyperthermia in a patient with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Anesth Analg. 1994 Nov;79(5):1012–1014. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199411000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larach M. G. Standardization of the caffeine halothane muscle contracture test. North American Malignant Hyperthermia Group. Anesth Analg. 1989 Oct;69(4):511–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Iaizzo P. A. Are myotonias and periodic paralyses associated with susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia? Br J Anaesth. 1990 Nov;65(5):692–697. doi: 10.1093/bja/65.5.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt R. C., Olckers A., Meyers S., Fletcher J. E., Rosenberg H., Isaacs H., Meyers D. A. Evidence for the localization of a malignant hyperthermia susceptibility locus (MHS2) to human chromosome 17q. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):562–566. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Duff C., Zorzato F., Fujii J., Phillips M., Korneluk R. G., Frodis W., Britt B. A., Worton R. G. Ryanodine receptor gene is a candidate for predisposition to malignant hyperthermia. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):559–561. doi: 10.1038/343559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Phillips M. S. Malignant hyperthermia. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):789–794. doi: 10.1126/science.1589759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouf N. N., McMahon D. K., Hainsworth C. N., Kay B. K. A two-motif isoform of the major calcium channel subunit in skeletal muscle. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90204-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty I., Robert M., Villaz M., De Jongh K., Lai Y., Catterall W. A., Ronjat M. Biochemical evidence for a complex involving dihydropyridine receptor and ryanodine receptor in triad junctions of skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2270–2274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Healy J. M., Heffron J. J., Lehane M., Deufel T., Lehmann-Horn F., Farrall M., Johnson K. Localization of the malignant hyperthermia susceptibility locus to human chromosome 19q12-13.2. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):562–564. doi: 10.1038/343562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai J., Dirksen R. T., Nguyen H. T., Pessah I. N., Beam K. G., Allen P. D. Enhanced dihydropyridine receptor channel activity in the presence of ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):72–75. doi: 10.1038/380072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olckers A., Meyers D. A., Meyers S., Taylor E. W., Fletcher J. E., Rosenberg H., Isaacs H., Levitt R. C. Adult muscle sodium channel alpha-subunit is a gene candidate for malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):829–831. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers P. A., Liu S., Hogan K., Gregg R. G. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding the gamma subunit of the human skeletal muscle 1,4-dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel (CACNLG), cDNA sequence, gene structure, and chromosomal location. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9275–9279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers P. A., Scherer S. W., Tsui L. C., Gregg R. G., Hogan K. Localization of the gene encoding the alpha 2/delta subunit (CACNL2A) of the human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel to chromosome 7q21-q22 by somatic cell hybrid analysis. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):192–193. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., De Waard M., Mori Y., Tanabe T., Snutch T. P., Campbell K. P. Calcium channel beta-subunit binds to a conserved motif in the I-II cytoplasmic linker of the alpha 1-subunit. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):67–70. doi: 10.1038/368067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptacek L. J., Gouw L., Kwieciński H., McManis P., Mendell J. R., Barohn R. J., George A. L., Jr, Barchi R. L., Robertson M., Leppert M. F. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Mar;33(3):300–307. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptácek L. J., Tawil R., Griggs R. C., Engel A. G., Layzer R. B., Kwieciński H., McManis P. G., Santiago L., Moore M., Fouad G. Dihydropyridine receptor mutations cause hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quane K. A., Healy J. M., Keating K. E., Manning B. M., Couch F. J., Palmucci L. M., Doriguzzi C., Fagerlund T. H., Berg K., Ording H. Mutations in the ryanodine receptor gene in central core disease and malignant hyperthermia. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):51–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quane K. A., Keating K. E., Healy J. M., Manning B. M., Krivosic-Horber R., Krivosic I., Monnier N., Lunardi J., McCarthy T. V. Mutation screening of the RYR1 gene in malignant hyperthermia: detection of a novel Tyr to Ser mutation in a pedigree with associated central cores. Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):236–239. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quane K. A., Keating K. E., Manning B. M., Healy J. M., Monsieurs K., Heffron J. J., Lehane M., Heytens L., Krivosic-Horber R., Adnet P. Detection of a novel common mutation in the ryanodine receptor gene in malignant hyperthermia: implications for diagnosis and heterogeneity studies. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):471–476. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudbrak R., Golla A., Hogan K., Powers P., Gregg R., Du Chesne I., Lehmann-Horn F., Deufel T. Exclusion of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility (MHS) from a putative MHS2 locus on chromosome 17q and of the alpha 1, beta 1, and gamma subunits of the dihydropyridine receptor calcium channel as candidates for the molecular defect. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):857–862. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudbrak R., Procaccio V., Klausnitzer M., Curran J. L., Monsieurs K., van Broeckhoven C., Ellis R., Heyetens L., Hartung E. J., Kozak-Ribbens G. Mapping of a further malignant hyperthermia susceptibility locus to chromosome 3q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):684–691. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunada Y., Campbell K. P. Dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: molecular organization and critical roles in skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Neurol. 1995 Oct;8(5):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takekura H., Bennett L., Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Franzini-Armstrong C. Restoration of junctional tetrads in dysgenic myotubes by dihydropyridine receptor cDNA. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):793–803. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80539-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S. Regions of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor critical for excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):567–569. doi: 10.1038/346567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamponi G. W., Bourinet E., Nelson D., Nargeot J., Snutch T. P. Crosstalk between G proteins and protein kinase C mediated by the calcium channel alpha1 subunit. Nature. 1997 Jan 30;385(6615):442–446. doi: 10.1038/385442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Chen H. S., Khanna V. K., De Leon S., Phillips M. S., Schappert K., Britt B. A., Browell A. K., MacLennan D. H. A mutation in the human ryanodine receptor gene associated with central core disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):46–50. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng W., Feng G., Ren D., Eberl D. F., Hannan F., Dubald M., Hall L. M. Cloning and characterization of a calcium channel alpha 1 subunit from Drosophila melanogaster with similarity to the rat brain type D isoform. J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1132–1143. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01132.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



