Abstract
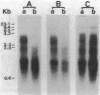
The treatment of woodchuck hepatitis virus infections with 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodocytosine (FIAC) and 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-methyluracil (FMAU), given intraperitoneally, caused complete and permanent decrease of serum virus endogenous DNA polymerase and viral DNA in all treated woodchucks but was associated with severe toxicity. By contrast 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ethyluracil (FEAU) induced a sustained, although less dramatic, decrease of viral replication without apparent toxic effect. FEAU was also effective when given orally. However, in both cases this inhibitory effect was transient.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellet D. H., Wands J. R., Isselbacher K. J., Bohuon C. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in human disease: perspective from a highly specific monoclonal radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3869–3873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cova L., Hantz O., Arliaud-Gassin M., Chevalier A., Berthillon P., Boulay J., Jacquet C., Chomel B., Vitvitski L., Trepo C. Comparative study of DHBV DNA levels and endogenous DNA polymerase activity in naturally infected ducklings in France. J Virol Methods. 1985 Mar;10(3):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Davis G. L., Peters M., Waggoner J. G., Goodman Z., Hoofnagle J. H. Pilot study of recombinant human alpha-interferon for chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommel D., Crevat D., Vitvitsky L., Pichoud C., Hantz O., Chevalier M., Grimaud J. A., Lindberg J., Trépo C. G. Immunopathologic aspects of woodchuck hepatitis. Am J Pathol. 1984 Apr;115(1):125–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Burrell C. J., Coulepis A. G., Robinson W. S., Zuckerman A. J. Taxonomic classification of human hepatitis B virus. Intervirology. 1986;25(1):14–29. doi: 10.1159/000149651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantz O., Allaudeen H. S., Ooka T., De Clercq E., Trepo C. Inhibition of human and woodchuck hepatitis virus DNA polymerase by the triphosphates of acyclovir, 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodocytosine and E-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine. Antiviral Res. 1984 Aug;4(4):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(84)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota K., Sherker A. H., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Okuda K. Effects of adenine arabinoside on serum and intrahepatic replicative forms of duck hepatitis B virus in chronic infection. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):24–28. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Hanson R. G., Minuk G. Y., Pappas S. C., Schafer D. F., Dusheiko G. M., Straus S. E., Popper H., Jones E. A. Randomized controlled trial of adenine arabinoside monophosphate for chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenfelt E., Widell A., Hansson B. G., Löfgren B., Möller-Nielsen C., Oberg B. No in vivo effect of trisodium phosphonoformate on woodchuck hepatitis virus production. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):449–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherker A. H., Hirota K., Omata M., Okuda K. Foscarnet decreases serum and liver duck hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected ducks. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):818–824. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90681-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trépo C., Ouzan D., Fontanges T., Chevallier M., Chossegros P., Degos F., Chevallier P., Hantz O. Therapeutic activity of vidarabine in symptomatic chronic active hepatitis related to HBV. J Hepatol. 1986;3 (Suppl 2):S97–105. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trépo C., Ouzan D., Fontanges T., Chevallier M., Chossegros P., Degos F., Chevallier P., Hantz O. Therapeutic potential of acyclovir and of the interferons in HBV-related chronic active hepatitis due to HBV with or without HDV superinfection. J Hepatol. 1986;3 (Suppl 2):S129–S135. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran P. S., Millman I., Blumberg B. S. Effects of an extract from Phyllanthus niruri on hepatitis B and woodchuck hepatitis viruses: in vitro and in vivo studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):274–278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Imazeki F., Hirota K., Mori J., Uchiumi K., Ito Y., Okuda K. Combination of short-term prednisolone and adenine arabinoside in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. A controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Aug;89(2):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]