Abstract
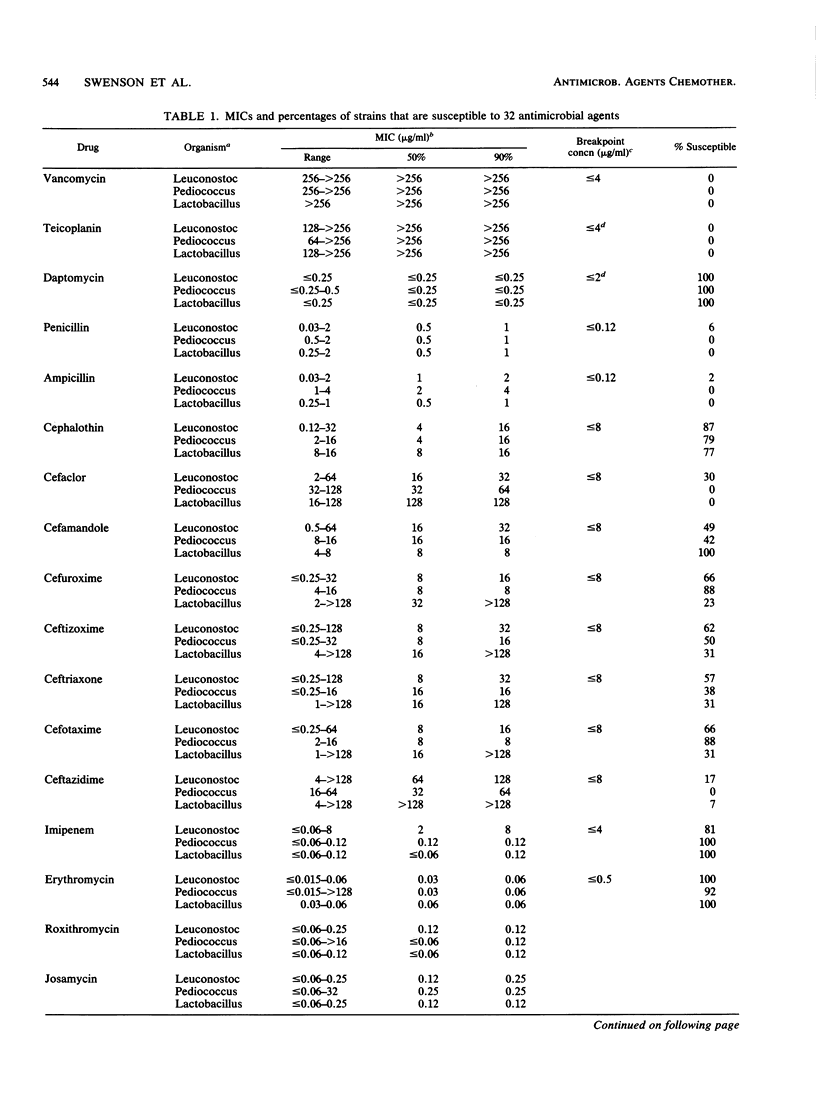
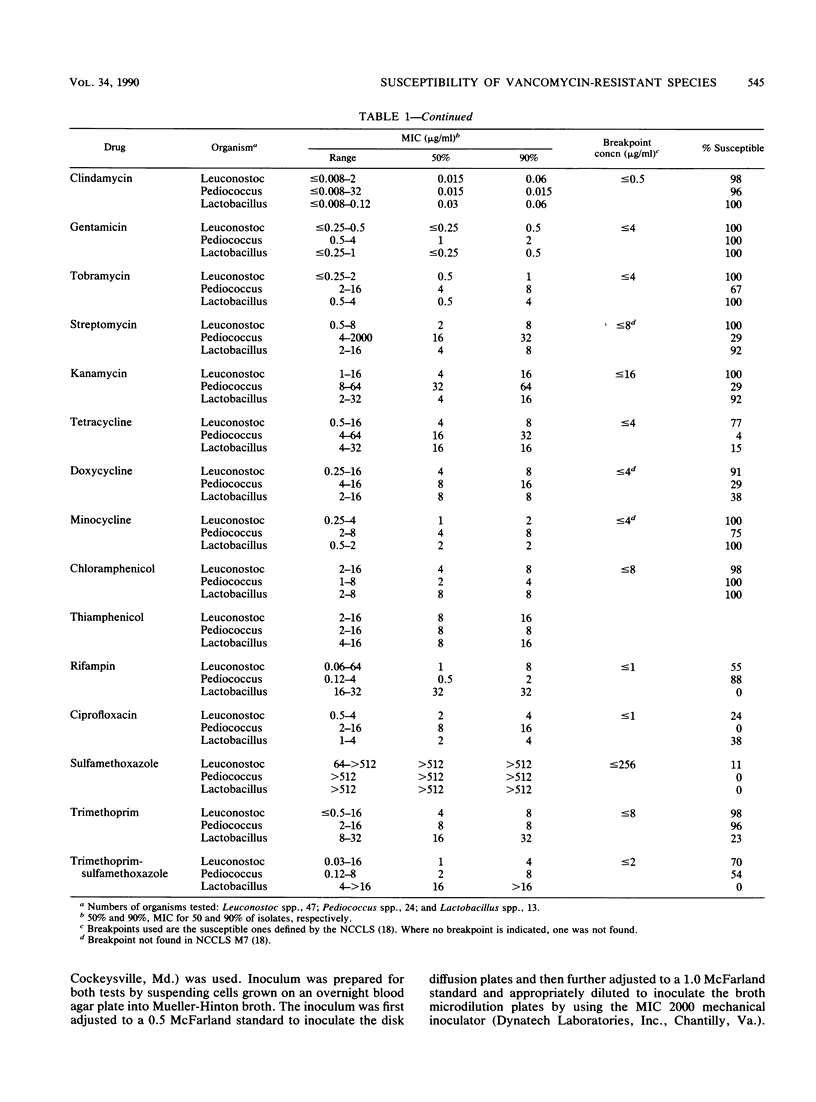
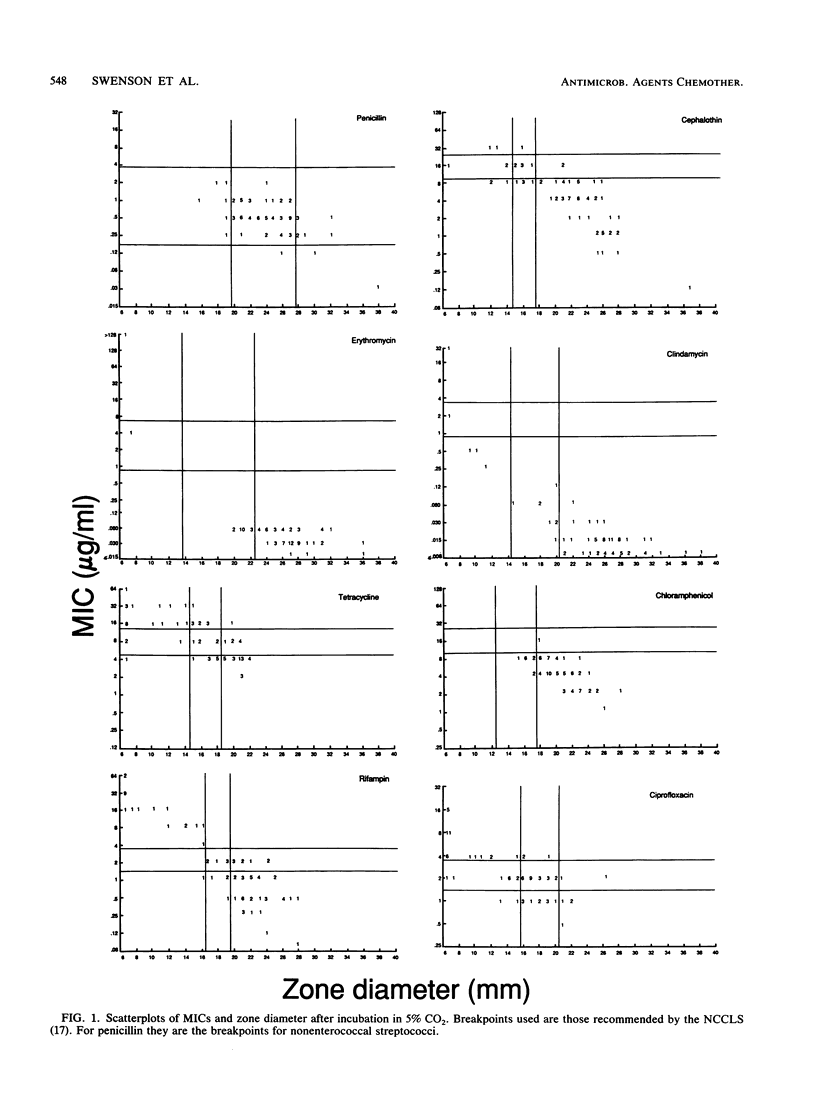
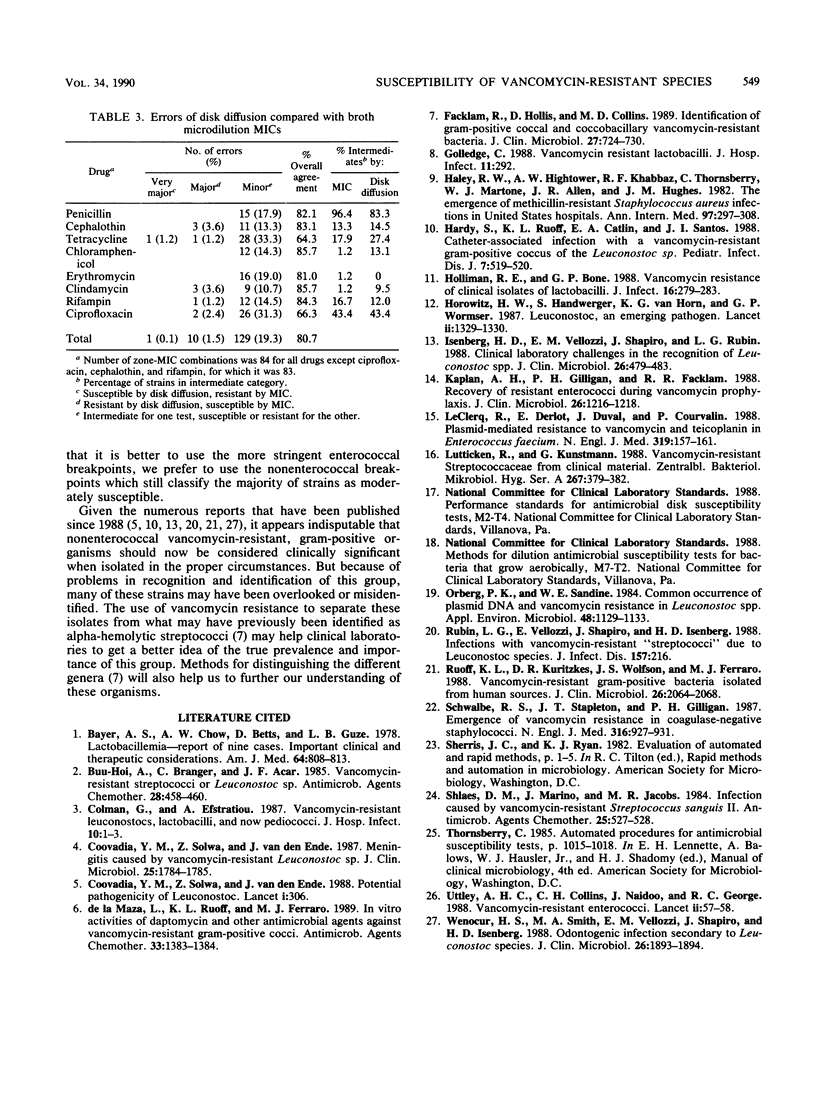
Eighty-five strains of vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria from three genera, Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, and Lactobacillus, were tested to determine susceptibility to 24 antimicrobial agents by broth microdilution and to 10 agents by disk diffusion. The MICs of vancomycin and teicoplanin ranged from 64 to greater than 512 micrograms/ml; however, the MICs of daptomycin, a new lipopeptide, were all less than or equal to 0.25 micrograms/ml. None of the organisms were resistant to imipenem, minocycline, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, or daptomycin. The MICs of penicillin were in the moderately susceptible range for all but three strains. Susceptibility to the other agents varied by genus and, in some cases, by species. When disk diffusion results were compared with MICs for drugs recommended for streptococci by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Villanova, Pa., few very major or major errors were obtained, but the number of minor errors was 19.3%. Therefore, we recommended that MIC testing be used instead of disk diffusion testing for these organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer A. S., Chow A. W., Betts D., Guze L. B. Lactobacillemia--report of nine cases. Important clinical and therapeutic considerations. Am J Med. 1978 May;64(5):808–813. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buu-Hoï A., Branger C., Acar J. F. Vancomycin-resistant streptococci or Leuconostoc sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):458–460. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Efstratiou A. Vancomycin-resistant leuconostocs, lactobacilli and now pediococci. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jul;10(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coovadia Y. M., Solwa Z., van Den Ende J. Potential pathogenicity of Leuconostoc. Lancet. 1988 Feb 6;1(8580):306–306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90395-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coovadia Y. M., Solwa Z., van den Ende J. Meningitis caused by vancomycin-resistant Leuconostoc sp. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1784–1785. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1784-1785.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R., Hollis D., Collins M. D. Identification of gram-positive coccal and coccobacillary vancomycin-resistant bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.724-730.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley R. W., Hightower A. W., Khabbaz R. F., Thornsberry C., Martone W. J., Allen J. R., Hughes J. M. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in United States hospitals. Possible role of the house staff-patient transfer circuit. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):297–308. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Ruoff K. L., Catlin E. A., Ignacio Santos J. Catheter-associated infection with a vancomycin-resistant gram-positive coccus of the Leuconostoc sp. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Jul;7(7):519–520. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198807000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliman R. E., Bone G. P. Vancomycin resistance of clinical isolates of lactobacilli. J Infect. 1988 May;16(3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(88)97676-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H. W., Handwerger S., van Horn K. G., Wormser G. P. Leuconostoc, an emerging vancomycin-resistant pathogen. Lancet. 1987 Dec 5;2(8571):1329–1330. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Rubin L. G. Clinical laboratory challenges in the recognition of Leuconostoc spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.479-483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. H., Gilligan P. H., Facklam R. R. Recovery of resistant enterococci during vancomycin prophylaxis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1216–1218. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1216-1218.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):157–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken R., Kunstmann G. Vancomycin-resistant Streptococcaceae from clinical material. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Jan;267(3):379–382. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orberg P. K., Sandine W. E. Common occurrence of plasmid DNA and vancomycin resistance in Leuconostoc spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1129–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1129-1133.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Vellozzi E., Shapiro J., Isenberg H. D. Infection with vancomycin-resistant "streptococci" due to Leuconostoc species. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):216–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kuritzkes D. R., Wolfson J. S., Ferraro M. J. Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria isolated from human sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2064–2068. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2064-2068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Stapleton J. T., Gilligan P. H. Emergence of vancomycin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):927–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Marino J., Jacobs M. R. Infection caused by vancomycin-resistant Streptococcus sanguis II. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):527–528. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley A. H., Collins C. H., Naidoo J., George R. C. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):57–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenocur H. S., Smith M. A., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Isenberg H. D. Odontogenic infection secondary to Leuconostoc species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1893–1894. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1893-1894.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L., Ruoff K. L., Ferraro M. J. In vitro activities of daptomycin and other antimicrobial agents against vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1383–1384. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



