Abstract
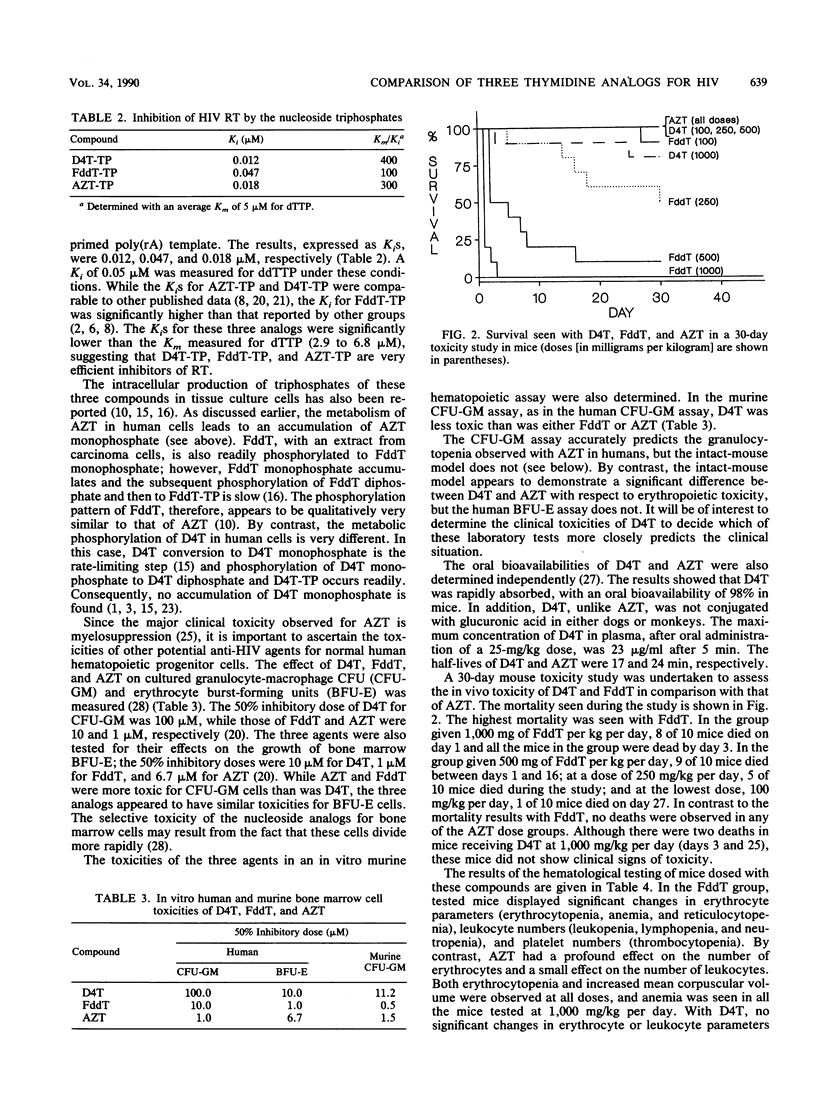
Three analogs of thymidine, D4T [2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxythymidine; 1-(2,3-dideoxy-beta-D-glyceropent-2-enofuranosyl)thymine], FddT (3'-fluoro-3'-deoxythymidine), and AZT (3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine), were compared in biological tests designed to assess their potential utility as anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) agents. The in vitro potencies of these compounds against HIV infection in CEM cells were measured, with FddT and AZT being more potent than D4T. The cytotoxicities of D4T, FddT, and AZT for CEM cells were comparable. The triphosphates of these three derivatives inhibited purified HIV reverse transcriptase, and their affinities for this polymerase were found to be 1 or 2 orders of magnitude greater than that for the normal substrate, dTTP. D4T was less toxic than FddT or AZT for cultured human and mouse bone marrow cells (granulocyte-macrophage CFU). The three compounds had similar toxicities for human progenitor erythrocyte burst-forming units. In a 30-day mouse toxicity study, AZT and FddT produced a similar spectrum of hematopoietic toxicities. These toxic effects occurred at much lower doses of FddT than of AZT. At the higher doses of FddT, a significant incidence of lethality occurred. By contrast, D4T was considerably less toxic than both AZT and FddT in this study. The dose-limiting toxicity of D4T in mice was hepatotoxicity. The very different phosphorylation patterns of D4T, its lower toxicity, and its comparable potency relative to FddT and AZT suggest that the potential of D4T as an anti-HIV agent should be further explored.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- August E. M., Marongiu M. E., Lin T. S., Prusoff W. H. Initial studies on the cellular pharmacology of 3'-deoxythymidin-2'-ene (d4T): a potent and selective inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 1;37(23):4419–4422. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90655-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Baba M., Pauwels R., Herdewijn P., De Clerq E. Anti-retrovirus activity of 3'-fluoro- and 3'-azido-substituted pyrimidine 2',3'-dideoxynucleoside analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 15;37(14):2847–2856. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Herdewijn P., De Clercq E. Differential patterns of intracellular metabolism of 2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxythymidine and 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine, two potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus compounds. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6127–6133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Pauwels R., Baba M., Herdewijn P., de Clercq E., Broder S., Johns D. G. The in vitro and in vivo anti-retrovirus activity, and intracellular metabolism of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine are highly dependent on the cell species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Chattopadhyaya J., Datema R., Ericson A. C., Gilljam G., Johansson N. G., Hansen J., Koshida R., Moelling K., Oberg B. An analysis of the inhibition of replication of HIV and MuLV by some 3'-blocked pyrimidine analogs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 1;38(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Oshana S. C. Inhibition of HIV reverse transcriptase by 2',3'-dideoxynucleoside triphosphates. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;36(24):4361–4362. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90685-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Dutschman G. E., Bastow K. F., Sarngadharan M. G., Ting R. Y. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. General properties and its interactions with nucleoside triphosphate analogs. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2187–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Schooley R. T. The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):185–191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., St Clair M. H., Weinhold K., Rideout J. L., Freeman G. A., Lehrman S. N., Bolognesi D. P., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Phosphorylation of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and selective interaction of the 5'-triphosphate with human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8333–8337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski R. P., Khan M. S., Kalamas R. L., Sporn M. B. Nucleotide synthesis. IV. Phosphorylated 3'-amino-3'-deoxythymidine and 5'-amino-5'-deoxythymidine and derivatives. J Org Chem. 1973 Dec 14;38(25):4299–4305. doi: 10.1021/jo00964a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H., Vogt M. W., Durno A. G., Hirsch M. S., Hunsmann G., Eckstein F. Enhanced in vitro inhibition of HIV-1 replication by 3'-fluoro-3'-deoxythymidine compared to several other nucleoside analogs. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):457–466. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdewijn P., Balzarini J., De Clercq E., Pauwels R., Baba M., Broder S., Vanderhaeghe H. 3'-substituted 2',3'-dideoxynucleoside analogues as potential anti-HIV (HTLV-III/LAV) agents. J Med Chem. 1987 Aug;30(8):1270–1278. doi: 10.1021/jm00391a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. T., Hitchcock M. J. Cellular pharmacology of 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine, a nucleoside analog active against human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):844–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langen P., Kowollik G., Etzold G., Venner H., Reinert H. The phosphorylation of 3'-deoxy-3'-fluorothymidine and its incorporation into DNA in a cellfree system from tumor cells. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1972;29(4):483–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Chen M. S., McLaren C., Gao Y. S., Ghazzouli I., Prusoff W. H. Synthesis and antiviral activity of various 3'-azido, 3'-amino, 2',3'-unsaturated, and 2',3'-dideoxy analogues of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides against retroviruses. J Med Chem. 1987 Feb;30(2):440–444. doi: 10.1021/jm00385a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Schinazi R. F., Prusoff W. H. Potent and selective in vitro activity of 3'-deoxythymidin-2'-ene (3'-deoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine) against human immunodeficiency virus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 1;36(17):2713–2718. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansuri M. M., Starrett J. E., Jr, Ghazzouli I., Hitchcock M. J., Sterzycki R. Z., Brankovan V., Lin T. S., August E. M., Prusoff W. H., Sommadossi J. P. 1-(2,3-Dideoxy-beta-D-glycero-pent-2-enofuranosyl)thymine. A highly potent and selective anti-HIV agent. J Med Chem. 1989 Feb;32(2):461–466. doi: 10.1021/jm00122a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes E., Lehmann C., Scholz D., Rosenthal H. A., Langen P. Phosphorylation, anti-HIV activity and cytotoxicity of 3'-fluorothymidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):825–831. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Weinhold K. J., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Lehrman S. N., Gallo R. C., Bolognesi D., Barry D. W., Broder S. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perno C. F., Yarchoan R., Cooney D. A., Hartman N. R., Webb D. S., Hao Z., Mitsuya H., Johns D. G., Broder S. Replication of human immunodeficiency virus in monocytes. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) potentiates viral production yet enhances the antiviral effect mediated by 3'-azido-2'3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT) and other dideoxynucleoside congeners of thymidine. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):933–951. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R. Toxicity of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine for normal human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):452–454. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Richards C. A., Spector T., Weinhold K. J., Miller W. H., Langlois A. J., Furman P. A. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine triphosphate as an inhibitor and substrate of purified human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1972–1977. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk S. R., Shipman C., Jr, Nassiri R., Genzlinger G., Krawczyk S. H., Townsend L. B., Drach J. C. Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleosides as inhibitors of human cytomegalovirus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):544–550. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Broder S. Development of antiretroviral therapy for the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and related disorders. A progress report. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 26;316(9):557–564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702263160925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


