Abstract
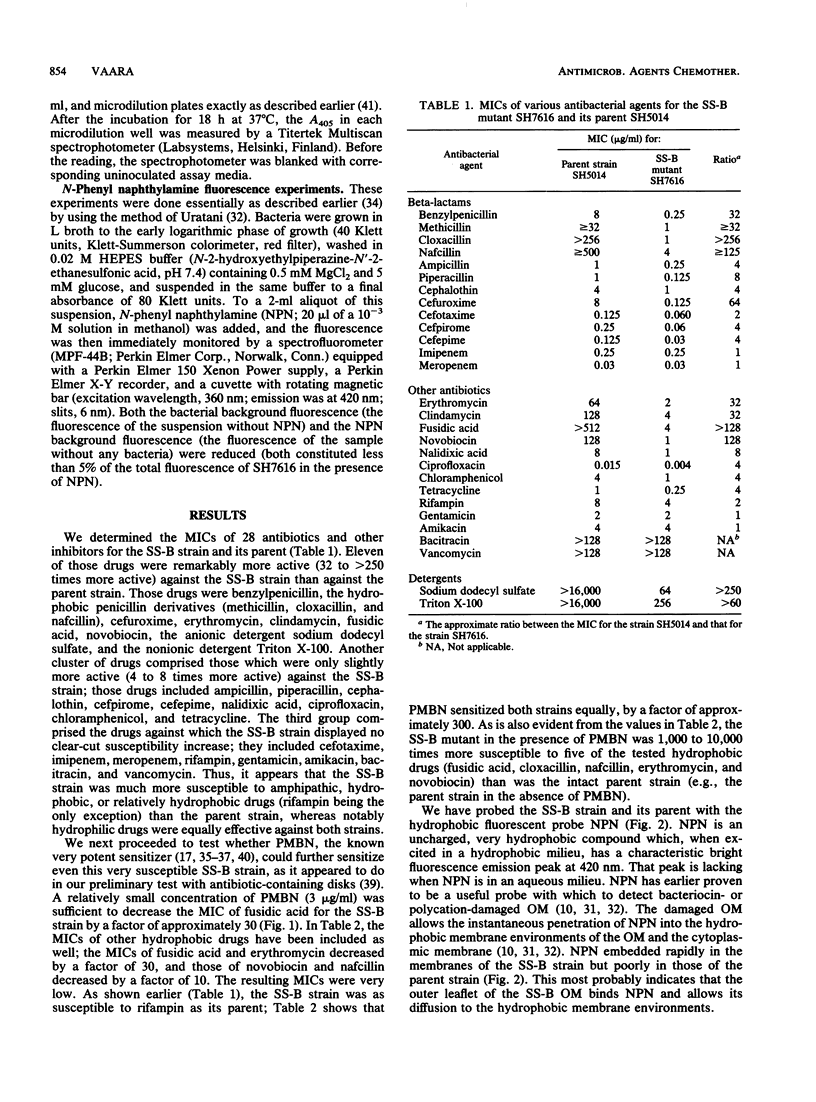
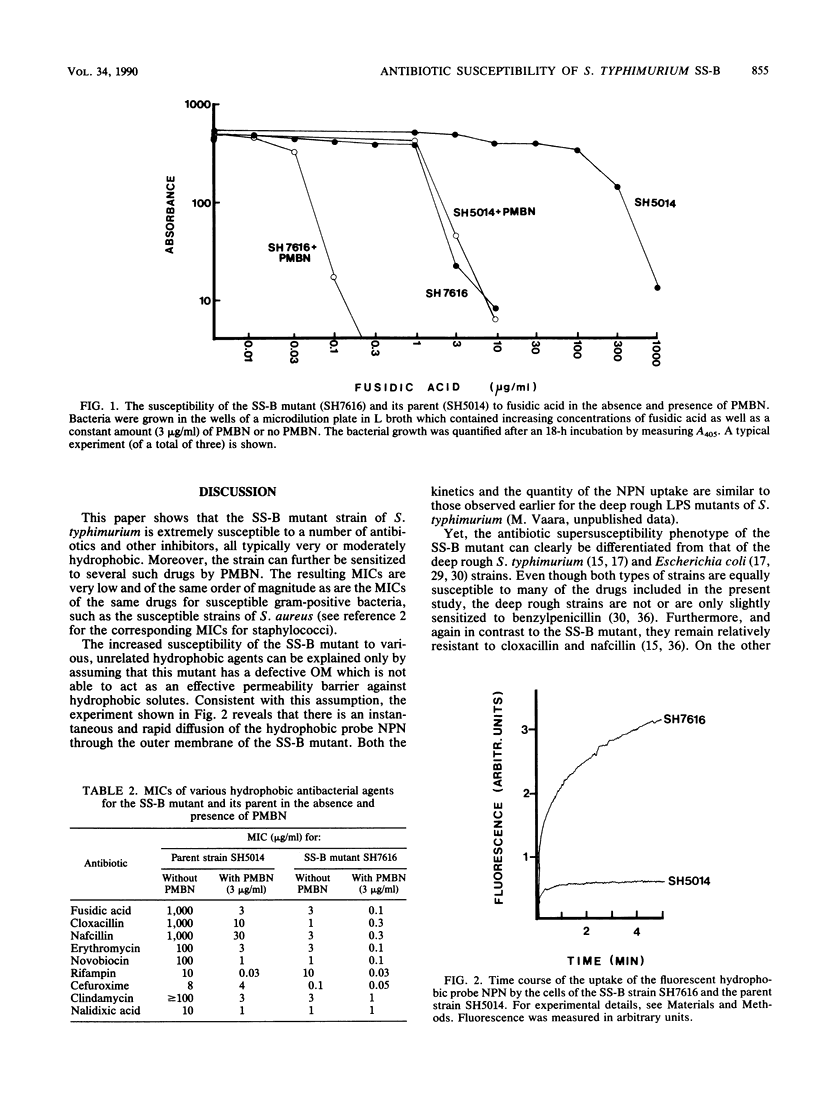
The antibiotic susceptibility profile of Salmonella typhimurium SS-B, a mutant susceptible to some antimicrobial agents, was studied in detail. Twenty-eight agents were tested, and eleven of these had MICs significantly lower (32- to greater than 250-fold) for the SS-B strain than for its parent. The drugs were generally hydrophobic or amphiphilic. Polymyxin B nonapeptide, which has a known outer membrane permeabilizing action, further reduced the MIC of several of these agents for the SS-B strain by a factor of approximately 10 to 30. In most cases, the resulting MICs were lower than the corresponding MICs for the parent strain grown in the presence of polymyxin B nonapeptide. In addition, the hydrophobic fluorescent probe N-phenyl naphthylamine was rapidly embedded in the membranes of the SS-B strain but was poorly embedded in those of the parent strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Bauer K. Permeation of hydrophilic molecules through the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Review on bacterial porins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. G., Jr, Leive L. Two mutations which affect the barrier function of the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):899–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.899-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Affinities of penicillins and cephalosporins for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and their antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):533–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson P., Nordström K., Normark S. Outer penetration barrier of Escherichia coli K-12: kinetics of the uptake of gentian violet by wild type and envelope mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.893-900.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane permeability barrier and how to overcome it. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:95–102. doi: 10.1159/000410475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara S., Hussain M., Mizushima S. Characterization of new membrane lipoproteins and their precursors of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3125–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Fecycz I. T., Campbell J. N. Nutritional factors controlling exocellular protease production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):844–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.844-847.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski P., Rhen M., Kantele J., Vaara M. Isolation, cloning, and primary structure of a cationic 16-kDa outer membrane protein of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18973–18980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. Practical aspects of preparing phage and plasmid DNA: growth, maintenance, and storage of bacteria and bacteriophage. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:145–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Transmembrane diffusion of some hydrophobic substances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):118–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Boman H. G., Matsson E. Mutant of Escherichia coli with anomalous cell division and ability to decrease episomally and chromosomally mediated resistance to ampicillin and several other antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1334–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1334-1342.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Clark D. C., Wotton S. Indirect method for assessing the penetration of beta-lactamase-nonsusceptible penicillins and cephalosporins in Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):215–218. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodolakis A., Thomas P., Starka J. Morphological mutants of Escherichia coli. Isolation and ultrastructure of a chain-forming envC mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):409–416. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. D., Furr J. R. Penetration of SQ 26,776, a new monobactam antibiotic, into Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Apr;9(4):329–331. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.4.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H. Mutants defective in the 33K outer membrane protein of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.376-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stárková Z., Bonnaveiro N., Stárka J. Hydrolysis of phospholipids by phospholipase C in intact cells of wild-type and envelope mutants of Escherichia coli K12. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukupolvi S., Vaara M., Helander I. M., Viljanen P., Mäkelä P. H. New Salmonella typhimurium mutants with altered outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.704-712.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. Increase in sensitivity to antibiotics and lysozyme on deletion of lipopolysaccharides in Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):453–454. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.453-454.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Sato T., Matsuhashi M. Role of lipopolysaccharides in antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage adsorption of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.968-975.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecoma E. S., Wu D. Membrane deenergization by colicin K affects fluorescence of exogenously added but not biosynthetically esterified parinaric acid probes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):931–938. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uratani Y. Dansyl chloride labeling of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with pyocin R1: change in permeability of the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.523-528.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Analytical and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography of the papain-cleaved derivative of polymyxin B. J Chromatogr. 1988 Jun 10;441(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)83889-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Jaakkola J. Sodium hexametaphosphate sensitizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, several other species of Pseudomonas, and Escherichia coli to hydrophobic drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Oct;33(10):1741–1747. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.10.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations sensitize enteric bacteria to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Viljanen P. Binding of polymyxin B nonapeptide to gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):548–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen P., Koski P., Vaara M. Effect of small cationic leukocyte peptides (defensins) on the permeability barrier of the outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2324–2329. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2324-2329.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen P., Vaara M. Susceptibility of gram-negative bacteria to polymyxin B nonapeptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


