Abstract
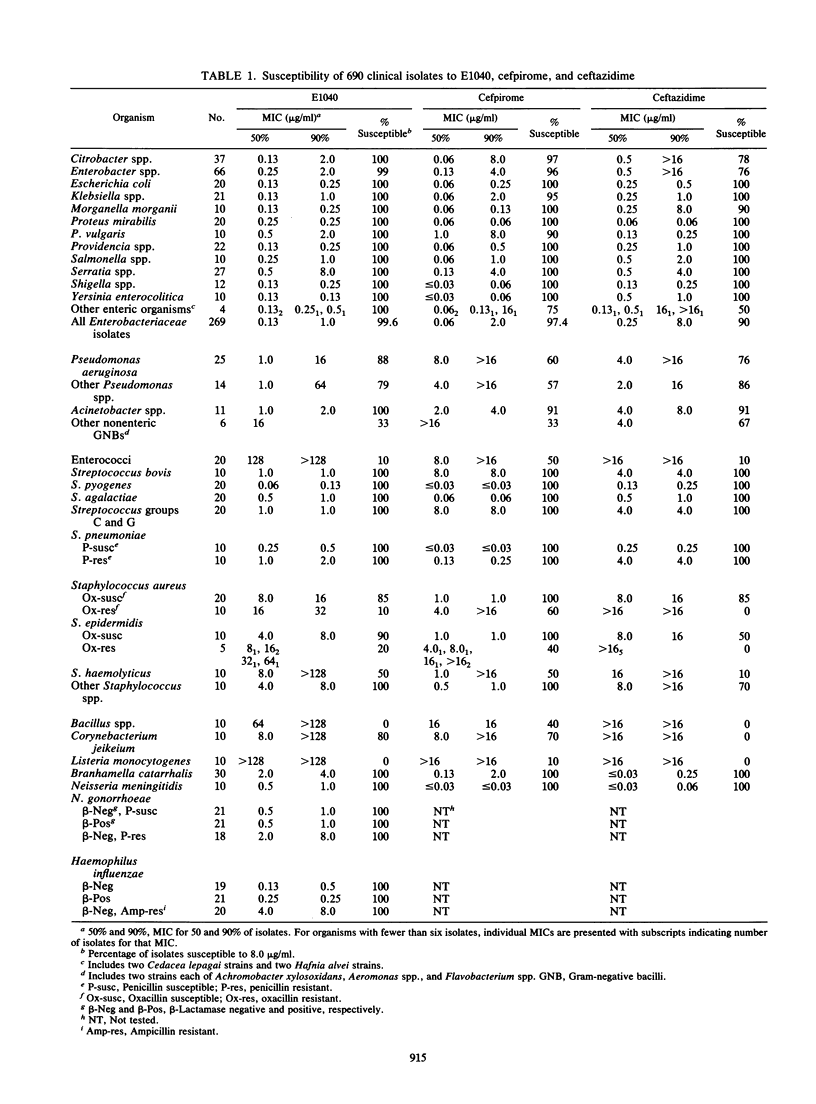
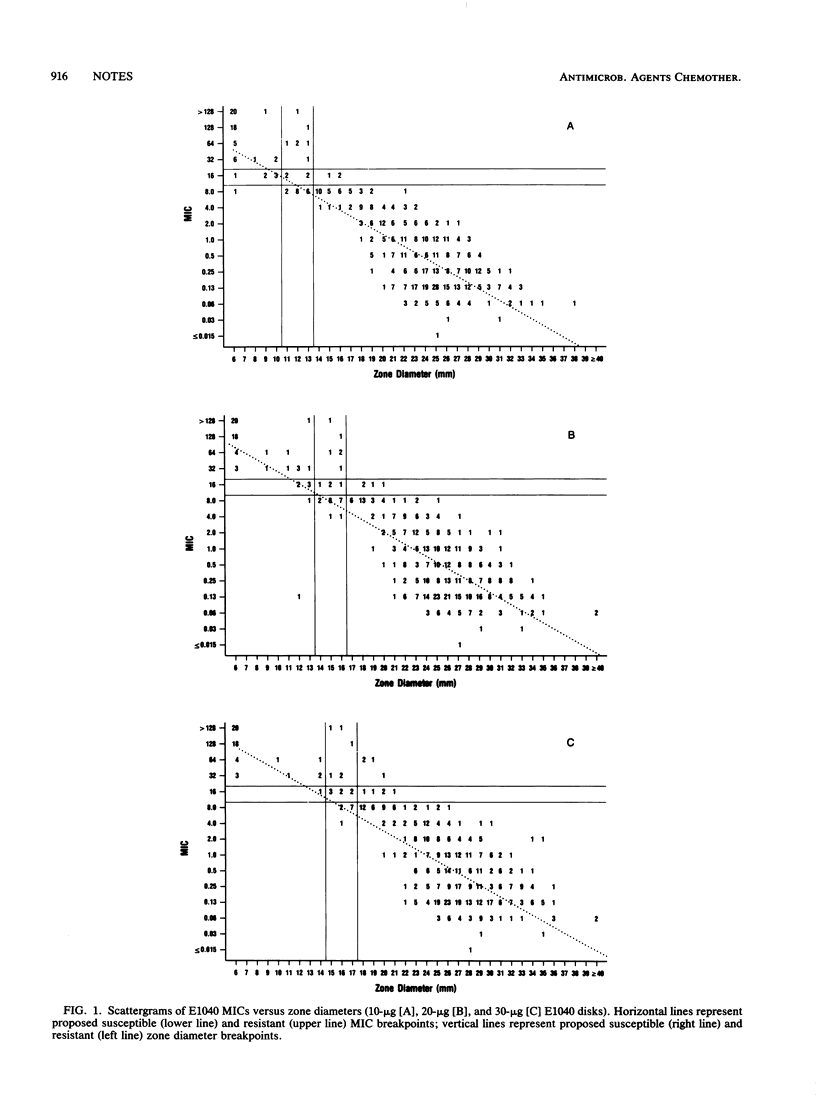
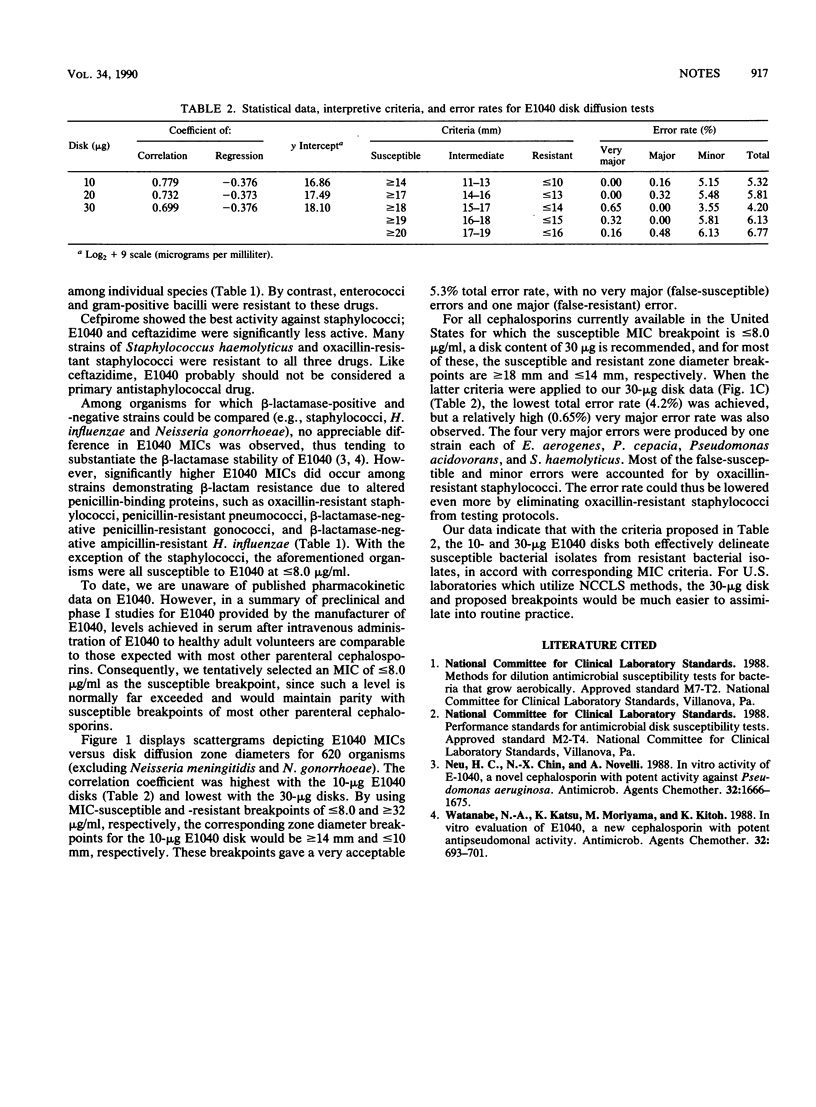
E1040 is a new parenteral cephalosporin which was tested against 690 clinical isolates and compared with cefpirome and ceftazidime. E1040 had the best activity of the three drugs against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, inhibiting 89% of strains at 8.0 micrograms/ml. E1040 demonstrated good activity against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, including cefpirome-resistant and ceftazidime-resistant strains. E1040 also had good activity against streptococci but much poorer activity against enterococci and staphylococci. When E1040 broth microdilution and disk diffusion susceptibility test results were compared, the 30-micrograms disk was recommended, with the following tentative interpretive criteria: susceptible, greater than or equal to 18 mm (MIC, less than or equal to 8.0 micrograms/ml); intermediate, 15 to 17 mm (MIC, 16 micrograms/ml); and resistant, less than or equal to 14 mm (MIC, greater than or equal to 32 micrograms/ml).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Novelli A. In vitro activity of E-1040, a novel cephalosporin with potent activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1666–1675. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Katsu K., Moriyama M., Kitoh K. In vitro evaluation of E1040, a new cephalosporin with potent antipseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


