Abstract
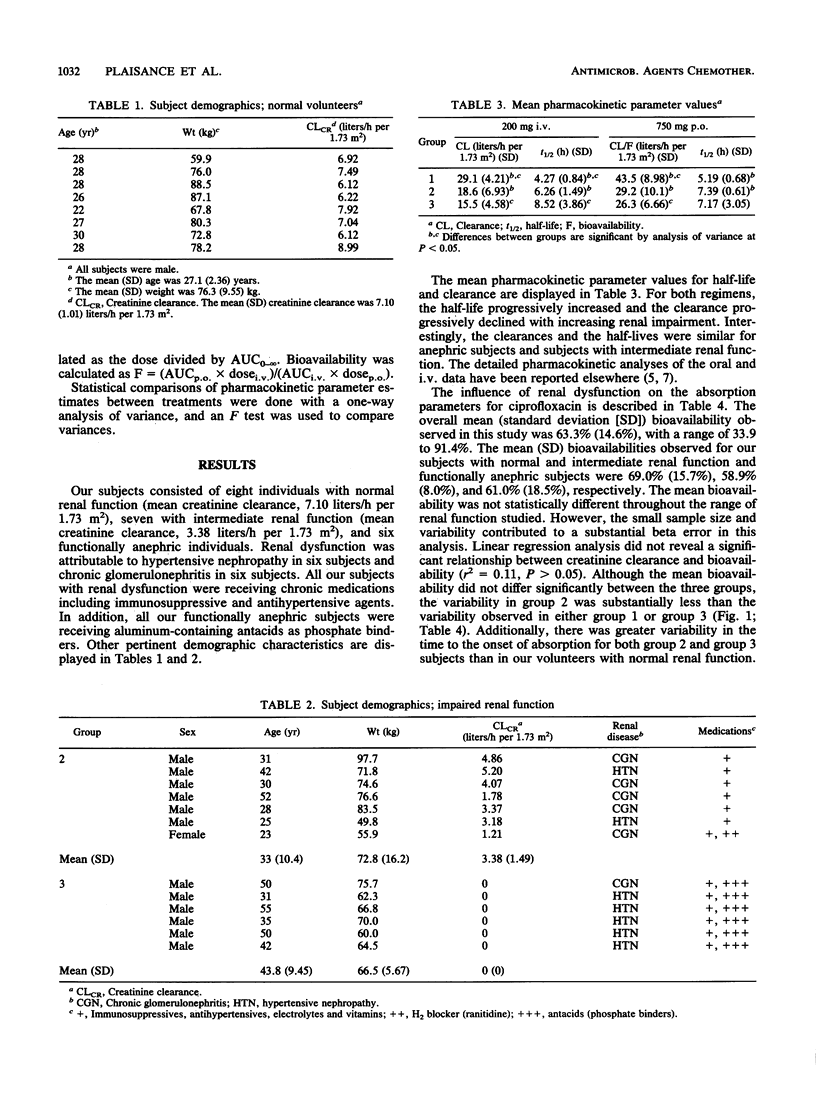
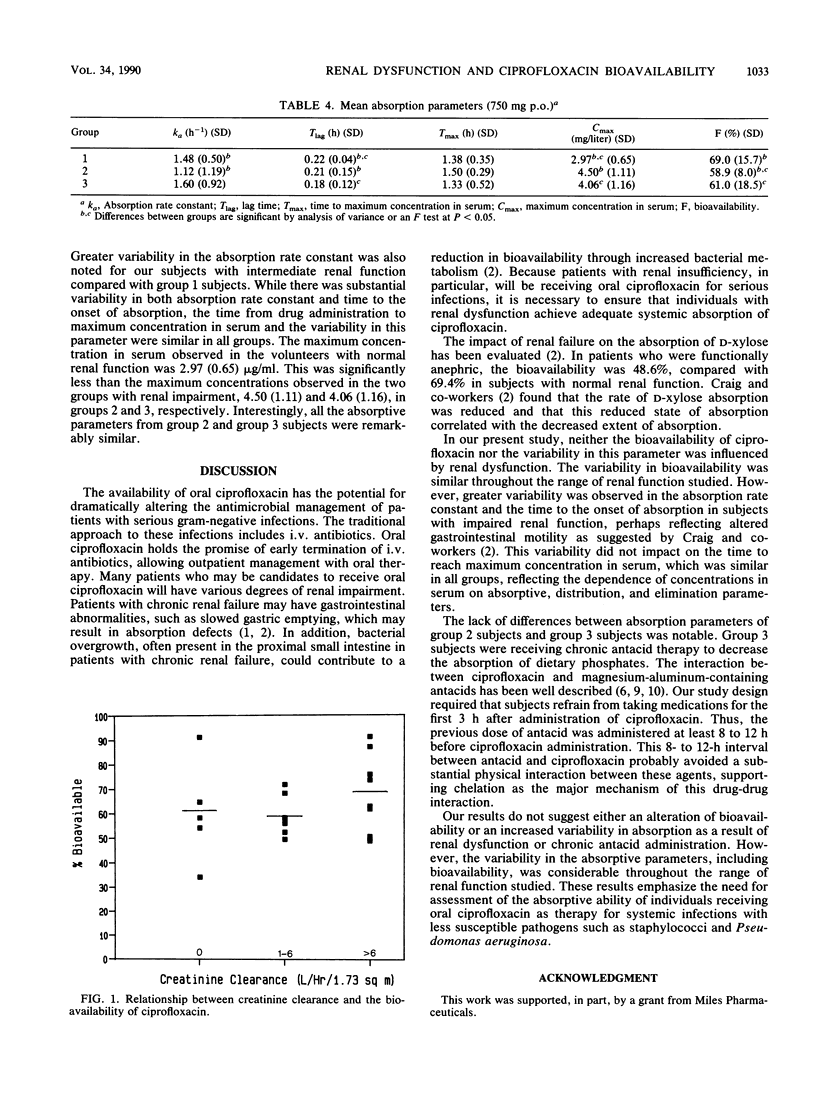
The effect of renal function on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin was studied in 21 subjects with measured creatinine clearances ranging from 0 to 8.99 liters/h per 1.73 m2. Each subject received ciprofloxacin, 200 mg intravenously and 750 mg orally, separated by at least 1 week. Serial (12 to 15) blood samples were obtained over 24 to 48 h. Concentrations in serum were assayed by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Area under the curve was calculated by the trapezoidal rule with extrapolation to infinity. Bioavailability was calculated as the ratio between the dose-normalized area under the curve of oral and intravenous administrations. The overall mean (standard deviation) bioavailability observed was 63.4% (14.6%), similar to that observed in those with normal renal function (69.0% [15.7%]). The mean bioavailability in the subgroup of subjects with renal insufficiency was 59.9% (13.3%). The observed range in bioavailability was 33.9 to 91.4%. Linear regression did not reveal a correlation between creatinine clearance and bioavailability. Renal insufficiency does not appear to affect ciprofloxacin bioavailability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chau N. P., Weiss Y. A., Safar M. E., Lavene D. E., Georges D. R., Milliez P. L. Pindolol availability in hypertensive patients with normal and impaired renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Nov;22(5 Pt 1):505–510. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977225part1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. M., Murphy P., Gibson T. P., Quintanilla A., Chao G. C., Cochrane C., Patterson A., Atkinson A. J., Jr Kinetic analysis of D-xylose absorption in normal subjects and in patients with chronic renal failure. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Mar;101(3):496–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Argenio D. Z., Schumitzky A. A program package for simulation and parameter estimation in pharmacokinetic systems. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Mar;9(2):115–134. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Standiford H. C., Plaisance K., Forrest A., Leslie J., Caldwell J. Absolute oral bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):444–446. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Weir M., Forrest A., Plaisance K., Emm T., Standiford H. C. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin in patients with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):860–864. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming L. W., Moreland T. A., Stewart W. K., Scott A. C. Ciprofloxacin and antacids. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):294–294. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest A., Weir M., Plaisance K. I., Drusano G. L., Leslie J., Standiford H. C. Relationships between renal function and disposition of oral ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1537–1540. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Borner K., Glatzel P. D., Koeppe P., Lode H. Reduced enteral absorption of ciprofloxacin in the presence of antacids. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02013667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilstone W. J., Fine A. Furosemide kinetics in renal failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jun;23(6):644–650. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978236644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


