Abstract
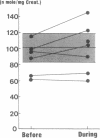
The effects of aztreonam on fecal flora and on descarboxy prothrombin (PIVKA-II) in plasma and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) in urine as an index of vitamin K metabolism were studied in seven children (age range, 2 months to 2 years) with urinary tract infections. Daily doses of aztreonam were 60 to 80 mg/kg. Stool specimens were obtained before the treatment, on days 3 to 5 of aztreonam use, and from 3 to 5 days after the cessation of treatment. The counts of enterobacteria decreased (P less than 0.01) and those of streptococci increased (P less than 0.05) during aztreonam treatment. The anaerobic organisms, especially bifidobacteria and bacteroides, showed no marked change. PIVKA-II and Gla were investigated before and during the treatment with aztreonam. PIVKA-II was not detected in seven patients before or during aztreonam use. There were no significant differences in the levels of Gla in urine before or during the treatment.
Full text
PDF
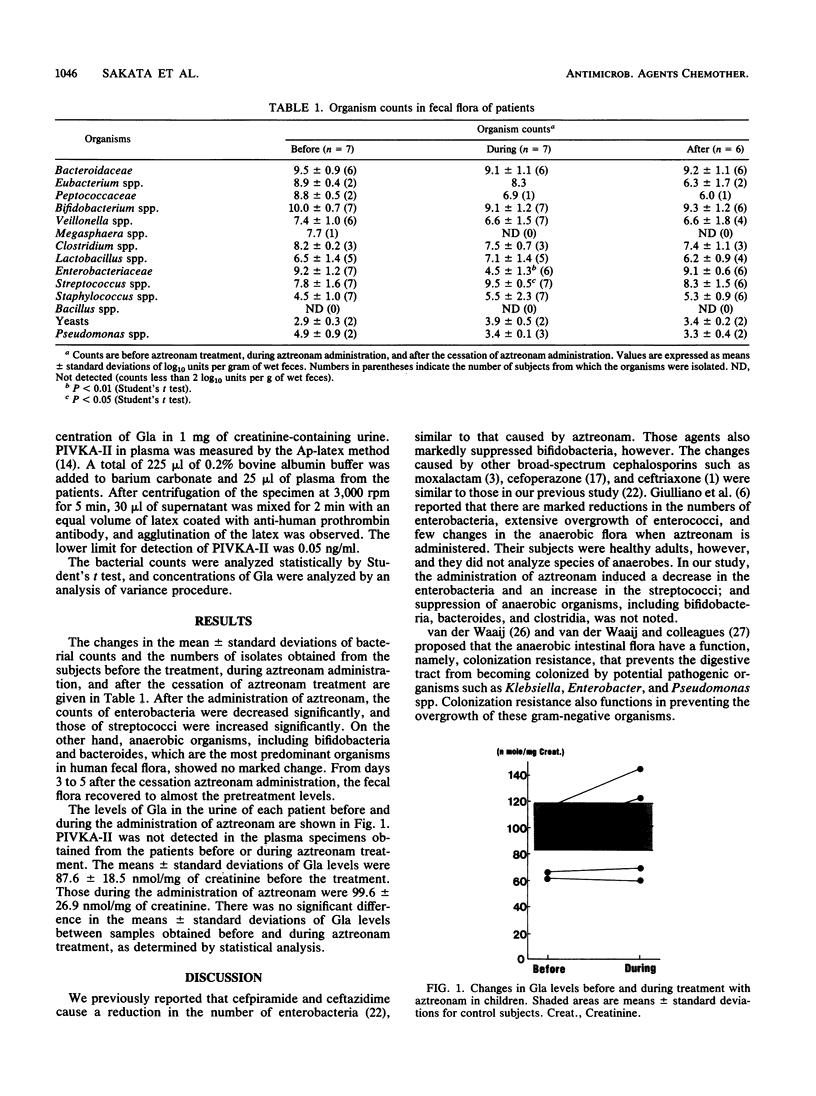

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidsson A., Alván G., Angelin B., Borgå O., Nord C. E. Ceftriaxone: renal and biliary excretion and effect on the colon microflora. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Sep;10(3):207–215. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.3.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang N. U., Tessler S. S., Heidenreich R. O., Marks C. A., Mattler L. E. Effects of moxalactam on blood coagulation and platelet function. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4 (Suppl):S546–S554. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_3.s546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benno Y., Shiragami N., Uchida K., Yoshida T., Mitsuoka T. Effect of moxalactam on human fecal microflora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., Weaver S., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of SQ26,776. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):294–298. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano M., Barza M., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. Effect of broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotics on composition of intestinal microflora of humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):202–206. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Reilly P. M., Luppen K. L., McMillian R., Bollinger M., Wolk S. M., Darji T. B., Noorani A. A. Treatment of serious gram-negative infections with aztreonam. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):623–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobus N. V., Ferreira M. C., Barza M. In vitro activity of azthreonam, a monobactam antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):832–838. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwada M., Katayama K. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and glutamic acid in proteins, bone, and urine. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90720-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A. A selective plate medium for Cl. welchii. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jul;70(1):105–109. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky J. J. N-methyl-thio-tetrazole inhibition of the gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid: possible mechanism for antibiotic-associated hypoprothrombinaemia. Lancet. 1983 Jul 23;2(8343):192–193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguro T., Yamada K. A simple and rapid test for PIVKA-II in plasma. Thromb Res. 1982 Jan 1;25(1-2):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Ohno K., Benno Y., Suzuki K., Namba K. Die Faekalflora bei Menschen. IV. Mitteilung: Vergleich des neu entwickelten Verfahrens mit dem bisherigen üblichen Verfahren zur Darmfloraanalyse. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Mar;234(2):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Sega T., Yamamoto S. Eine verbesserte Methodik der qualitativen und quantitativen Analyse der Darmflora von Menschen und Tieren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Mar;195(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Citron D. M., McNamara B. T., Finegold S. M. Impact of cefoperazone therapy on fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):226–230. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. A. Anaerobiosis with iron wool. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Feb;33(1):33–37. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Bailey R. R. Vitamin K deficiency developing in patients with renal failure treated with cephalosporin antibiotics. N Z Med J. 1980 Nov 26;92(672):378–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Fujita K., Yoshioka H. The effect of antimicrobial agents on fecal flora of children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):225–229. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M. J., Bechtold H., Andrassy K., Koderisch J., McCarthy P. T., Trenk D., Jähnchen E., Ritz E. Mechanism of cephalosporin-induced hypoprothrombinemia: relation to cephalosporin side chain, vitamin K metabolism, and vitamin K status. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;28(1):88–95. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman H. R., Chartrand S. A., Tolentino T., Friedhoff L., Marks M. I. Aztreonam therapy for serious gram-negative infections in children. Am J Dis Child. 1986 Nov;140(11):1147–1151. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140250073038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. The effect of antimicrobial agents on human faecal flora: studies with cephalexin, cyclacillin and clindamycin. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1974;3(0):229–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegersma N., Jansen G., van der Waaij D. Effect of twelve antimicrobial drugs on the colonization resistance of the digestive tract of mice and on endogenous potentially pathogenic bacteria. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):221–230. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D. Colonization resistance of the digestive tract: clinical consequences and implications. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Oct;10(4):263–270. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.4.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]