Abstract
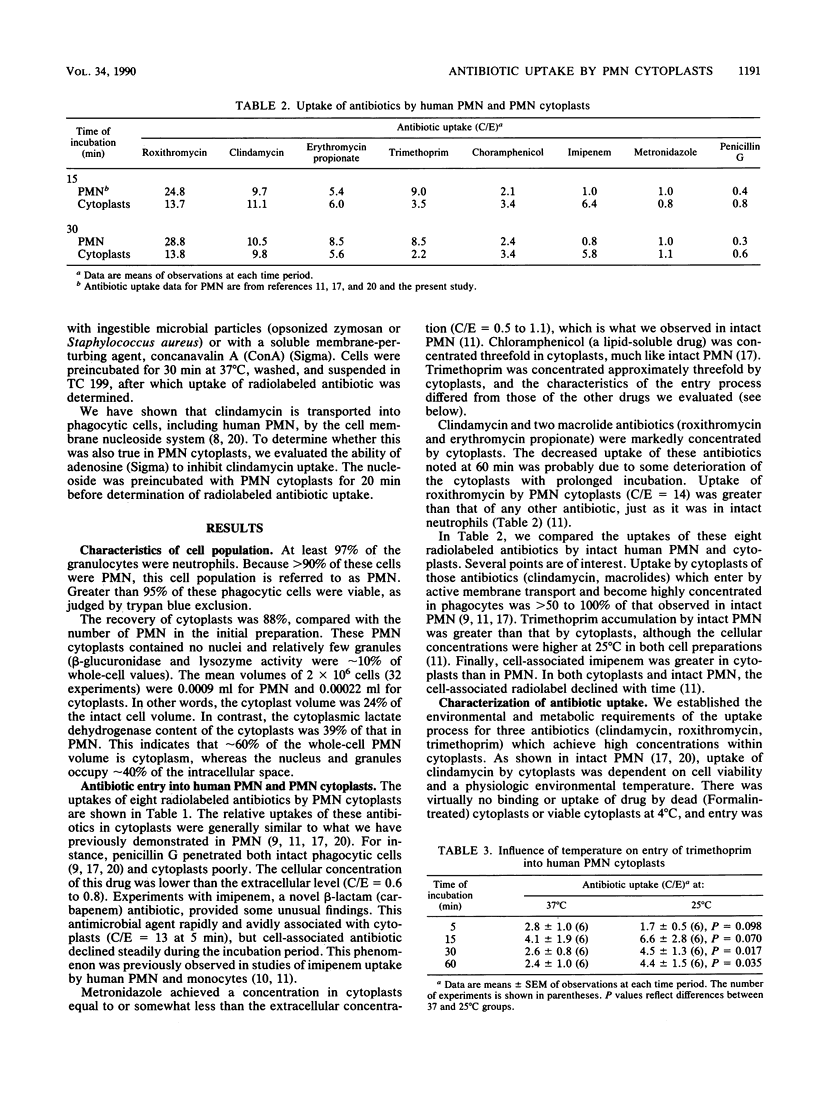
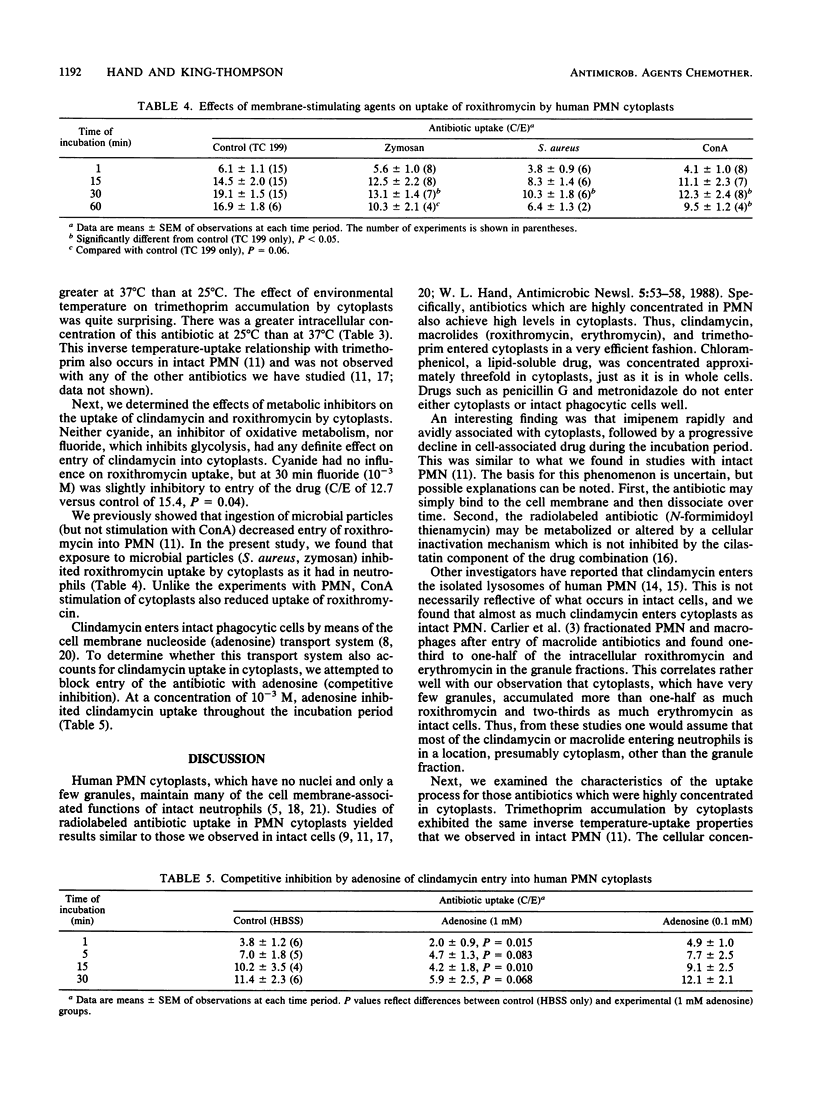
Enucleated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN cytoplasts), which have no nuclei and only a few granules, retain many of the functions of intact neutrophils. To better define the mechanisms and intracellular sites of antimicrobial agent accumulation in human neutrophils, we studied the antibiotic uptake process in PMN cytoplasts. Entry of eight radiolabeled antibiotics into PMN cytoplasts was determined by means of a velocity gradient centrifugation technique. Uptakes of these antibiotics by cytoplasts were compared with our findings in intact PMN. Penicillin entered both intact PMN and cytoplasts poorly. Metronidazole achieved a concentration in cytoplasts (and PMN) equal to or somewhat less than the extracellular concentration. Chloramphenicol, a lipid-soluble drug, and trimethoprim were concentrated three- to fourfold by cytoplasts. An unusual finding was that trimethroprim, unlike other tested antibiotics, was accumulated by cytoplasts more readily at 25 degrees C than at 37 degrees C. After an initial rapid association with cytoplasts, cell-associated imipenem declined progressively with time. Clindamycin and two macrolide antibiotics (roxithromycin, erythromycin) were concentrated 7- to 14-fold by cytoplasts. This indicates that cytoplasmic granules are not essential for accumulation of these drugs. Adenosine inhibited cytoplast uptake of clindamycin, which enters intact phagocytic cells by the membrane nucleoside transport system. Roxithromycin uptake by cytoplasts was inhibited by phagocytosis, which may reduce the number of cell membrane sites available for the transport of macrolides. These studies have added to our understanding of uptake mechanisms for antibiotics which are highly concentrated in phagocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADOR E., DORFMAN L. E., WACKER W. E. SERUM LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY: AN ANALYTICAL ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT ASSAYS. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. B., Zenebergh A., Tulkens P. M. Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of roxithromycin and erythromycin in phagocytic cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20 (Suppl B):47–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.suppl_b.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Metcalf J. A., Roos D., Seligmann B., Friedman M. M. Organelle-depleted human neutrophil cytoplasts used to study fmet-leu-phe receptor modulation and cell function. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):415–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., Boozer R. M., King-Thompson N. L. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages of smokers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., Corwin R. W., Steinberg T. H., Grossman G. D. Uptake of antibiotics by human alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jun;129(6):933–937. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Contrasts between phagocyte antibiotic uptake and subsequent intracellular bactericidal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Membrane transport of clindamycin in alveolar macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):241–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. The entry of antibiotics into human monocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 May;23(5):681–689. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N., Holman J. W. Entry of roxithromycin (RU 965), imipenem, cefotaxime, trimethoprim, and metronidazole into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1553–1557. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Alkalinization of the intralysosomal pH by clindamycin and its effects on neutrophil function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):39–50. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., Voetman A. A., Meerhof L. J. Functional activity of enucleated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):368–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Hand W. L. Effects of phagocytosis on antibiotic and nucleoside uptake by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):397–403. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voetman A. A., Bot A. A., Roos D. Cryopreservation of enucleated human neutrophils (PMN cytoplasts). Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):234–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


