Abstract
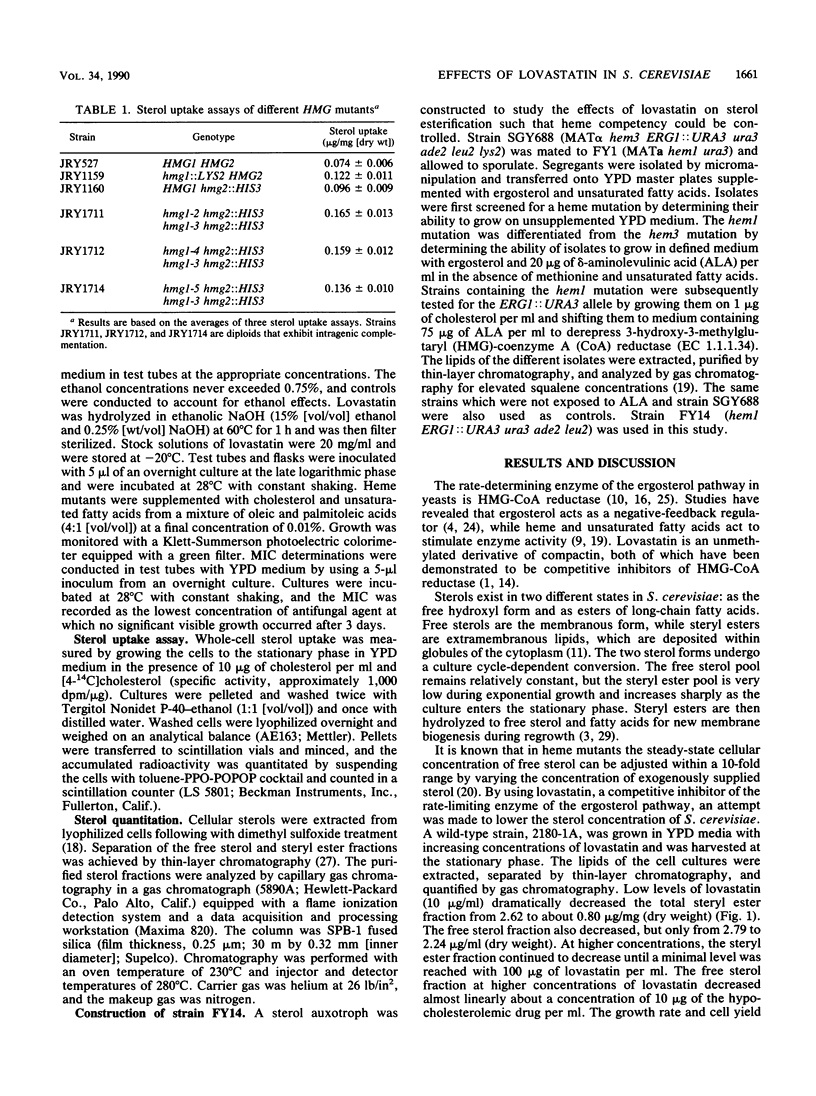
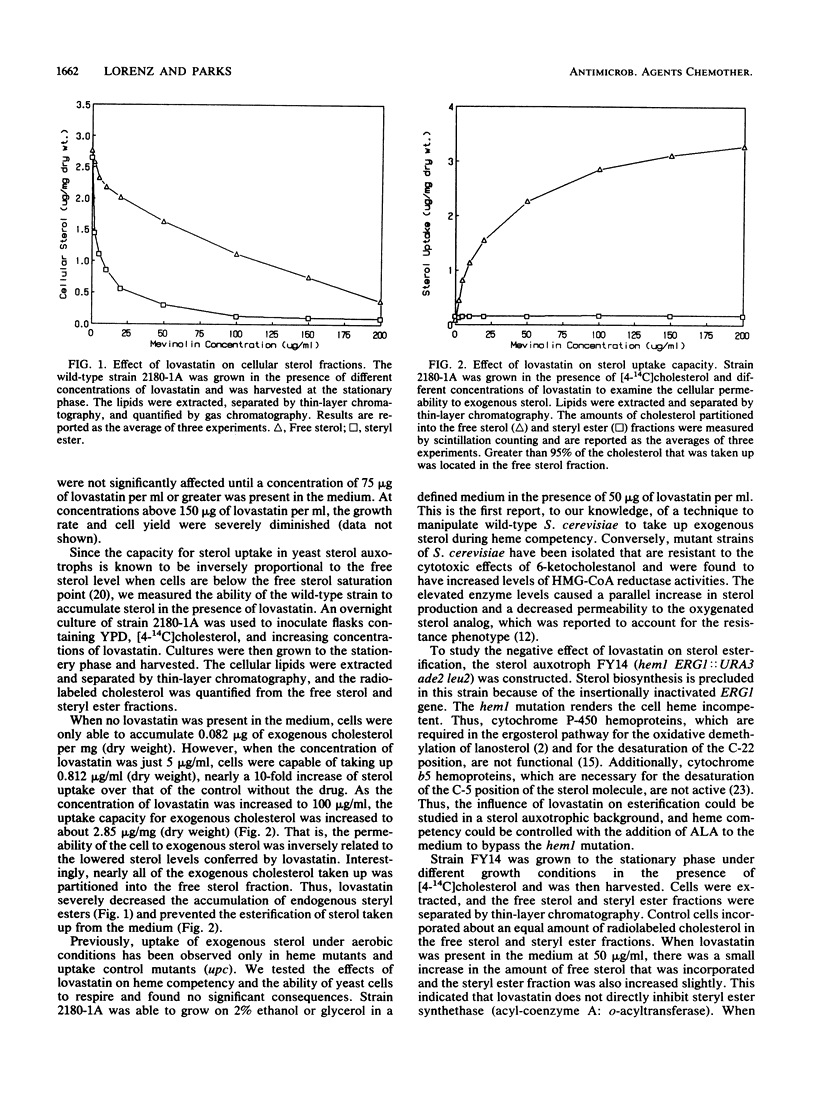
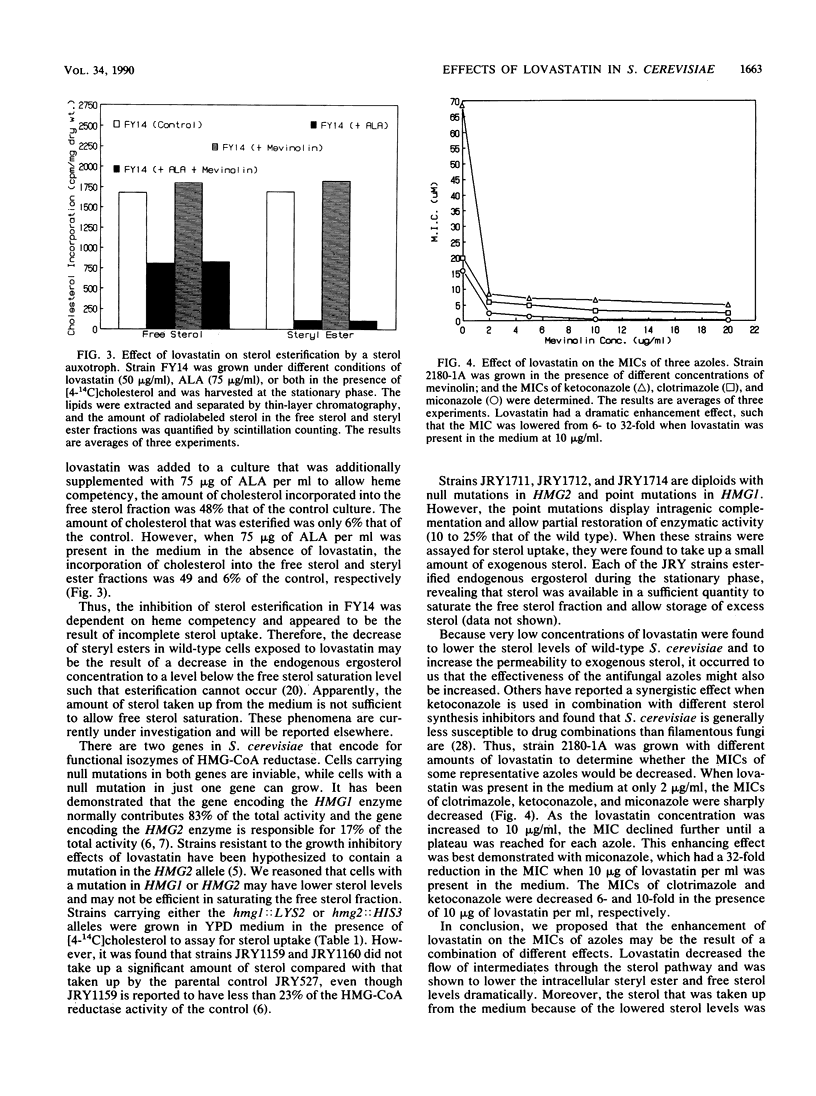
The hypocholesterolemic drug lovastatin (mevinolin) was found to be very effective in lowering the sterol levels of the wild-type yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Lovastatin dramatically decreased the steryl ester content from 2.62 to 0.8 micrograms/mg (dry weight), whereas the free sterol content decreased only from 2.79 to 2.24 micrograms/mg (dry weight) when lovastatin was present in the medium at 10 micrograms/ml. At higher concentrations (100 micrograms/ml), lovastatin nearly abolished the accumulation of steryl esters and decreased the free sterol concentration to less than 1.3 micrograms/mg (dry weight). As a result of the lowered sterol levels, proportional amounts of exogenous sterol were taken up from the medium during aerobic, respiratory conditions. Nearly all of the exogenous sterol taken up was partitioned into the free sterol fraction. The inhibition of sterol esterification in the presence of lovastatin was dependent on heme synthesis. The result of these combined effects caused the MICs of three azole antifungal drugs (ketoconazole, clotrimazole, and miconazole) to be lowered from 6- to 32-fold when lovastatin was present in the medium at 10 micrograms/ml.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama Y., Yoshida Y. The 14alpha-demethylation of lanosterol by a reconstituted cytochrome P-450 system from yeast microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Parks L. W. Yeast sterol esters and their relationship to the growth of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):606–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.606-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard M., Downing J. F. Genetic and biochemical aspects of yeast sterol regulation involving 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Aug;125(2):415–420. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-2-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard M., Lees N. D., Burnett A. S., Parker R. A. Isolation and characterization of mevinolin resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):1071–1078. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. E., Moore R. L., O'Rear J., Rine J. Identifying mutations in duplicated functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: recessive mutations in HMG-CoA reductase genes. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):645–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. E., Thorsness M., Rine J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains two functional genes encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5563–5567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boll M., Löwel M., Berndt J. Effect of unsaturated fatty acids on sterol biosynthesis in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 5;620(3):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen M. K., Christiansen K., Jensen P. K., Behnke O. Isolation of lipid particles from baker's yeast. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80994-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULANEY E. L., STAPLEY E. O., SIMPF K. Studies on ergosterol production by yeasts. Appl Microbiol. 1954 Nov;2(6):371–379. doi: 10.1128/am.2.6.371-379.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. F., Burrows L. S., Bard M. The isolation of two mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae which demonstrate increased activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 16;94(3):974–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80996-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata S., Nishino T., Komori M., Katsuki H. Involvement of cytochrome P-450 in delta 22-desaturation in ergosterol biosynthesis of yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 16;103(1):272–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi A. Control of ergosterol biosynthesis in yeast. Existence of lipid inhibitors. J Biochem. 1970 Feb;67(2):219–227. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis T. L., Keesler G. A., Fenner G. P., Parks L. W. Pleiotropic mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae affecting sterol uptake and metabolism. Yeast. 1988 Jun;4(2):93–106. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. T., Parks L. W. Regulation of ergosterol biosynthesis and sterol uptake in a sterol-auxotrophic yeast. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3707–3711. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3707-3711.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. T., Rodriguez R. J., Lewis T. A., Parks L. W. Characteristics of sterol uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):981–985. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.981-985.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcireau C., Guilloton M., Karst F. In vivo effects of fenpropimorph on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and determination of the molecular basis of the antifungal property. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas R. O., Kerridge D. Correlation of inhibition of sterol synthesis with growth-inhibitory action of imidazole antimycotics in Candida albicans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Jan;23(1):7–19. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Nishino T., Katsuki H. Studies on the delta 5-desaturation in ergosterol biosynthesis in yeast. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):819–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto W. J., Lozano R., Nes W. R. Inhibition of sterol biosynthesis by ergosterol and cholesterol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 22;836(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. J., Parks L. W. Structural and physiological features of sterols necessary to satisfy bulk membrane and sparking requirements in yeast sterol auxotrophs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Smolowe A. F., Sullivan R. C., Barclay M. Separation of lipid classes by thin-layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Effect of ketoconazole in combination with other inhibitors of sterol synthesis on fungal growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):532–534. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. R., Parks L. W. Adaptation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to growth on cholesterol: selection of mutants defective in the formation of lanosterol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1437–1445. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. R., Parks L. W. An assessment of the specificity of sterol uptake and esterification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13048–13054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. R., Parks L. W. Metabolic interconversion of free sterols and steryl esters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):531–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.531-537.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. F., Rose M. E., Ellis S. W., England H., Kelly S. L. Defective sterol C5-6 desaturation and azole resistance: a new hypothesis for the mode of action of azole antifungals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1170–1175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91792-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Iwata K., Nagano M., Osumi M. Ultrastructure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae treated with econazole. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1981;30(4):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Aoyama Y. Interaction of azole antifungal agents with cytochrome P-45014DM purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 15;36(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]