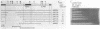Abstract
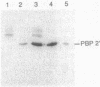
A region was identified on the methicillin resistance determinant (mec) isolated from Staphylococcus epidermidis and cloned into Staphylococcus carnosus which was responsible for a novel downregulation of the expression of methicillin resistance. The presence of this region reduced the overall expression of methicillin resistance and the synthesis of the mec-encoded penicillin-binding protein 2' (PBP 2') in S. carnosus. This region was located by Bal31 deletion mutagenesis upstream of the structural gene for PBP 2'. Deletions within this region resulted in higher levels of expression of methicillin resistance and increased levels of PBP 2' synthesis. We tentatively called this region mecR. Analysis of selected Mcr strains of Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis by Southern hybridization suggested that the natural occurrence of two types of mec resistance determinants differ by the presence or absence of mecR-specific sequences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis-Maino L., Berger-Bächi B., Weber H., Beck W. D., Kayser F. H. IS431, a staphylococcal insertion sequence-like element related to IS26 from Proteus vulgaris. Gene. 1987;59(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Barberis-Maino L., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. FemA, a host-mediated factor essential for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: molecular cloning and characterization. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00261186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B. Insertional inactivation of staphylococcal methicillin resistance by Tn551. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):479–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.479-487.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. Characterization of an isogenic set of methicillin-resistant and susceptible mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):697–701. doi: 10.1007/BF02013308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics in vivo produce penicillin-binding protein 2a. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1919–1924. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Increased amounts of a novel penicillin-binding protein in a strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus exposed to nafcillin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):325–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI111965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Hallander H. O. Transduction of penicillinase production and methicillin resistance-enterotoxin B production in strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis B., Matthews P. R., Stewart P. R. The expression in Staphylococcus aureus of cloned DNA encoding methicillin resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1465–1469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblum J., Hartman B. J., Novick R. P., Tomasz A. Conversion of a homogeneously methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus to heterogeneous resistance by Tn551-mediated insertional inactivation. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):714–718. doi: 10.1007/BF02013311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutz B., Götz F. Construction of Staphylococcus plasmid vector pCA43 conferring resistance to chloramphenicol, arsenate, arsenite and antimony. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madiraju M. V., Brunner D. P., Wilkinson B. J. Effects of temperature, NaCl, and methicillin on penicillin-binding proteins, growth, peptidoglycan synthesis, and autolysis in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1727–1733. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Katakura Y., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Enzymatic and nucleotide sequence studies of a kanamycin-inactivating enzyme encoded by a plasmid from thermophilic bacilli in comparison with that encoded by plasmid pUB110. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.413-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. R., Reed K. C., Stewart P. R. The cloning of chromosomal DNA associated with methicillin and other resistances in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1919–1929. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Nomura K., Doi M., Yoshida T. Production of low-affinity penicillin-binding protein by low- and high-resistance groups of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Tomasz A. Involvement of multiple genetic determinants in high-level methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):874–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.874-879.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara D. M., Harrington C. R., Reynolds P. E. Immunological detection of penicillin-binding protein 2' in clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Brown D. F. Penicillin-binding proteins of beta-lactam-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Effect of growth conditions. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi L., Tonin E., Cheng Y. R., Fontana R. Regulation of penicillin-binding protein activity: description of a methicillin-inducible penicillin-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):828–831. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song M. D., Wachi M., Doi M., Ishino F., Matsuhashi M. Evolution of an inducible penicillin-target protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by gene fusion. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesch W., Strässle A., Berger-Bächi B., O'Hara D., Reynolds P., Kayser F. H. Cloning and expression of methicillin resistance from Staphylococcus epidermidis in Staphylococcus carnosus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1494–1499. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Nonoguchi R., Matsuhashi M., Konno M. Expression and inducibility in Staphylococcus aureus of the mecA gene, which encodes a methicillin-resistant S. aureus-specific penicillin-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2882–2885. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2882-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]