Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (143.8 KB).
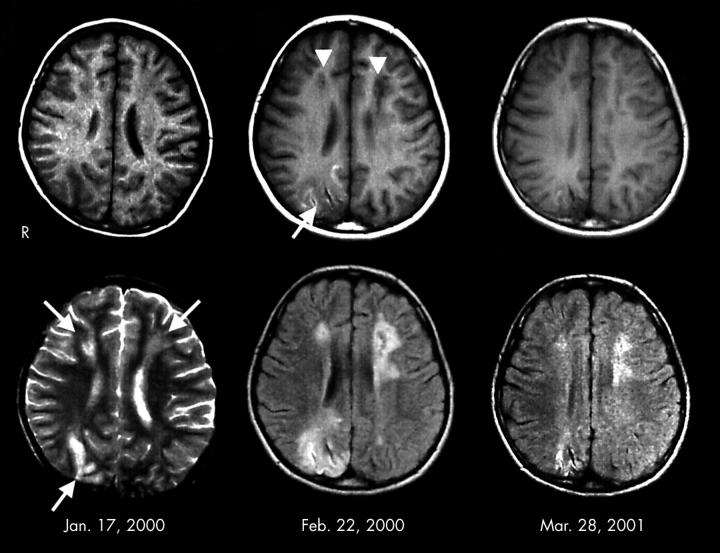
Figure 1 .
MRI findings. Left: MRI on admission. T2 weighted image (lower) showed high intensity areas in the deep white matter in the bilateral frontal lobes, and in the cortex and subcortex in the right occipital lobe (arrows). T1 weighted image (upper) showed low intensity areas in the corresponding place. Middle: MRI one month after admission. T1 weighted image (upper) showed cavity formation in the deep white matter in the bilateral frontal lobes (arrowheads). Abnormal low intensity was recognised in the cortex and subcortex in the right occipital lobe (arrow). Fluid attenuated inversion recovery image (lower) showed high intensity areas around the cavity formations. Right: MRI one year after discharge. The size of cavity and the extent of abnormal high intensity areas were remarkably reduced.