Abstract
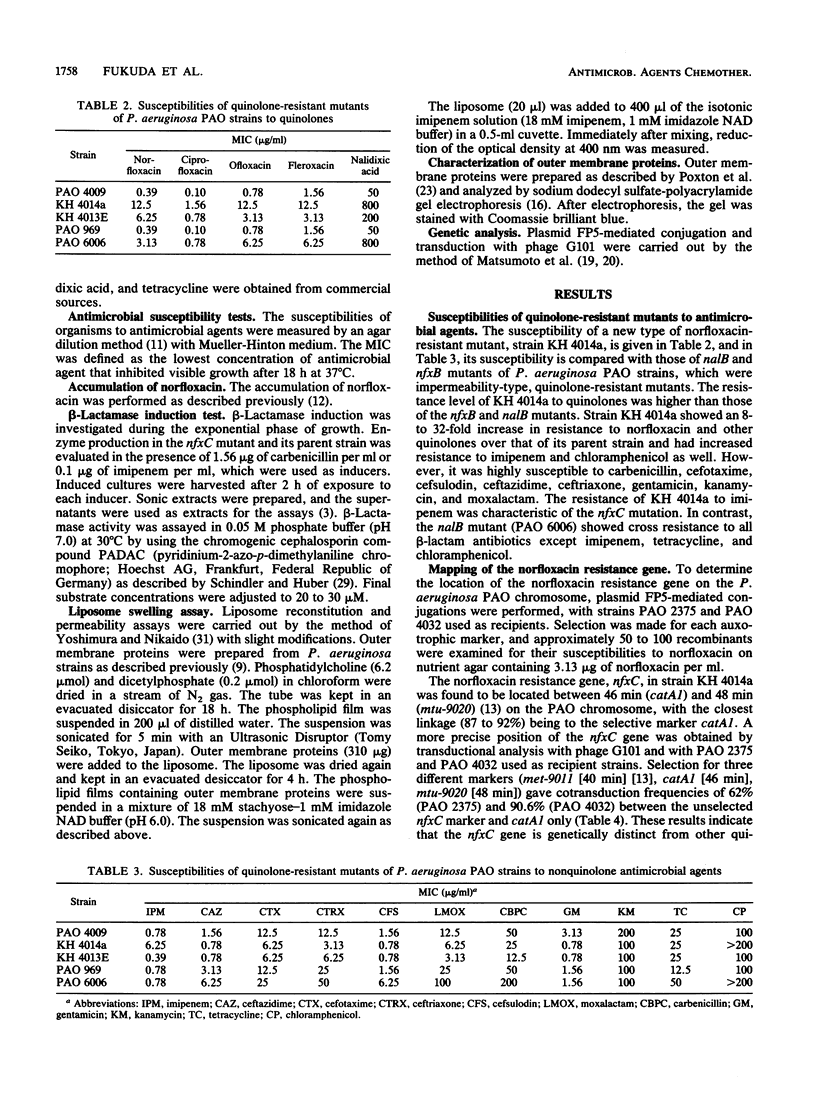
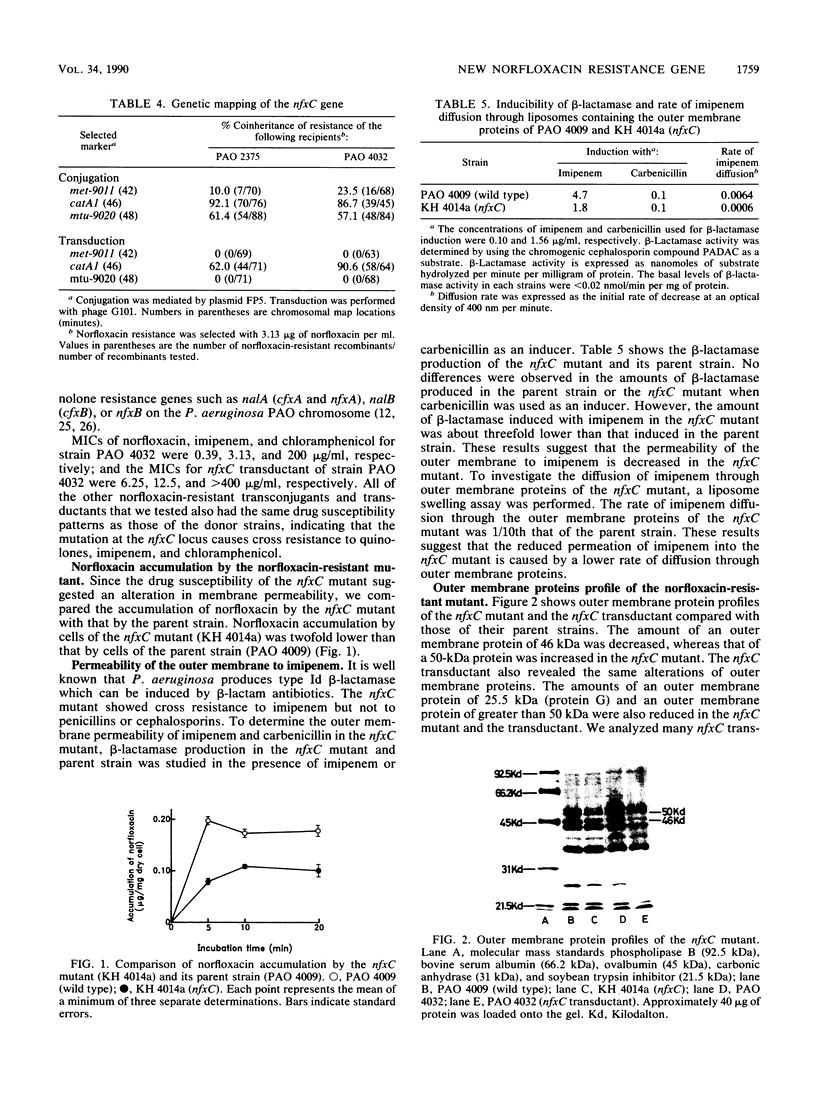
A new type of norfloxacin-resistant mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO was isolated. This mutant showed cross resistance to imipenem and chloramphenicol and hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics. The new norfloxacin resistance gene nfxC was mapped near catA (46 min) on the PAO chromosome. Norfloxacin accumulation was decreased in the nfxC mutant; furthermore, the rate of imipenem diffusion through the outer membrane of the nfxC mutant was lower than that of the parent strain. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of outer membrane proteins showed a decrease of a 46-kilodalton protein and an increase of a 50-kilodalton protein in the nfxC mutant. We conclude the nfxC is a new norfloxacin resistance gene that affects outer membrane permeability to quinolones and other antimicrobial agents.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama H., Fujimaki K., Sato K., Fujii T., Inoue M., Hirai K., Mitsuhashi S. Clinical isolate of Citrobacter freundii highly resistant to new quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):922–924. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama H., Sato K., Kato T., Hirai K., Mitsuhashi S. Norfloxacin resistance in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1640–1641. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa resulting from diminished expression of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberland S., Bayer A. S., Schollaardt T., Wong S. A., Bryan L. E. Characterization of mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated in vitro and in vivo during experimental endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):624–634. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimaki K., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Sato K., Inoue Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Quinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Sato K., Fujii T., Hirai K., Inoue M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Some properties of subunits of DNA gyrase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and its nalidixic acid-resistant mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2322–2325. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2322-2325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Tzouvelekis L. S., Makris A., Kotsifaki H. Outer membrane alterations in multiresistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa selected by ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):124–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. J., Drusano G. L., Mobley H. L. Emergence of resistance to imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1892–1896. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Nakazawa T., Ohta S., Terawaki Y. Chromosomal locations of catA, pobA, dcu and chu genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1981 Dec;38(3):251–266. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ohta S., Kobayashi R., Terawaki Y. Chromosomal location of genes participating in the degradation of purines in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 29;167(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00266910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michéa-Hamzehpour M., Auckenthaler R., Regamey P., Pechère J. C. Resistance occurring after fluoroquinolone therapy of experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1803–1808. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okii M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mapping of the gene specifying aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase II on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.643-649.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Haas D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO to nalidixic acid and low levels of beta-lactam antibiotics: mapping of chromosomal genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):242–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Watanakunakorn C. Emergence of resistance to beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and quinolones during combination therapy for infection due to Serratia marcescens. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):617–619. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue Y., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of DNA gyrase from a fluoroquinolone-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studemeister A. E., Quinn J. P. Selective imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with diminished outer membrane permeability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1267–1268. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



