Abstract
Background and Aims: The measurement of airway resistance using the interrupter technique (Rint) is feasible in preschool children and other subjects unable to undertake spirometry. This makes it potentially useful for the measurement of lung function in these groups. Commercial devices use different algorithms to measure pressure and flow from which Rint is derived. This study provides normative values for British children using devices from a single manufacturer.
Methods: Rint was measured in 236 healthy children of three ethnic groups (Afro-Caribbean and black African, Bangladeshi, and white British) aged 2–10 years using Micro Medical devices. Software in the devices calculated Rint from pressure measured by the two point, back extrapolation method from the pressure transient during valve closure, with flow measured just before valve closure.
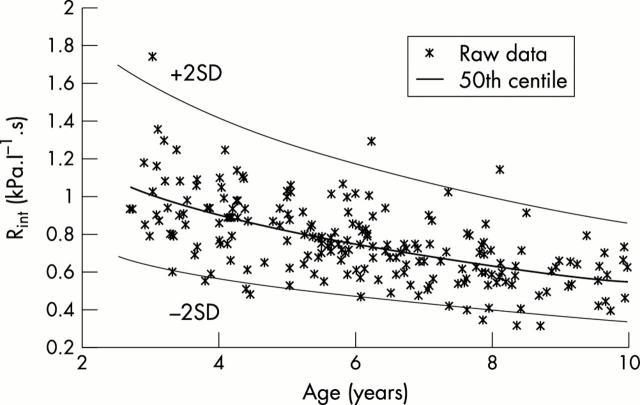
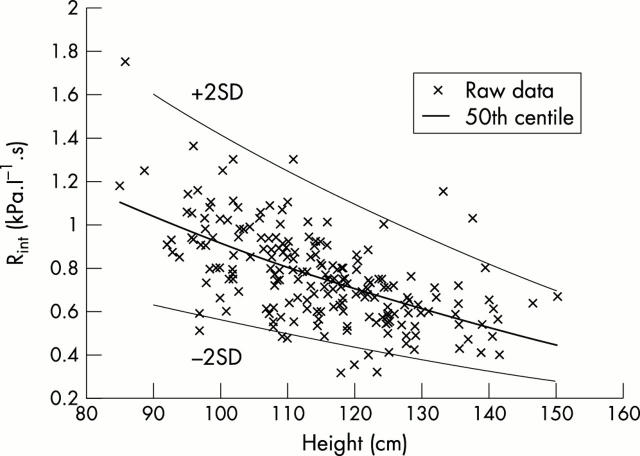
Results: Rint is related to both age and height, but when age is allowed for there is not a significant relation with height. Neither gender nor any of the ethnicities studied was significantly related to Rint.
Discussion: These measurements in healthy children using this technique may be used as reference data for similar populations.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (180.7 KB).
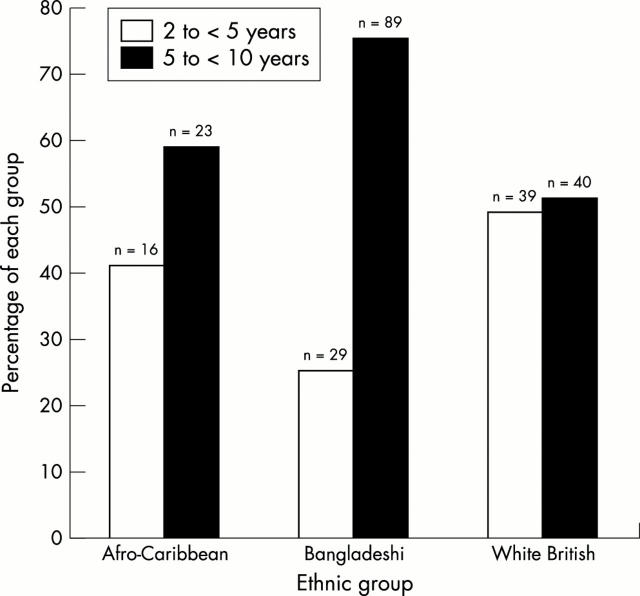
Figure 1 .
Ethnicity and age.
Figure 2 .
Measurements of Rint related to age.
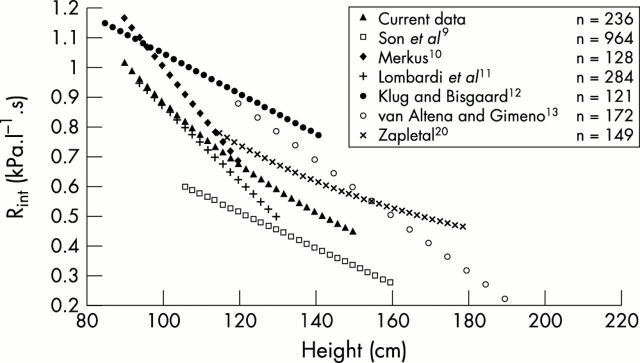
Figure 3 .
Measurements of Rint related to height.
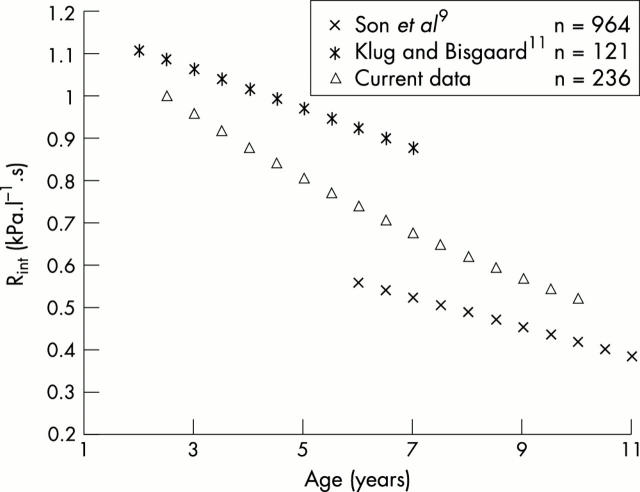
Figure 4 .
Published regression lines for age.
Figure 5 .
Published regression lines for height.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisgaard H., Klug B. Lung function measurement in awake young children. Eur Respir J. 1995 Dec;8(12):2067–2075. doi: 10.1183/09031936.95.08122067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge P. D., Lee H., Silverman M. A portable device based on the interrupter technique to measure bronchodilator response in schoolchildren. Eur Respir J. 1996 Jul;9(7):1368–1373. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09071368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge P. D., McKenzie S. A. Airway resistance measured by the interrupter technique: expiration or inspiration, mean or median? Eur Respir J. 2001 Mar;17(3):495–498. doi: 10.1183/09031936.01.17304950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge P. D., McKenzie S. A. Bronchodilator responsiveness testing in young children. Arch Dis Child. 2001 Jun;84(6):525–525. doi: 10.1136/adc.84.6.525n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge P. D., Ranganathan S., McKenzie S. A. Measurement of airway resistance using the interrupter technique in preschool children in the ambulatory setting. Eur Respir J. 1999 Apr;13(4):792–796. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.13d16.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter E. R. It is time to consider standardizing the interrupter technique. Eur Respir J. 1997 Jun;10(6):1428–1429. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10061428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter E. R., Stecenko A. A., Pollock B. H., Jaeger M. J. Evaluation of the interrupter technique for the use of assessing airway obstruction in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1994 Apr;17(4):211–217. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child F., Clayton S., Davies S., Fryer A. A., Jones P. W., Lenney W. How should airways resistance be measured in young children: mask or mouthpiece? Eur Respir J. 2001 Jun;17(6):1244–1249. doi: 10.1183/09031936.01.00089501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowienczyk P. J., Lawson C. P., Lane S., Johnson R., Wilson N., Silverman M., Cochrane G. M. A flow interruption device for measurement of airway resistance. Eur Respir J. 1991 May;4(5):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezateux C., Stocks J., Dundas I., Fletcher M. E. Impaired airway function and wheezing in infancy: the influence of maternal smoking and a genetic predisposition to asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Feb;159(2):403–410. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.159.2.9712029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. V., Cole T. J., Chinn S., Jones P. R., White E. M., Preece M. A. Cross sectional stature and weight reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995 Jul;73(1):17–24. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy M. J. The disciplining of medical data. Br Med Bull. 1968 Sep;24(3):210–214. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug B., Bisgaard H. Specific airway resistance, interrupter resistance, and respiratory impedance in healthy children aged 2-7 years. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1998 May;25(5):322–331. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0496(199805)25:5<322::aid-ppul6>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi E., Sly P. D., Concutelli G., Novembre E., Veneruso G., Frongia G., Bernardini R., Vierucci A. Reference values of interrupter respiratory resistance in healthy preschool white children. Thorax. 2001 Sep;56(9):691–695. doi: 10.1136/thorax.56.9.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. A., Bridge P. D., Healy M. J. Airway resistance and atopy in preschool children with wheeze and cough. Eur Respir J. 2000 May;15(5):833–838. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.15e04.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. A., Bridge P. D., Pao C. S. Lung function tests for pre-school children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2001 Mar;2(1):37–45. doi: 10.1053/prrv.2000.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkus P. J., Mijnsbergen J. Y., Hop W. C., de Jongste J. C. Interrupter resistance in preschool children: measurement characteristics and reference values. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001 May;163(6):1350–1355. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.6.2005076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. G., Bisgaard H. Lung function response to cold air challenge in asthmatic and healthy children of 2-5 years of age. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Jun;161(6):1805–1809. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.6.9905098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald-Mammosser M., Llerena C., Speich J. P., Donata L., Lonsdorfer Measurements of respiratory system resistance by the interrupter technique in healthy and asthmatic children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997 Aug;24(2):78–85. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0496(199708)24:2<78::aid-ppul2>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phagoo S. B., Wilson N. M., Silverman M. Evaluation of a new interrupter device for measuring bronchial responsiveness and the response to bronchodilator in 3 year old children. Eur Respir J. 1996 Jul;9(7):1374–1380. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09071374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quanjer P. H., Stocks J., Polgar G., Wise M., Karlberg J., Borsboom G. Compilation of reference values for lung function measurements in children. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1989 Mar;4:184S–261S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocks J., Henschen M., Hoo A. F., Costeloe K., Dezateux C. Influence of ethnicity and gender on airway function in preterm infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Dec;156(6):1855–1862. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.6.9607056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig L. M., Chernick V., Wood R., Farrell P., Mellins R. B. Standardization of lung function testing in children. Proceedings and Recommendations of the GAP Conference Committee, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):668–676. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapletal A., Samanek M., Paul T. Upstream and total airway conductance in children and adolescents. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1982 Jan-Feb;18(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Altena R., Gimeno F. Respiratory resistance measured by flow-interruption in a normal population. Respiration. 1994;61(5):249–254. doi: 10.1159/000196347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plas K., Vooren P. The "opening" interruptor. A new variant of a technique for measuring respiratory resistance. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;63(5):449–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]