Abstract
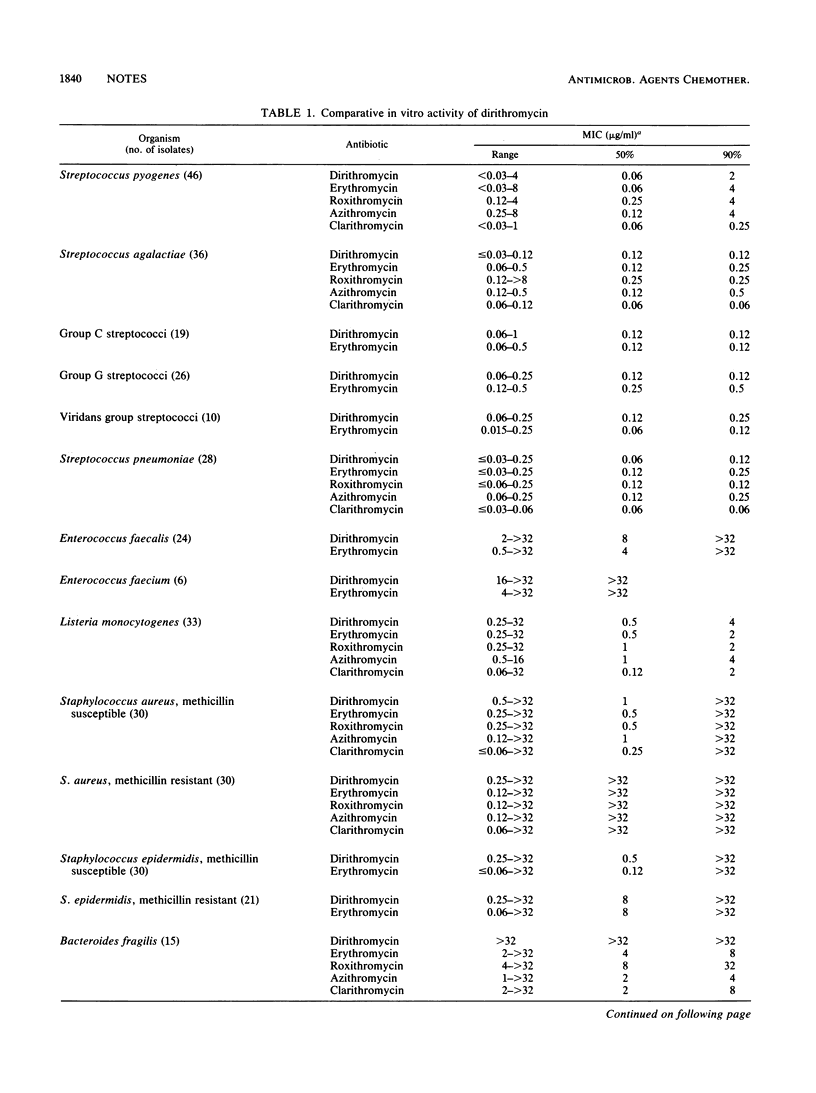
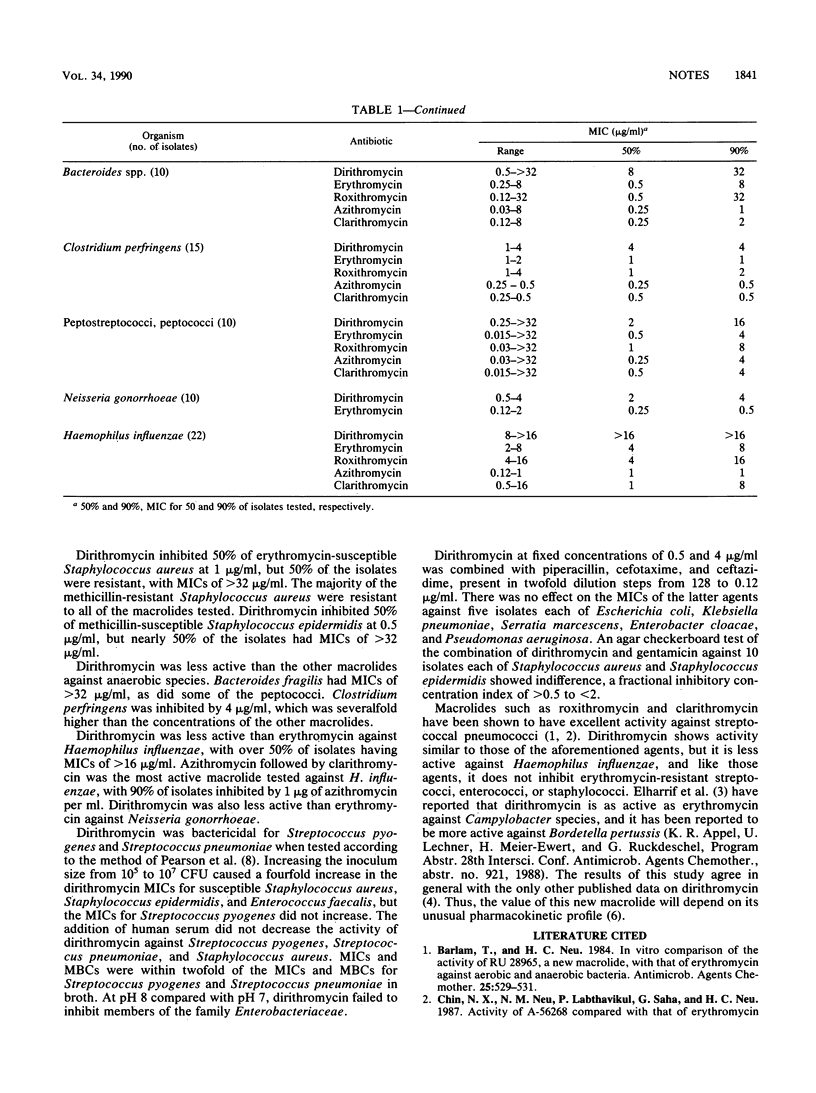
Dirithromycin inhibited Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and other hemolytic streptococci at concentrations of less than or equal to 0.03 to 0.12 micrograms/ml, with 90% inhibition at 0.12 micrograms/ml, which is comparable to results using erythromycin. Group A streptococci, listeriae, and enterococci resistant to erythromycin were resistant to dirithromycin. Erythromycin-susceptible staphylococci were inhibited by 0.5 micrograms/ml, but for erythromycin-resistant isolates MICs were greater than or equal to 8 micrograms/ml. For Haemophilus influenzae, MICs were greater than or equal to 8 micrograms/ml, two- to fourfold greater than for erythromycin. The activity of dirithromycin against staphylococci and streptococci was not decreased by the addition of human serum.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlam T., Neu H. C. In vitro comparison of the activity of RU 28965, a new macrolide, with that of erythromycin against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):529–531. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elharrif Z., Mégraud F., Marchand A. M. Susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to macrolides and related compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):695–697. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Hensey D. M., Beyer J. M., Vojtko C., McDonald E. J., Fernandes P. B. Comparative in vitro activities of new 14-, 15-, and 16-membered macrolides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1710–1719. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirst H. A., Sides G. D. New directions for macrolide antibiotics: pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1419–1422. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirst H. A., Sides G. D. New directions for macrolide antibiotics: structural modifications and in vitro activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1413–1418. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Wilson W. R. Erythromycin: a microbial and clinical perspective after 30 years of clinical use (2). Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Apr;60(4):271–278. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60322-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


