Abstract
Aims: To ascertain whether the reduction in nasopharyngeal carriage of vaccine serotypes induced by pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PnCV) administered to infants persists beyond the age of 2 years.
Methods: Non-randomised, unblinded controlled study of 2–5 year old children who had received three doses of heptavalent PnCV (7VPnCV) in infancy and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at 13 months, and unimmunised controls. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken in summer (150 vaccinated subjects, 126 controls) and winter (143 vaccinated subjects, 188 controls). The swabs were cultured and serotyped for Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Results: Carriage rates (vaccinated subjects: 24.7% and 43.4%; controls: 27.0% and 41.0%, in summer and winter respectively) and carriage of vaccine serotypes (subjects: 10.0% and 30.0%; controls: 13.5% and 31.5%, in summer and winter respectively) were similar in the two groups.
Conclusions: Effects of vaccination in infancy on rates of nasal carriage of pneumococcus and serotype replacement in children living in a largely unvaccinated population are no longer evident by 2–5 years of age.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (130.5 KB).
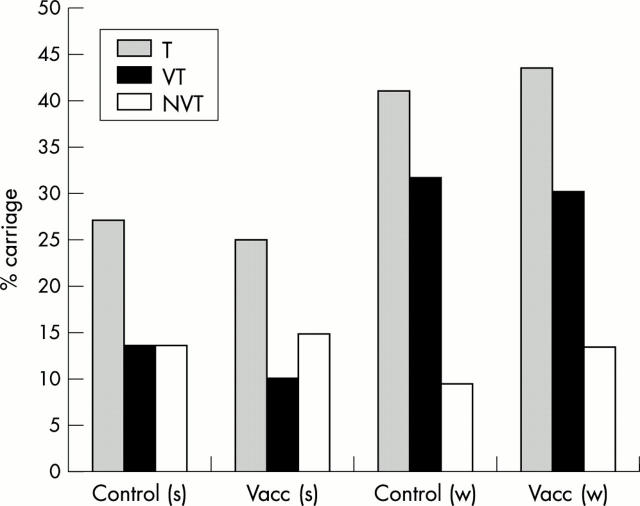
Figure 1 .
Pneumococcal carriage in summer (s) and winter (w) in control and vaccinated (vacc) subjects. T, total carriage; VT, carriage of vaccine serotypes; NVT, carriage of non-vaccine serotypes.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour M. L., Booy R., Crook D. W., Griffiths H., Chapel H. M., Moxon E. R., Mayon-White D. Haemophilus influenzae type b carriage and immunity four years after receiving the Haemophilus influenzae oligosaccharide-CRM197 (HbOC) conjugate vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1993 Jun;12(6):478–484. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199306000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum M. D., Dagan R., Mendelman P. M., Pinsk V., Giordani M., Li S., Bohidar N., McNeely T. B. A comparison of multiple regimens of pneumococcal polysaccharide-meningococcal outer membrane protein complex conjugate vaccine and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in toddlers. Vaccine. 2000 May 8;18(22):2359–2367. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo S., Seymour L., Morris R., Quataert S., Lockhart S., Cartwright K., Finn A. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine administered combined with a haemophilus influenzae type B conjugate vaccine in United Kingdom infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000 Sep;19(9):854–862. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200009000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo S., Zhang Q., Seymour L., Akhtar S., Finn A. Primary and booster salivary antibody responses to a 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in infants. J Infect Dis. 2000 Aug 31;182(4):1260–1263. doi: 10.1086/315834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan R., Fraser D. Conjugate pneumococcal vaccine and antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae: herd immunity and reduction of otitis morbidity. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000 May;19(5 Suppl):S79–S88. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200005001-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan R., Melamed R., Muallem M., Piglansky L., Greenberg D., Abramson O., Mendelman P. M., Bohidar N., Yagupsky P. Reduction of nasopharyngeal carriage of pneumococci during the second year of life by a heptavalent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1996 Dec;174(6):1271–1278. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagan R., Muallem M., Melamed R., Leroy O., Yagupsky P. Reduction of pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in early infancy after immunization with tetravalent pneumococcal vaccines conjugated to either tetanus toxoid or diphtheria toxoid. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997 Nov;16(11):1060–1064. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199711000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J., Kilpi T., Palmu A., Jokinen J., Haapakoski J., Herva E., Takala A., Käyhty H., Karma P., Kohberger R. Efficacy of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against acute otitis media. N Engl J Med. 2001 Feb 8;344(6):403–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200102083440602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar F., Friedland I. R., McCracken G. H., Jr Dynamics of nasopharyngeal colonization by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999 Jul;18(7):638–646. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199907000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Converse G. M., 3rd, Dillon H. C., Jr Epidemiologic studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants: acquisition, carriage, and infection during the first 24 months of life. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):923–933. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Turner M. E., Dillon H. C., Jr Epidemiologic studies of Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants. The effects of season and age on pneumococcal acquisition and carriage in the first 24 months of life. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Oct;116(4):692–703. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbelle N., Huebner R. E., Wasas A. D., Kimura A., Chang I., Klugman K. P. Immunogenicity and impact on nasopharyngeal carriage of a nonavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1999 Oct;180(4):1171–1176. doi: 10.1086/315009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien K. L., Bronsdon M. A., Dagan R., Yagupsky P., Janco J., Elliott J., Whitney C. G., Yang Y. H., Robinson L. G., Schwartz B. Evaluation of a medium (STGG) for transport and optimal recovery of Streptococcus pneumoniae from nasopharyngeal secretions collected during field studies. J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(3):1021–1024. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.1021-1024.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obaro S. K., Adegbola R. A., Banya W. A., Greenwood B. M. Carriage of pneumococci after pneumococcal vaccination. Lancet. 1996 Jul 27;348(9022):271–272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)65585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway E. J., Tremlett C. H., Allen K. D. Capsular serotypes and antibiotic sensitivity of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from primary-school children. J Infect. 1995 May;30(3):245–251. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(95)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen R. K., Kilpi T. M., Kaijalainen T. H., Herva E. E., Takala A. K. Nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae in Finnish children younger than 2 years old. J Infect Dis. 2001 Jul 6;184(4):451–459. doi: 10.1086/322048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takala A. K., Eskola J., Leinonen M., Käyhty H., Nissinen A., Pekkanen E., Mäkelä P. H. Reduction of oropharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) in children immunized with an Hib conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):982–986. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]