Abstract
PCAF plays a role in transcriptional activation, cell-cycle arrest, and cell differentiation in cultured cells. PCAF contributes to transcriptional activation by acetylating chromatin and transcription factors through its intrinsic histone acetylase activity. In this report, we present evidence for the in vivo function of PCAF and the closely related PCAF-B/GCN5. Mice lacking PCAF are developmentally normal without a distinct phenotype. In PCAF null-zygous mice, protein levels of PCAF-B/GCN5 are drastically elevated in lung and liver, where PCAF is abundantly expressed in wild-type mice, suggesting that PCAF-B/GCN5 functionally compensates for PCAF. In contrast, animals lacking PCAF-B/GCN5 die between days 9.5 and 11.5 of gestation. Normally, PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNA is expressed at high levels already by day 8, whereas PCAF mRNA is first detected on day 12.5, which may explain, in part, the distinct knockout phenotypes. These results provide evidence that PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 play distinct but functionally overlapping roles in embryogenesis.
Human (h)PCAF (p300/CBP associated factor; ref. 1) is a transcriptional coactivator with intrinsic histone acetylase activity, which contributes to transcriptional activation by modifying chromatin and transcriptional factors (for reviews, see refs. 2–5). Although an exact mechanism of how acetylation of histones contribute to transcriptional activation has not been clarified, it has been thought that acetylation of nucleosomal histones leads to relaxation of chromatin structure such that various transcription factors can gain access and function onto chromatin DNA. Although histones are physiologically relevant substrates for PCAF, PCAF also acetylates transcriptional activators p53 (6, 7) and MyoD (8), as originally demonstrated by p300 acetylase (9), and stimulates DNA binding.
PCAF is present in a stable multisubunit complex consisting of more than 20 distinct polypeptides, whose molecular masses range from 10 to 400 kDa (10). Although recombinant PCAF per se cannot efficiently acetylate histones in nucleosomal contexts, the PCAF complex that we purified can, strongly suggesting that subunits in the PCAF complex could stimulate acetylation of relevant substrates (10). Moreover, characterization of subunits of the PCAF complex has revealed that they are TATA box-binding protein-associated factors (TAFs), which were originally found in TFIID; TAF-related PAF65α and β; human homologs of yeast transcriptional cofactors ADA2, ADA3, and Spt3 as well as PAF400, which exhibits sequence similarity to members of the ATM superfamily (10, 11). Importantly, TAF80, TAF-like PAF65α, and TAF20/15 bear sequence similarities to core histones (10) and thus may form a histone octamer-like structure in the PCAF complex, as has been proposed for TFIID (12–14). Furthermore, TAF-like PAF65β has WD40-repeats, motifs often found in factors that target chromatin (10).
The second family member is hPCAF-B/GCN5 (5, 15). PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 are well conserved over their entire sequence, and both exhibit p300/CBP binding and intrinsic histone acetylase activities (ref. 1 and unpublished observations). Further, both are present in the complexes with the indistinguishable subunit compositions (10). Thus, it has been considered that PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 could be redundant. However, herein, we show somewhat unexpected results showing distinct phenotypes in PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 knockout mice.
Materials and Methods
Gene Targeting.
Genomic clones for murine (m)PCAF and mPCAF-B/GCN5 were isolated from a bacterial artificial chromosome mouse embryonic stem (ES) genomic library (strain, 129/SVJ; Genome Systems, St. Louis). The targeting vectors were constructed by subcloning the genomic fragments into a plasmid pPNT (16), as illustrated in Figs. 1A and 2A. ES cell clones, stably transfected with the NotI-linearized targeting vectors, were obtained with a positive-negative selection strategy. Homologous recombinants were identified by Southern blot analysis, as described in Figs. 1B and 2B. The positive ES clones were confirmed further by hybridization with a neo gene probe. Two independent, targeted ES clones were injected into C57BL/6 mouse blastocysts and implanted into foster mothers, resulting in several chimeric offspring. Chimeras were bred with CD1 or C57BL/6 females to produce heterozygous mice. Although CD1 mice were used for all experiments in this paper, the same phenotypes were reproduced in C57BL/6 mice.
Figure 1.
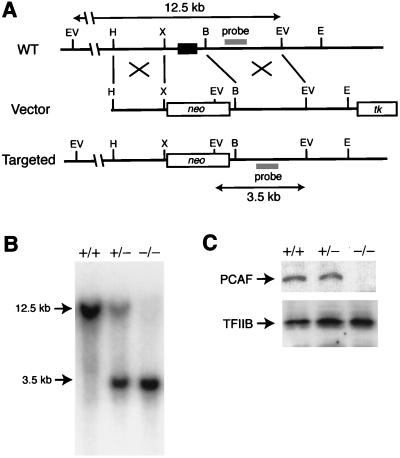
Targeted disruption of the PCAF locus. (A) Targeting strategy for PCAF gene. The configuration of the wild-type (WT) allele is shown (Top). The exon encoding the N terminus of PCAF (shown by a box) was replaced by a neomycin resistance gene cassette in the targeting vector (Middle). The thymidine kinase (tk) gene was used for negative selection. The structure of the targeted allele is shown (Bottom). The location of the probe used for the Southern blot in B is indicated. Restriction sites: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; EV, EcoRV; H, HindIII; X, XhoI. kb, kilobase. (B) Southern blot of EcoRV-digested genomic DNAs isolated from offspring of heterozygous mice. The probe hybridizes with 12.5- and 3.5-kb fragments in the wild-type and targeted allele, respectively. Typical results obtained from PCAF+/+, PCAF+/−, and PCAF−/− mice are shown. (C) Immunoblot of protein extracts from lung of PCAF+/+, PCAF+/−, and PCAF−/− embryos. PCAF could not be detected in PCAF−/− mice (Upper). As an internal control, TFIIB was also detected (Lower).
Figure 2.
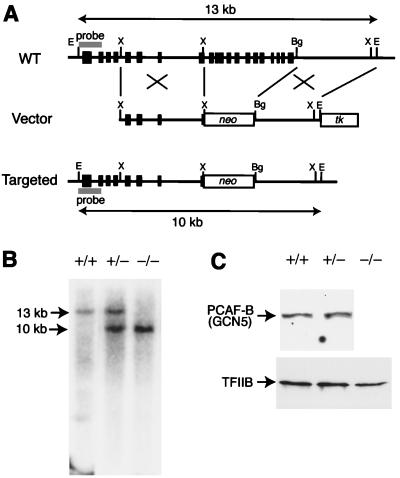
Targeted disruption of the PCAF-B/GCN5 locus. (A) Targeting strategy for PCAF-B/GCN5 gene. The configuration of the wild-type (WT) allele is shown (Top). The genomic region containing exons encoding the 3′ terminus of PCAF-B/GCN5 (shown by boxes) was replaced by a neomycin resistance gene cassette in the targeting vector (Middle), yielding the targeted allele (Bottom) by homologous recombination. Restriction sites: Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; X, XhoI. (B) Southern blot of EcoRI-digested genomic DNAs isolated from offspring of heterozygous mice. The probe hybridizes with 13- and 10-kb fragments in the wild-type and targeted allele, respectively. (C) Immunoblot of protein extracts from PCAF-B/GCN5+/+, PCAF-B+/−, and PCAF-B−/− embryos. PCAF-B/GCN5 could not be detected in PCAF-B−/− embryos (Upper). Note that an immunoreactive band around 55 kDa could not be detected. Further characterization would be required to resolve the issue of the N-terminally truncated form of mouse PCAF-B/GCN5. As an internal control, TFIIB was also detected (Lower).
Antibodies.
Affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibodies against hPCAF and hPCAF-B/GCN5 were used for immunoblot analysis. Amino acids 583–832 of hPCAF and 362–837 of hPCAF-B/GCN5, the region displaying 94% and 97% identity between human and mouse, were expressed in and purified from Escherichia coli and used as antigens to raise antibodies. Although antibodies are specific to respective proteins, anti-PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 antibodies were preincubated with PCAF-B/GCN5 and PCAF, respectively, when required.
In Situ Hybridization Analysis.
The cDNA fragments used as hybridization probes correspond to amino acids 87–177 of mPCAF and 722–822 of mPCAF-B/GCN5. Antisense and sense RNA probes were synthesized by in vitro transcription in the presence [35S]UTP. The antisense probes are considered specific, because a single band corresponding to the respective mRNA was detected by Northern blot analysis of total mouse poly(A)+ RNAs. In situ hybridization analysis was performed by standard procedures (17).
Results and Discussion
Targeted Disruption of the PCAF Gene in Mice.
We isolated mouse homologs of hPCAF and hPCAF-B/GCN5 by screening mouse cDNA libraries with the corresponding human clones as probes. Like the human factors, mPCAF and mPCAF-B/GCN5 are highly conserved over their entire sequence, showing 81% sequence similarity (ref. 18 and unpublished data). Subsequently, mouse genomic clones for mPCAF and mPCAF-B/GCN5 were isolated.
Our targeting strategy for the PCAF gene is shown in Fig. 1A. The exon encoding the N terminus of PCAF (amino acids 1–88) was replaced with a neo gene cassette by homologous recombination in ES cells. Targeted ES cell clones were identified by Southern blot analysis of EcoRV-digested genomic DNA with the probe that is depicted in Fig. 1A (clone identification data not shown). The targeted alleles were confirmed by Southern blot analysis of ApaI–SpeI-digested genomic DNA with the neo gene as a probe, yielding a 6-kb positive band (data not shown). Germ-line-transmitting chimeric mice were generated by blastocyst microinjection and were used to breed heterozygous mutant mice. Genotyping of 160 offspring of heterozygous mice revealed that PCAF+/+, PCAF+/−, and PCAF−/− mice were born at a close to expected ratio (Table 1 and Fig. 1A). Homozygous mice showed no obvious phenotypic debilities, gained weight at a rate indistinguishable from that of wild-type and heterozygous littermates, and reached sexual maturity at a comparable age. In the analysis of PCAF homozygous mice, no PCAF protein was detected by immunoblot analysis (Fig. 1C).
Table 1.
Genotyping of offspring from matings of PCAF heterozygous mice
| Age of offspring | Genotype of offspring (no. of mice)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-type (+/+) | Heterozygous (+/−) | Homozygous (−/−) | |
| 3 weeks | 30 | 83 | 47 |
The genotype of each offspring of PCAF heterozygous mice was determined by Southern blotting as shown in Fig. 2B.
Targeted Disruption of the PCAF-B/GCN5 Gene in Mice.
Next, we performed knockout of PCAF-B/GCN5 gene. The targeting strategy is to delete the region that contains exons encoding the C terminus (amino acids 472–830) of PCAF-B/GCN5, which are located within the C-terminal, GCN5-related region of PCAF-B/GCN5 (Fig. 2A). Therefore, this strategy could inactivate both the full-length and the N-terminally truncated PCAF-B/GCN5 even if the transcript encoding the short form of PCAF-B/GCN5 is synthesized from its own promoter. Gene targeting of PCAF-B/GCN5 was performed in a manner similar to PCAF targeting. Heterozygous PCAF-B/GCN5 mutants were born at the expected ratio, grew normally, and reached sexual maturity at an age comparable to that of wild-type mice. However, in contrast to PCAF knockout mice, genotyping of 98 offspring of heterozygous PCAF-B+/− mice revealed that the null-zygous PCAF-B/GCN5 mutation results in embryonic lethality (Table 2).
Table 2.
Genotyping of offspring from matings of PCAF-B/GCN5 heterozygous mice
| Age of offspring | Genotype of
offspring (no. of mice)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-type (+/+) | Heterozygous (+/−) | Homozygous (−/−) | |
| 3 weeks | 37 | 61 | 0 |
| E9.5* | 12 | 42 | 16 |
The genotype of each offspring of PCAF-B/GCN5 heterozygous mice was determined by Southern blotting as shown in Fig. 3B.
E, embryonic day.
Although most PCAF-B−/− embryos were still alive at E9.5 judging from their heartbeat, they died before E11.5 in utero. Immunoblot analyses of E9.5 embryos are shown in Fig. 2C. The 100-kDa protein that corresponds to PCAF-B/GCN5 was detected in wild-type and heterozygous embryos. No significant difference was observed in the levels of PCAF-B/GCN5 between wild-type and heterozygous embryos, whereas PCAF-B/GCN5 protein could not be detected in PCAF-B/GCN5−/− embryos.
In PCAF-B/GCN5 null-zygous embryos, blood vessels in the yolk sac were poorly developed at E9.5 when compared with those of wild-type and heterozygous littermates. The yolk sacs of wild-type and heterozygous embryos had well developed, branching vitelline vessels with smooth contours, whereas the vitelline vessels of PCAF-B/GCN5−/− embryos seemed to have disintegrated. Moreover, the contours of the vessels looked unclear, and the connections of vessels were poorly formed in PCAF-B/GCN5−/− embryos (data not shown).
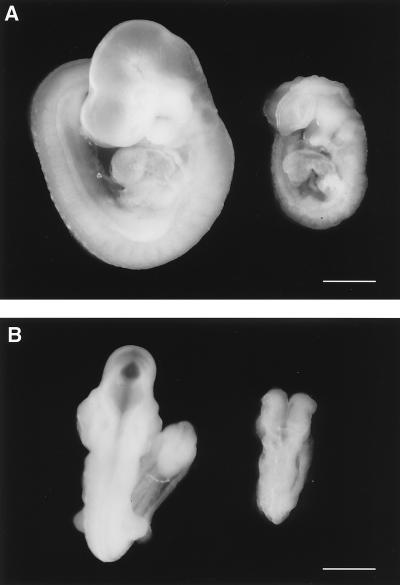
Although the wild-type and heterozygous mutant embryos were indistinguishable by their appearance (data not shown), the homozygous mutant embryos were significantly smaller and developmentally retarded (Fig. 3). Some PCAF-B−/− embryos showed hemorrhage in the central nervous system (data not shown). Although the homozygous mutant embryos had completed an embryonic process referred to as “turning,” their development seemed to be arrested at ≈E8.5–E9.0, judging from their size and the defect in neural tube closure.
Figure 3.
Developmental retardation of PCAF-B/GCN5−/− embryos. Lateral (A) and dorsal (B) views of wild-type (Left) and homozygous (Right) littermates on E9.5. (Bar = 0.5 mm.)
Embryonic Lethality of PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 Compound Null-Zygous Animals.
Although PCAF−/− mice display no obvious phenotype, we expect a role of PCAF in the PCAF-B/GCN5 null-zygous background. PCAF-B/GCN5+/− and PCAF−/− compound mutant mice were mated to obtain PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 compound null-zygous animals. Embryos with a compound null-zygous genotype were not found at E9.5, suggesting that they had been adsorbed at an earlier stage. To support this view, at E7.5, almost a quarter of the embryos had serious growth defects (data not shown). Although the genotypes of these growth-defective embryos could not be identified because of our technical limitations, they are likely to be PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 compound null-zygous embryos, because the size of PCAF-B/GCN5−/− embryos is indistinguishable from that of wild-type embryos at E7.5. These results indicate that both PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 play roles during embryogenesis, but neither is required at a very early stage of embryogenesis.
Overproduction of PCAF-B/GCN5 in PCAF Null-Zygous Mice.
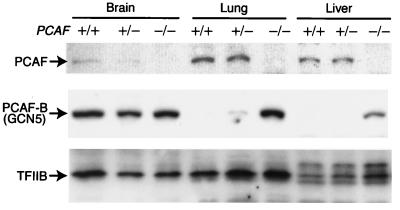
The lack of obvious phenotypic differences in PCAF knockout mice suggests that PCAF-B/GCN5 functionally compensates for the missing PCAF. To understand such a compensatory mechanism, we determined levels of PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 in various mutant mice (Fig. 4). Importantly, in PCAF null-zygous mice, PCAF-B/GCN5 protein was drastically overproduced in lung and liver, whereas in wild-type mice PCAF is dominantly expressed in such tissues. In brain, on the other hand, where PCAF is poorly expressed in wild-type mice, no obvious change in PCAF-B/GCN5 levels was observed. These results strongly suggest that PCAF-B/GCN5 functionally compensates for the missing PCAF by up-regulating PCAF-B/GCN5 expression. On the other hand, PCAF-B/GCN5 is down-regulated in PCAF-overexpressing HeLa cells (5). Therefore, the protein level of PCAF-B/GCN5 is exquisitely regulated and able to keep the total level of PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 constant. This mechanism contrasts with the regulatory mode of the p300 and cbp genes, which encode the closely related coactivators p300 and CBP. In these genes, loss of one allele results in decrease in the protein level, causing severely compromised phenotypes (19, 20).
Figure 4.
Overproduction of PCAF-B/GCN5 in PCAF null-zygous mice. Immunoblot analyses of protein extracts from brain, lung, and liver of PCAF+/+, PCAF+/−, and PCAF−/− mice were performed. No PCAF was detected in tissues isolated from PCAF−/− mice (Top), whereas PCAF-B/GCN5 was significantly up-regulated in lung and liver of PCAF−/− mice (Middle). TFIIB levels were determined as an internal control (Bottom).
Distinct Expression Profiles Between PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNA During Embryogenesis.
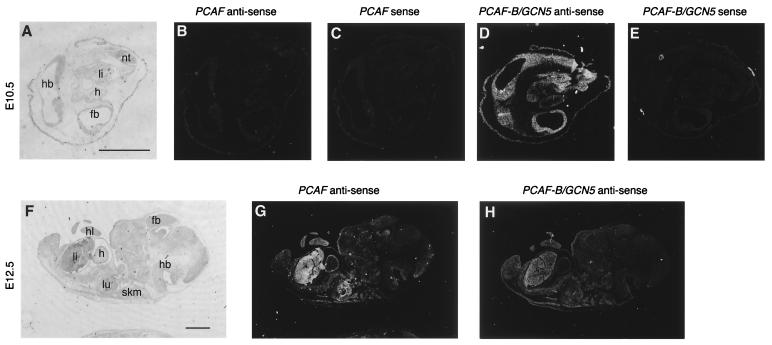
Although no obvious phenotypic difference in PCAF knockout mice could be explained from the overexertion of PCAF-B/GCN5 in the PCAF null-zygous mice, it is still unclear why PCAF cannot compensate for missing PCAF-B/GCN5. To address this problem, we determined expression profiles of PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 in wild-type mouse embryos by in situ analysis. PCAF mRNA was not detectable at E8, although it was detected in maternal decidua (data not shown). In contrast, PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNA was detected in all embryonic and extraembryonic tissues at this stage (data not shown). PCAF mRNA was still not detectable in E10.5 embryos (Fig. 5 B and C), whereas PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNA was generally expressed (Fig. 5 D and E); PCAF mRNA was first detected in E12.5 embryos, expression being widespread, with an elevated abundance in liver, heart, hind limb, and skeletal muscle (Fig. 5G). PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNA continued to be expressed on E12.5 and was widespread (Fig. 5H). These results suggest that, especially in early embryogenesis, PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 are regulated distinctly, and this regulation may explain, in part, the distinct knockout phenotypes.
Figure 5.
In situ analysis of PCAF and PCAF-B/GCN5 mRNAs in mouse embryos. Dark-field micrographs of parasagittal sections of E10.5 (B–E) and E12.5 (G and H) mouse embryos after hybridization with a PCAF-specific antisense probe (B and E), a PCAF-B/GCN5-specific antisense probe (B and G), or the respective sense probes as a control (C and E). Bright-field micrographs of toluidine blue-stained sections of E10.5 (A) and E12.5 (F) are also shown. Abbreviations: fb, forebrain; h, heart; hb, hindbrain; hl, hind limb; li, liver; lu, lung; nt; neural tube; skm, skeletal muscle. (Bar = 1 mm.)
Acknowledgments
We thank Alex Grinberg and Eric Lee for technical assistance, Naoyuki Takuma and Yoshimobu Hara for advice on in situ hybridization, and Birgit An der Lan (BAAR Biomed) for editing the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- h
human
- m
murine
- ES
embryonic stem
- kb
kilobase
- En
embryonic day n
References
- 1.Yang X J, Ogryzko V V, Nishikawa J, Howard B H, Nakatani Y. Nature (London) 1996;382:319–324. doi: 10.1038/382319a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kuo M H, Allis C D. BioEssays. 1998;20:615–626. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199808)20:8<615::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Struhl K. Genes Dev. 1998;12:599–606. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Workman J, Kingston R E. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:545–579. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schiltz R L, Nakatani Y. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1470:M37–M53. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(99)00037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sakaguchi K, Herrera J E, Saito S, Miki T, Bustin M, Vassilev A, Anderson C W, Appella E. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2831–2841. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.18.2831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu L, Scolnick D M, Trievel R C, Zhang H B, Marmorstein R, Halazonetis T D, Berger S L. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1202–1209. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.2.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sartorelli V, Puri P L, Hamamori Y, Ogryzko V, Chung G, Nakatani Y, Wang J Y, Kedes L. Mol Cell. 1999;4:725–734. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gu W, Roeder R. Cell. 1997;90:595–606. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ogryzko V V, Kotani T, Zhang X, Schlitz R L, Howard T, Yang X J, Howard B H, Qin J, Nakatani Y. Cell. 1998;94:35–44. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vassilev A, Yamauchi J, Kotani T, Prives C, Avantaggiati M L, Qin J, Nakatani Y. Mol Cell. 1998;2:869–875. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hoffmann A, Chiang C, Oelgeschlager T, Xie X, Burley S, Nakatani Y, Roeder R. Nature (London) 1996;380:356–359. doi: 10.1038/380356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nakatani Y, Bagby S, Ikura M. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:6575–6578. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xie X, Kokubo T, Cohen S, Mirza U, Hoffmann A, Chait B, Roeder R, Nakatani Y, Burley S. Nature (London) 1996;380:316–322. doi: 10.1038/380316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith E R. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:2948–2954. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.12.2948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tybulewicz V L J, Crawford C E, Jackson P K, Bronson R T, Mulligan R C. Cell. 1991;65:1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lyons G E, Schiaffino S, Barton P, Sassoon D, Buckingham M. J Cell Biol. 1990;111:2427–2436. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu W, Edmondson D G, Roth S Y. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:5659–5669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.10.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tanaka Y, Naruse I, Maekawa T, Masuya H, Shiroishi T, Ishii S. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:10215–10220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yao T P, Oh S P, Fuchs M, Zhou N D, Ch'ng L E, Newsome D, Bronson R T, Li E, Livingston D M, Eckner R. Cell. 1998;93:361–372. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]