Abstract
The Escherichia coli gyrase A gene was cloned in the broad-host-range cosmid vector pLA2917. The resulting plasmid, pNJR3-2, conferred quinolone susceptibility on a gyrA mutant of E. coli. To analyze the expression of this E. coli gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pNJR3-2 or pLA2917 was mobilized via conjugation into P. aeruginosa PAO2 and several well-characterized quinolone-resistant mutants of this strain. The vector pLA2917 did not significantly affect the quinolone susceptibilities of any of the P. aeruginosa strains. However, pNJR3-2 conferred wild-type quinolone susceptibility on P. aeruginosa cfxA (gyrA) mutants and intermediate quinolone susceptibility on cfxA-cfxB double mutants of P. aeruginosa. The quinolone susceptibility of P. aeruginosa PAO2 gyrA+ was unaffected by pNJR3-2. Also, pNJR3-2 had no significant effect on P. aeruginosa cfxB (permeability) mutants. These results demonstrate that the DNA gyrase A gene from E. coli is expressed in P. aeruginosa and confers dominant susceptibility on gyrA mutants. Thus, pNJR3-2 can be used to detect the quinolone resistance mutations that occur in the gyrase A gene of this organism. pNJR3-2 also appears to discriminate between mutations in gyrA and mutations which alter permeability. This gyrase A probe was used successfully in the analysis of quinolone resistance in clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF

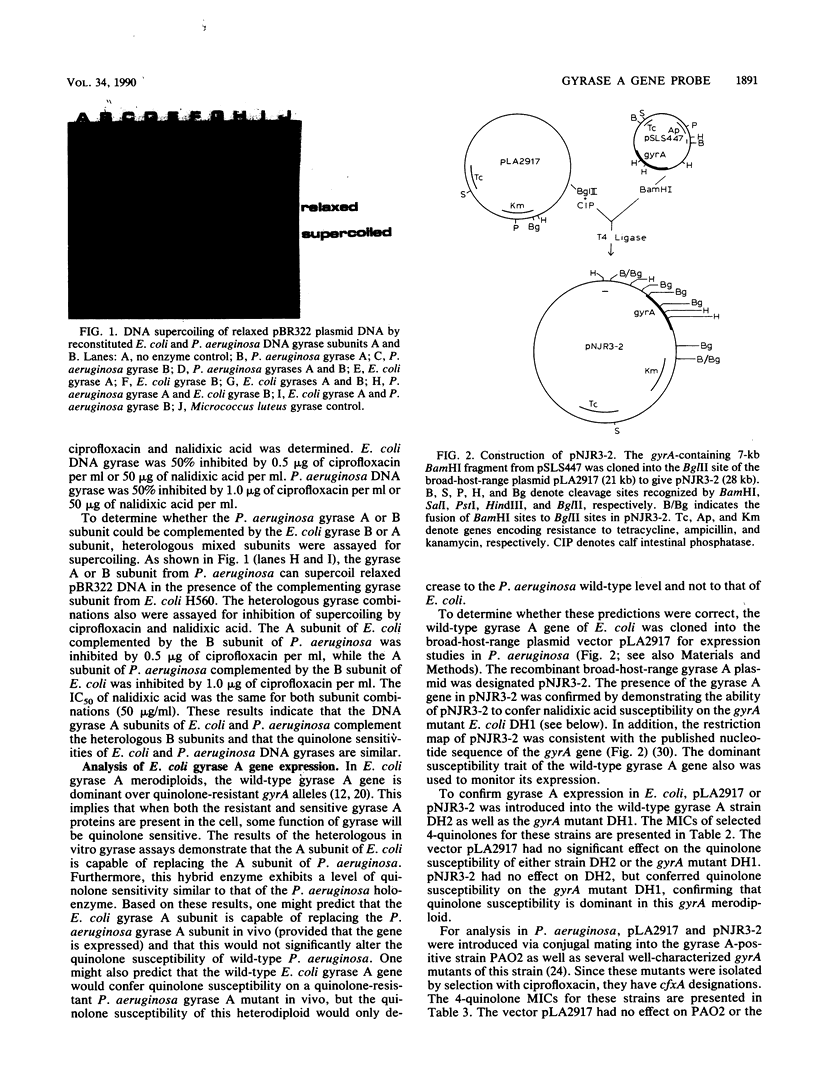
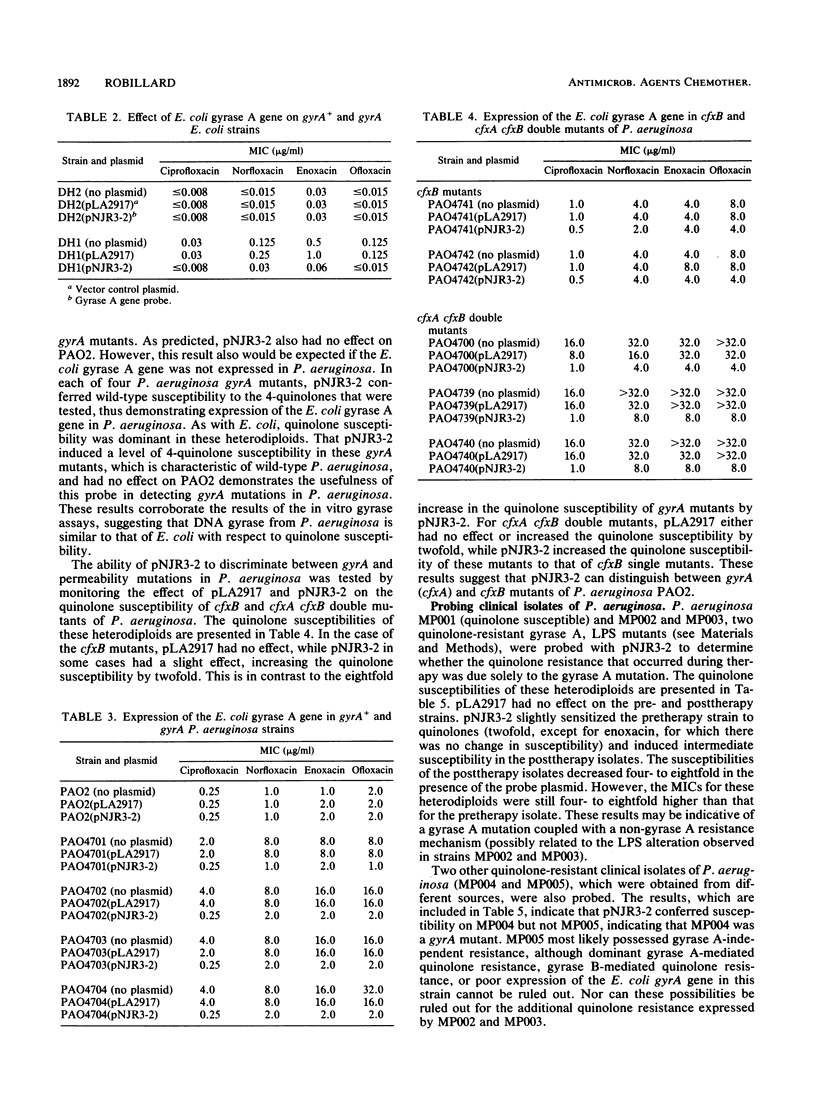
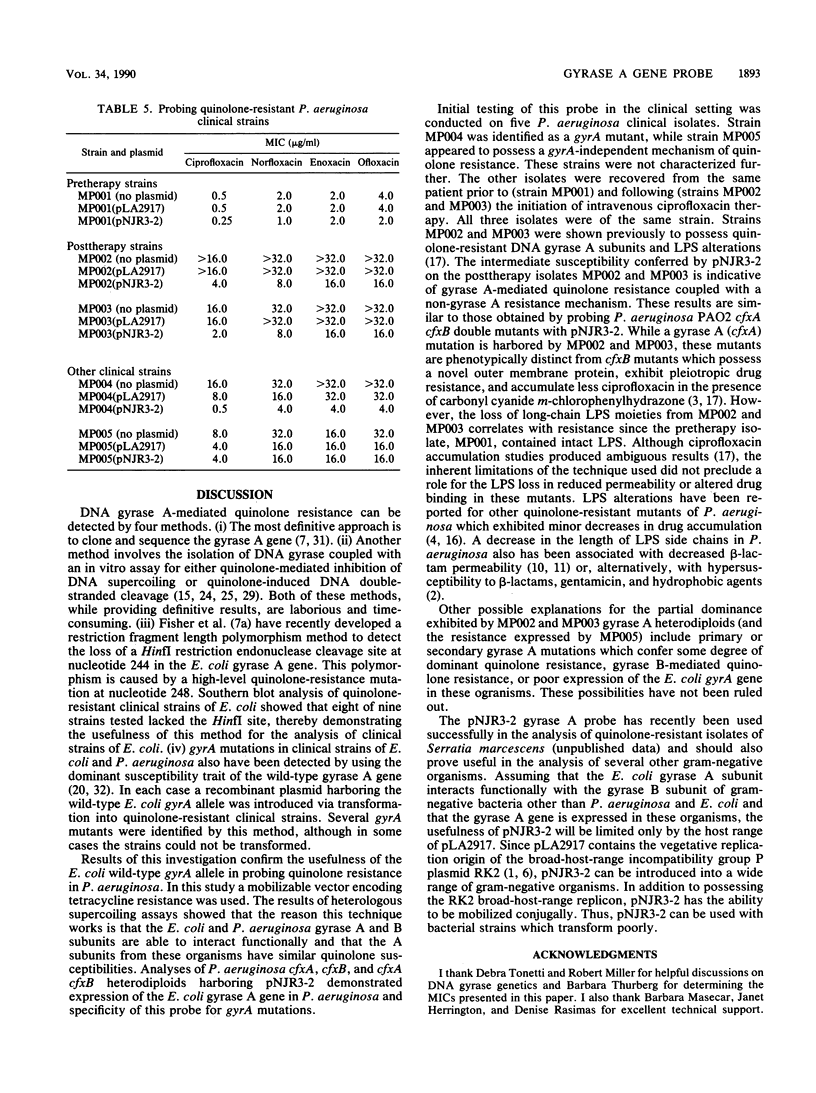

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L. N., Hanson R. S. Construction of broad-host-range cosmid cloning vectors: identification of genes necessary for growth of Methylobacterium organophilum on methanol. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):955–962. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.955-962.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus B. L., Fyfe J. A., Hancock R. E. Mapping and characterization of two mutations to antibiotic supersusceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Oct;133(10):2905–2914. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-10-2905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Factors influencing the accumulation of ciprofloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1921–1926. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberland S., Bayer A. S., Schollaardt T., Wong S. A., Bryan L. E. Characterization of mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated in vitro and in vivo during experimental endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):624–634. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M. A., Warne S. R., Thomas C. M. Analysis of the vegetative replication origin of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 by transposon mutagenesis. Plasmid. 1986 Mar;15(2):132–146. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. E., Wyke A. W., Kuroda R., Fisher L. M. Cloning and characterization of a DNA gyrase A gene from Escherichia coli that confers clinical resistance to 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):886–894. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Bryan L. E. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to new beta-lactamase-resistant beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):485–488. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Hatlelid L., Bryan L. E. Correlation between lipopolysaccharide structure and permeability resistance in beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Ng E. Y., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of action of and resistance to ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Sato K., Fujii T., Hirai K., Inoue M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Some properties of subunits of DNA gyrase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and its nalidixic acid-resistant mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2322–2325. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2322-2325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Tzouvelekis L. S., Makris A., Kotsifaki H. Outer membrane alterations in multiresistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa selected by ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):124–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masecar B. L., Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Analysis of acquired ciprofloxacin resistance in a clinical strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):281–286. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Malamy M. H. Comparisons of F factors and R factors: existence of independent regulation groups in F factors. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.81-88.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Nakamura M., Kojima T., Yoshida H. gyrA and gyrB mutations in quinolone-resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):254–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Reller L. B., Vasil M. L. Development of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin during therapy: proof provided by typing with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):743–748. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Haas D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO to nalidixic acid and low levels of beta-lactam antibiotics: mapping of chromosomal genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):242–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue Y., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of DNA gyrase from a fluoroquinolone-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman R. A. Central catheter infection: single-versus triple-lumen catheters. Am J Med. 1989 Jul;87(1):2–3. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80469-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. The intrinsic ATPase of DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6299–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanberg S. L., Wang J. C. Cloning and sequencing of the Escherichia coli gyrA gene coding for the A subunit of DNA gyrase. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Kojima T., Yamagishi J., Nakamura S. Quinolone-resistant mutations of the gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00338386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Nakamura M., Bogaki M., Nakamura S. Proportion of DNA gyrase mutants among quinolone-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1273–1275. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]