Abstract
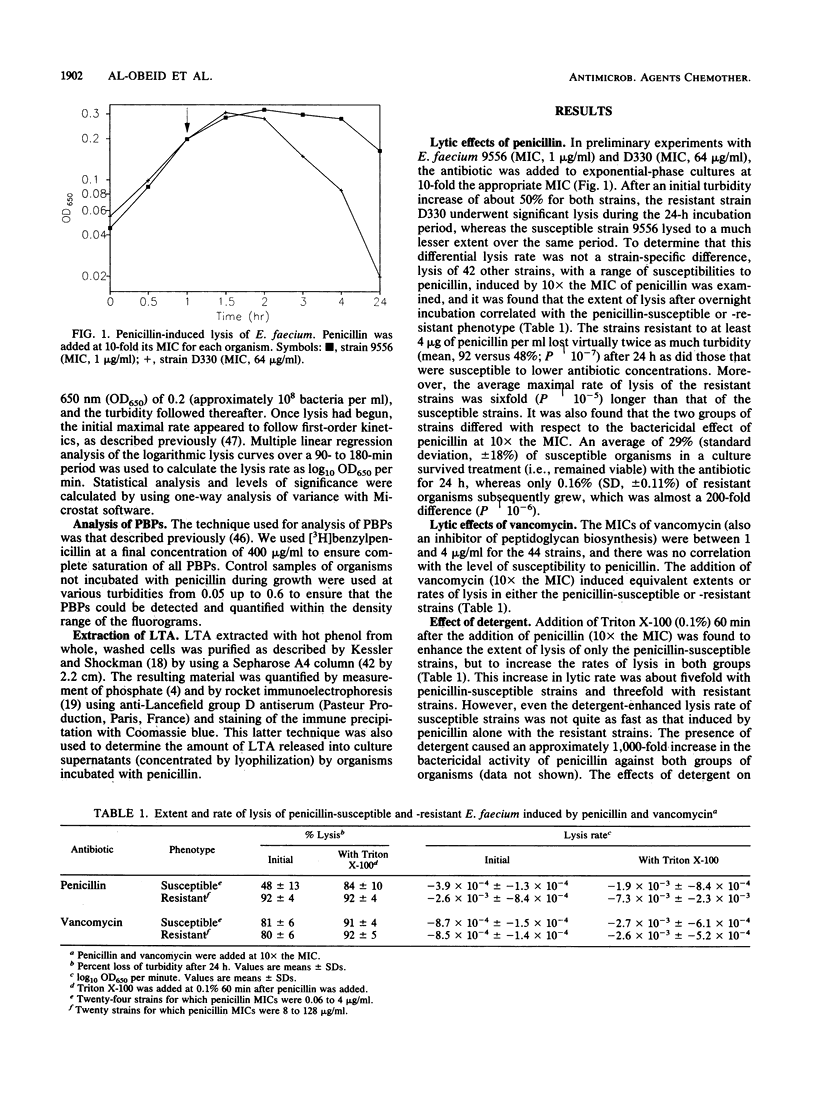
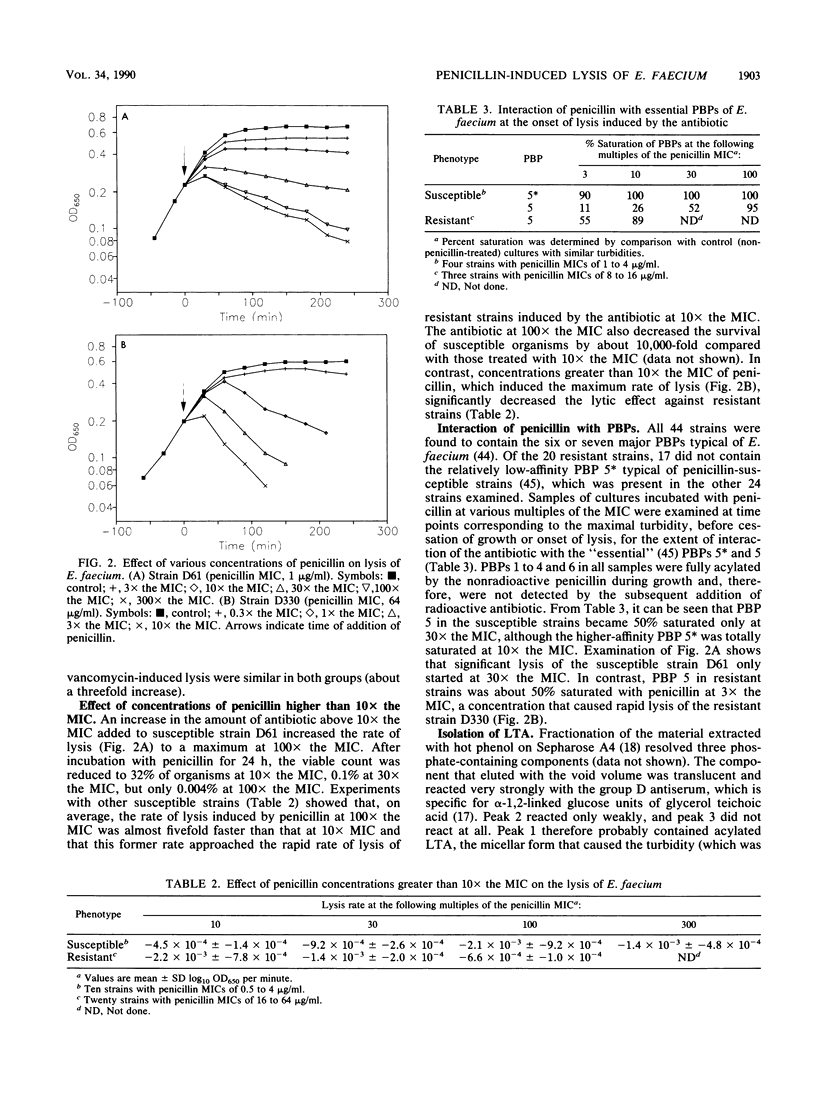
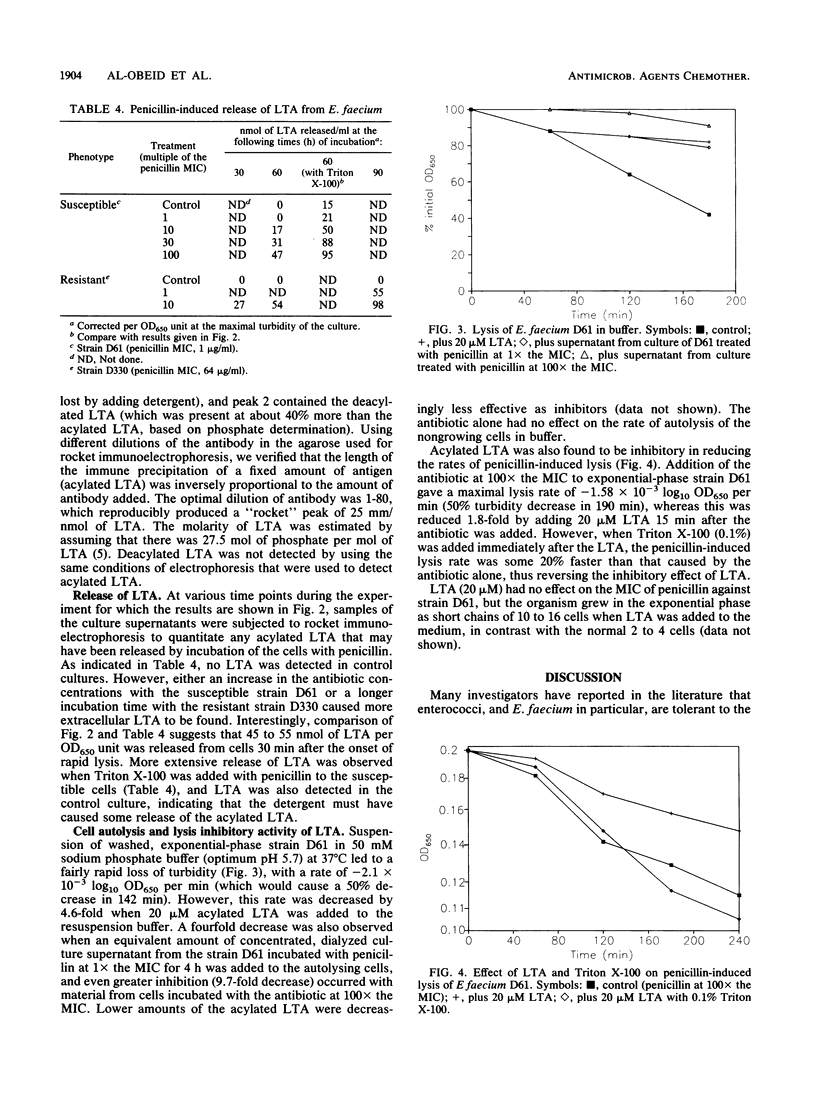
Clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium that had a range of susceptibilities to penicillin were found to differ significantly in their responses to the antibiotic. In the penicillin-susceptible group (MIC, less than or equal to 4 micrograms/ml), the cessation of growth (bacteriostasis) at 10 x the MIC of penicillin appeared to correlate with the inhibition of penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 5*, whereas the onset of lysis (bactericidal effect) at higher antibiotic concentrations (100 x the MIC) was concomitant with the inhibition of the lower-affinity PBP 5. In contrast, in the resistant (MIC, greater than or equal to 8 micrograms/ml) group (in which most of the strains did not contain PBP 5*), the degree of saturation of PBP 5 seemed to determine the physiological response to the antibiotic: low levels of saturation caused growth inhibition, whereas almost complete saturation correlated with lysis. The penicillin-induced cell lysis of both penicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains was attributed, at least in part, to the extensive loss of acylated lipoteichoic acid into the growth medium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brissette J. L., Shockman G. D., Pieringer R. A. Effects of penicillin on synthesis and excretion of lipid and lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus mutans BHT. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.838-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush L. M., Calmon J., Cherney C. L., Wendeler M., Pitsakis P., Poupard J., Levison M. E., Johnson C. C. High-level penicillin resistance among isolates of enterococci. Implications for treatment of enterococcal infections. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Apr 1;110(7):515–520. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-7-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillon J., Juvin M. E., Pirault J. L., Drugeon H. B. Activité bactéricide de la daptomycine (LY 146032) comparée à celle de la vancomycine et de la teicoplanine sur les bactéries à gram positif. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1989 Jun;37(5 Pt 2):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Holtje J. V., Wicken A. J., Tomasz A., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of bacterial wall lysins by lipoteichoic acids and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Wicken A. J., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of wall autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis by lipoteichoic acid and lipids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):192–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.192-197.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Cellular lysis of Streptococcus faecalis induced with triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.153-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneo-Moore L., Bourbeau P., Weinstein R., Carson D. Effects of cerulenin on antibiotic-induced lysis of streptococcus faecalis (S. faecium). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):858–861. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri A., Manno G., Tacchella A., Belli M. L., Palmero C. Susceptibility of enterococci. I. Inhibitory and bactericidal activity of several chemoantibiotics against Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium. Chemioterapia. 1986 Oct;5(5):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Canepari P., Satta G., Coyette J. Streptococcus faecium ATCC 9790 penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin sensitivity are heavily influenced by growth conditions: proposal for an indirect mechanism of growth inhibition by beta-lactams. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):916–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.916-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtje J. V., Tomasz A. Biological effects of lipoteichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1023–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1023-1027.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Release of lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus sanguis: stimulation of release during penicillin treatment. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1180–1184. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1180-1184.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Maher L. A., Redding J. S. In vitro activity of LY146032 (daptomycin) against selected aerobic bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;6(1):91–96. doi: 10.1007/BF02097209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Cellular localization of lipoteichoic acid in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1375-1386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Shockman G. D. Precursor-product relationship of intracellular and extracellular lipoteichoic acids of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.869-877.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., van de Rijn I. Effects of penicillin on group A streptococci: loss of viability appears to precede stimulation of release of lipoteichoic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., van de Rijn I. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes membrane. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):892–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.892-902.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouguenec C., Buu-Hoï A. Bactericidal activity of five combinations of penicillin G with aminoglycosides against Streptococcus faecium. Eur Heart J. 1984 Oct;5 (Suppl 100):29–32. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/5.suppl_c.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouguenec C., Horodniceanu T. Conjugative R plasmids in Streptococcus faecium (group D). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):698–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lleó M. M., Canepari P., Cornaglia G., Fontana R., Satta G. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of beta-lactams against Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecium are associated with saturation of different penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1618–1626. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machka K., Braveny I. Comparative in vitro activity of LY146032 (daptomycin) against gram-positive cocci. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;6(1):96–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02097210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer P. D., Wouters J. T. Lipoteichoic acid from Bacillus subtilis subsp. niger WM: isolation and effects on cell wall autolysis and turnover. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):973–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.973-980.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Wennersten C. B. Species-specific resistance to antimocrobial synergism in Streptococcus faecium and Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Watson B. K., Kunz L. J. Endocarditis due to group D streptococci. Comparison of disease caused by streptococcus bovis with that produced by the enterococci. Am J Med. 1974 Aug;57(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mederski-Samaroj B. Transferable beta-lactamase. A new mechanism for in vitro penicillin resistance in Streptococcus faecalis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1168–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI111042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri D., Chatterjee A. N. Use of resistant mutants to study the interaction of triton X-100 with Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1337–1349. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1337-1349.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said I., Fletcher H., Volpe A., Daneo-Moore L. Penicillin tolerance in Streptococcus faecium ATCC 9790. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1150–1152. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimatani M. [Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus: regulation of autolysis and killing of penicillin. I. Role of lipoteichoic acid as a regulator of autolysis]. Osaka Daigaku Shigaku Zasshi. 1979 Jun;24(1):54–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimatani M. [Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus: regulation of autolysis and killing of penicillin. II. Prevention of penicillin-induced lysis by cellular lipoteichoic acid]. Osaka Daigaku Shigaku Zasshi. 1979 Jun;24(1):68–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shungu D. L., Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Lipids and lipoteichoic acid of autolysis-defective Streptococcus faecium strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.741-746.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shungu D. L., Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Morphological and physiological study of autolytic-defective Streptococcus faecium strains. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):598–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.598-608.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suginaka H., Shimatani M., Ogawa M., Kotani S. Prevention of penicillin-induced lysis of Staphylococcus aureus by cellular lipoteichoic acid. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Jan;32(1):73–77. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Waks S. Mechanism of action of penicillin: triggering of the pneumococcal autolytic enzyme by inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsui Y., Ohya S., Takenouchi Y., Tajima M., Sugawara S., Deguchi K., Suginaka H. Release of lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus by treatment with cefmetazole and other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Oct;36(10):1380–1386. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waks S., Tomasz A. Secretion of cell wall polymers into the growth medium of lysis-defective pneumococci during treatment with penicillin and other inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):293–301. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Al-Obeid S., Shlaes J. H., Goldstein F. W., Shlaes D. M. Inducible resistance to vancomycin in Enterococcus faecium D366. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1095–1104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Gutmann L., Horaud T., Delbos F., Acar J. F. Use of penicillin-binding proteins for the identification of enterococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1929–1937. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Tomasz A. Inhibition of cell wall synthesis and acylation of the penicillin binding proteins during prolonged exposure of growing Streptococcus pneumoniae to benzylpenicillin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., le Bouguénec C., Gutmann L., Horaud T. One or two low affinity penicillin-binding proteins may be responsible for the range of susceptibility of Enterococcus faecium to benzylpenicillin. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1933–1940. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Autolytic enzyme associated with cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3462–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


