Abstract
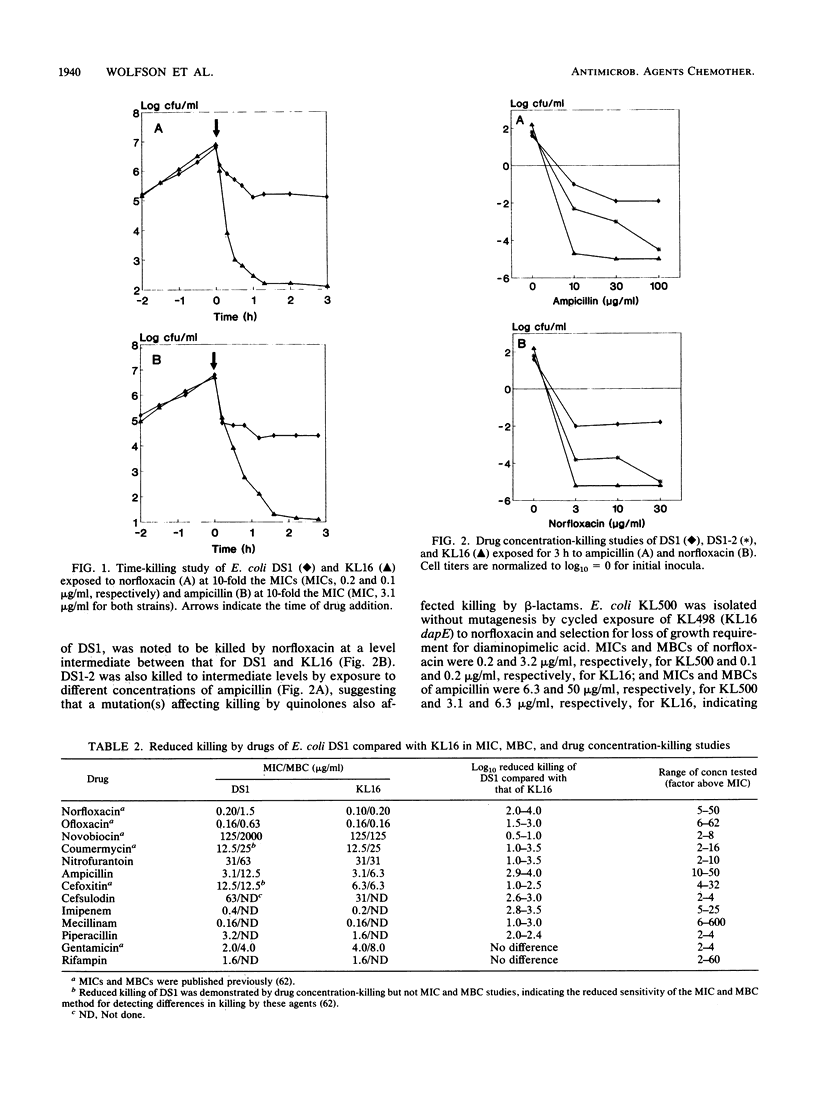
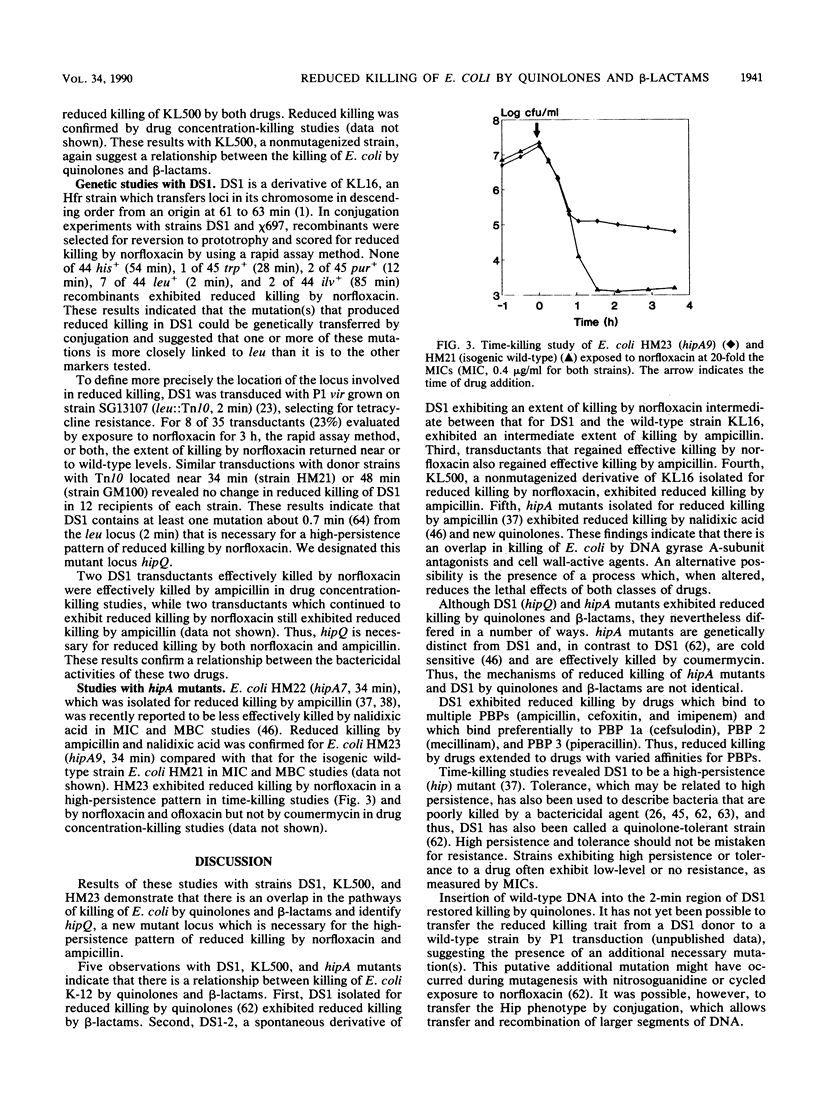
Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and other new quinolones, which are antagonists of the enzyme DNA gyrase, rapidly kill bacteria by largely unknown mechanisms. Earlier, we isolated, after mutagenesis, Escherichia coli DS1, which exhibited reduced killing by quinolones. We evaluated the killing of DS1 and several other strains by quinolones and beta-lactams. In time-killing studies with norfloxacin, DS1 was killed 1 to 2 log10 units compared to 4 to 5 log10 units for the wild-type parent strain KL16, thus revealing that DS1 is a high-persistence (hip) mutant. DS1 exhibited a similar high-persistence pattern for the beta-lactam ampicillin and reduced killing by drugs that differed in their affinities for penicillin-binding proteins, including cefoxitin, cefsulodin, imipenem, mecillinam, and piperacillin. Conjugation and P1 transduction studies identified a novel mutant locus (termed hipQ) in the 2-min region of the DS1 chromosome necessary for reduced killing by norfloxacin and ampicillin. E. coli KL500, which was isolated for reduced killing by norfloxacin without mutagenesis, exhibited reduced killing by ampicillin. E. coli HM23, a hipA (34 min) mutant that was isolated earlier for reduced killing by ampicillin, also exhibited high persistence to norfloxacin. DS1 differed from HM23, however, in the map location of its hip mutation, lack of cold sensitivity, and reduced killing by coumermycin. Results of these studies with strains DS1, KL500, and HM23 demonstrate overlap in the pathways of killing of E. coli by quinolones and beta-lactams and identify hipQ, a new mutant locus that is involved in a high-persistence pattern of reduced killing by norfloxacin and ampicillin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Cell shape and division in Escherichia coli: experiments with shape and division mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):615–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botta G. A., Park J. T. Evidence for involvement of penicillin-binding protein 3 in murein synthesis during septation but not during cell elongation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. T., Dougherty T. J., Fraimow H. S., Bellin E. Y., Miller M. H. Association between early inhibition of DNA synthesis and the MICs and MBCs of carboxyquinolone antimicrobial agents for wild-type and mutant [gyrA nfxB(ompF) acrA] Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. M., Deitz W. H., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. IV. Effects on the stability of cellular constituents. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):774–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.774-779.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtright J. B., Turowski D. A., Sonstein S. A. Alteration of bacterial DNA structure, gene expression, and plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance following exposure to enoxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21 (Suppl B):1–18. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Kenwright M., Hirst T. Investigations into the mechanism of action of the antibacterial agent norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 May;13 (Suppl B):9–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.suppl_b.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Smith J. T. Nalidixic acid and bacterial chromosome replication. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):643–645. doi: 10.1038/260643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Smith J. T. Nalidixic acid: an antibacterial paradox. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):251–261. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitz W. H., Cook T. M., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. 3. Conditions required for lethality. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.768-773.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver J. M., Wise R. Morphological and biochemical changes in Escherichia coli after exposure to ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):31–41. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Saukkonen J. J. Membrane permeability changes associated with DNA gyrase inhibitors in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):200–206. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Shelton A., Greenwood D. The response of Escherichia coli to ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Feb;23(1):83–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI.II. INHIBITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1068-1074.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Halpern E., Trisler P. Role of sulA and sulB in filamentation by lon mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):265–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.265-273.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. Phenotypic resistance to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jun;15(6):653–655. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.6.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. DNA synthesis inhibition and the induction of protein X in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Antibiotic tolerance among clinical isolates of bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):368–386. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Fangman W. L. Single-strand breaks in deoxyribonucleic acid and viability loss during deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis inhibition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1329-1335.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. Mode of action of the quinolone antimicrobial agents: review of recent information. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S902–S911. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritzkes D. R., Zhang X. Y., Lin E. C. Use of phi(glp-lac) in studies of respiratory regulation of the Escherichia coli anaerobic sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes (glpAB). J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.591-598.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Howard B. M., Ratcliffe N. T., Smith J. T. 4-quinolones and the SOS response. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):139–144. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Smith J. T. Bactericidal mechanisms of ofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):1–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Smith J. T. DNA breakdown by the 4-quinolones and its significance. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jan;31(1):65–70. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F. Coupling of DNA replication and cell division: sulB is an allele of ftsZ. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1339–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1339-1346.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyed H. S., Bertrand K. P. hipA, a newly recognized gene of Escherichia coli K-12 that affects frequency of persistence after inhibition of murein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.768-775.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyed H. S., Broderick S. H. Molecular cloning and expression of hipA, a gene of Escherichia coli K-12 that affects frequency of persistence after inhibition of murein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):399–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.399-403.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Culebras E., Moreno F., Baquero F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):631–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramareddy G., Reiter H. Specific loss of newly replicated deoxyribonucleic acid in nalidixic acid-treated Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):724–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.724-729.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronda C., García J. L., García E., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., López R. Biological role of the pneumococcal amidase. Cloning of the lytA gene in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):621–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer R., Moyed H. S. Conditional impairment of cell division and altered lethality in hipA mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3321–3326. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3321-3326.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P. J. Bactericidal effect against Escherichia coli of nalidixic acid and four structurally related compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jul;6(4):535–542. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Schwartz J. Penicillin-binding protein 7 and its relationship to lysis of nongrowing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4912–4915. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4912-4915.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt W. H., Zeiler H. J. Influence of ciprofloxacin on the ultrastructure of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(10):1600–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. R., Pardee A. B. Evidence for a relationship between deoxyribonucleic acid metabolism and septum formation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.123-131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. R., Ussery C. L., Allen J. S. Bacterial cell division regulation: lysogenization of conditional cell division lon - mutants of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1326–1332. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1326-1332.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton L., Elwell L. P. In vitro cleavable-complex assay to monitor antimicrobial potency of quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1086–1089. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winshell E. B., Rosenkranz H. S. Nalidixic Acid and the Metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1168–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1168-1175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):378–424. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., Shih D. J., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Isolation and characterization of an Escherichia coli strain exhibiting partial tolerance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):705–709. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfrey B. F., Lally R. T., Ederer M. N. Evaluation of oxacillin tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus by a novel method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):381–388. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J. Evaluation of the in vitro bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin on cells of Escherichia coli in the logarithmic and stationary phases of growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):524–527. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



