Abstract
The antimalarial compound qinghaosu (artemisinin) was tested in vitro for the ability to inhibit plaque formation by Toxoplasma gondii in fibroblasts. Qinghaosu at 0.4 microgram/ml for 5 days eliminated all plaques and microscopic foci of T. gondii. At 1.3 micrograms/ml for 14 days, qinghaosu completely eliminated T. gondii. Pretreatment of host cells or T. gondii with qinghaosu had no effect on T. gondii growth. There was no apparent toxicity to human fibroblasts in long-term studies. Of the six qinghaosu derivatives tested, dihydroqinghaosu, 1-propyl-ether-qinghaosu, and 1-butyl-ether-qinghaosu were comparable to qinghaosu. Ethyl-ether-qinghaosu (arteether) and sec-butyl-ether-qinghaosu were more effective. Methyl-ether-qinghaosu (artemether) was the most effective, with a potency approximately 10-fold greater than that of qinghaosu.
Full text
PDF
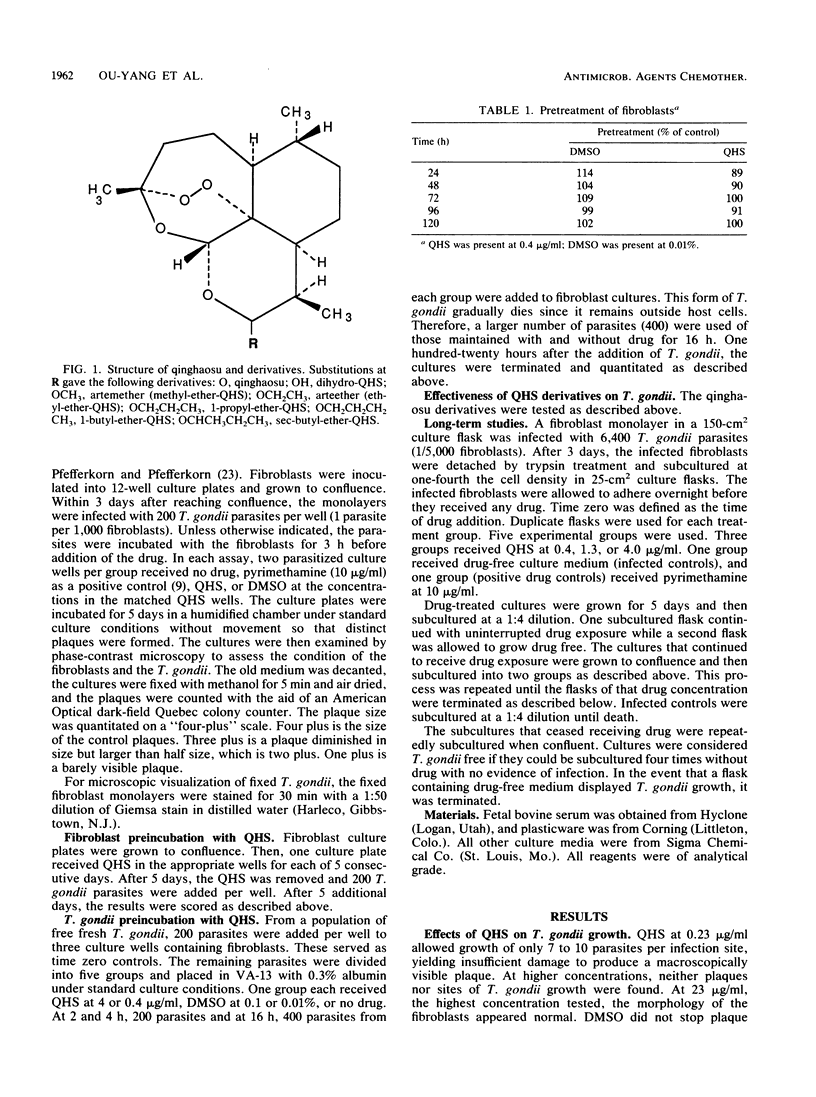


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPARAS S. D., SCHLESINGER R. W. Plaque assay of Toxoplasma on monolayers of chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Nov;102:431–437. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK M. K., JACOBS L. In vitro investigations on the action of pyrimethamine against Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1958 Jun;44(3):280–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. R., Pechère J. C. Arteether, a qinghaosu derivative, in toxoplasmosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(6):867–867. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawira A. N., Warhurst D. C. The effect of artemisinin combined with standard antimalarials against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Feb;90(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke D. W., Lallinger G. J., Durack D. T. In vitro sensitivity of Naegleria fowleri to qinghaosu and dihydroqinghaosu. J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;73(2):411–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt A. E., Chirgwin K., Landesman S. H. Current concepts. Treatment of infections associated with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1439–1448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H. M., Liu M. Z., Lu B. F., Xu J. Y., Chen L. J., Wang M. Y., Sun W. K., Xu B., Ji R. Y. [Antimalarial effect and toxicity of methyl-dihydro-artemisinine in animals (author's transl)]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1981 Jun;2(2):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H. M., Lu B. F., Qu Z. X. [Antimalarial activities of 25 derivatives of artemisinine against chloroquine-resistant plasmodium berghei (author's transl)]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1980 Sep;1(1):48–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klayman D. L., Lin A. J., Acton N., Scovill J. P., Hoch J. M., Milhous W. K., Theoharides A. D., Dobek A. S. Isolation of artemisinin (qinghaosu) from Artemisia annua growing in the United States. J Nat Prod. 1984 Jul-Aug;47(4):715–717. doi: 10.1021/np50034a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klayman D. L. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1049–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.3887571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le W. J., You J. Q., Mei J. Y. [Chemotherapeutic effect of artesunate in experimental schistosomiasis]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1983 Aug;18(8):619–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le W. J., You J. Q., Yang Y. Q., Mei J. Y., Guo H. F., Yang H. Z., Zhang C. W. [Studies on the efficacy of artemether in experimental schistosomiasis (author's transl)]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1982 Mar;17(3):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Yu P. L., Chen Y. X., Li L. Q., Gai Y. Z., Wang D. S., Zheng Y. P. [Studies on analogs of artemisinine. I. The synthesis of ethers, carboxylic esters and carbonates of dihydroartemisinine (author's transl)]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1981 Jun;16(6):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. L., Gu H. M., Warhurst D. C., Peters W. Effects of qinghaosu and related compounds on incorporation of [G-3H] hypoxanthine by Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):522–523. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Toxoplasma gondii: isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Jun;39(3):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishan Z., Mei-Yi Z. Application of precolumn reaction to high-performance liquid chromatography of qinghaosu in animal plasma. Anal Chem. 1986 Feb;58(2):289–292. doi: 10.1021/ac00293a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. J., Yang H. Z., Yang Y. Q. [Histological and histochemical changes of Schistosoma japonicum and host liver caused by artemether]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1983 Jan;18(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue W. J., You J. Q., Mei J. Y. [Effects of artemether on Schistosoma japonicum adult worms and ova]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1984 Mar;5(1):60–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



