Abstract
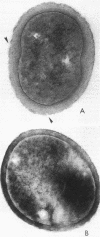
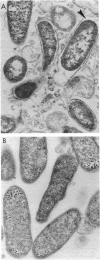
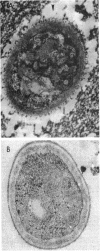
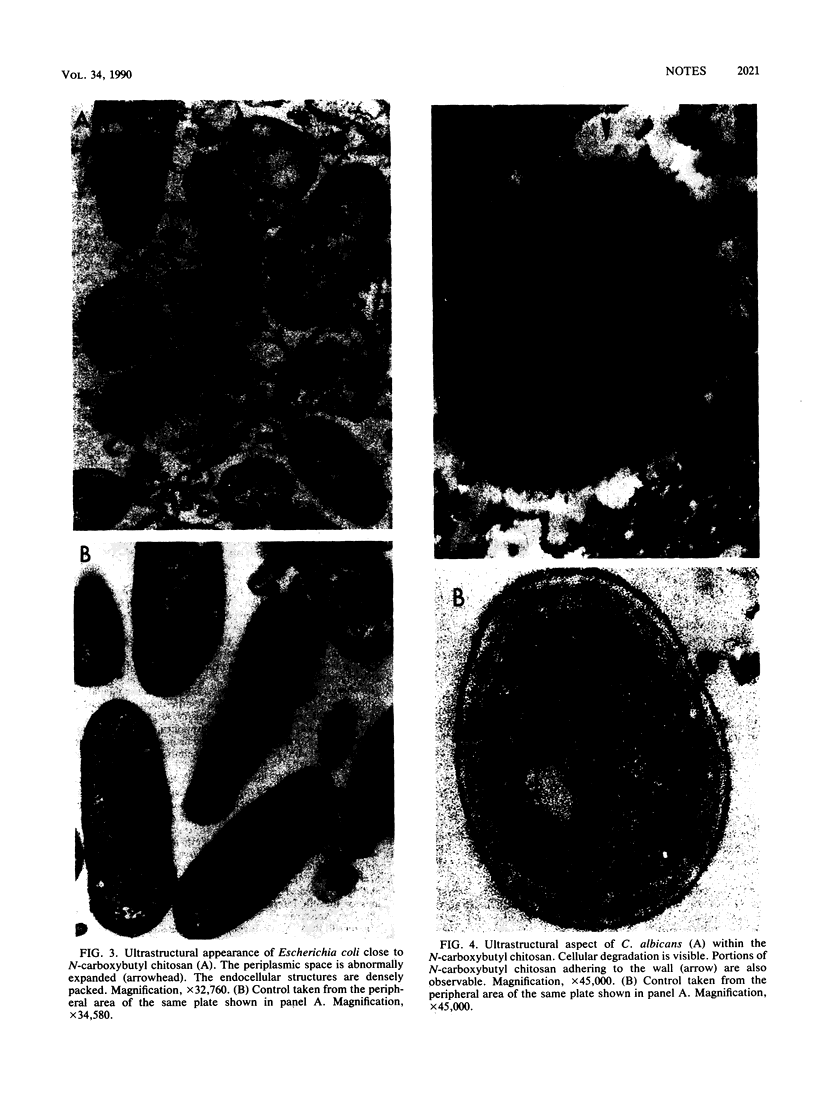
N-Carboxybutyl chitosan, a modified chitin of crustacean origin, displayed inhibitory, bactericidal, and candidacidal activities when tested against 298 cultures of various pathogens. Examination by electron microscopy showed that microbial cells exposed to N-carboxybutyl chitosan underwent marked morphological alterations. The data are of importance in defining the suitability of N-carboxybutyl chitosan as a wound dressing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HATTA S., KUWABARA S., MIYAMOTO H., AOYAMA K., UTSUNOMIYA N., TANJI S. Studies on macramin, a new high-molecular antibacterial substance derived from chitin. Jpn Med J (Natl Inst Health Jpn) 1950 Apr;3(2):119–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M., Clerc M. F. Chitosan-colloidal gold complexes as polycationic probes for the detection of anionic sites by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Histochemistry. 1988;90(3):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00492504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida J., Une T., Ishihara C., Nishimura K., Tokura S., Mizukoshi N., Azuma I. Stimulation of non-specific host resistance against Sendai virus and Escherichia coli infections by chitin derivatives in mice. Vaccine. 1987 Dec;5(4):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(87)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Yamamoto K., Tajima K. Bromo (methylthio) benzenes and related sulfur-containing compounds: minor urinary metabolites of bromobenzene in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 14;82(3):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90854-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher K. S., Coil J. A., Jr Effects of oxidized cellulose and microfibrillar collagen on infection. Surgery. 1982 Mar;91(3):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]