Abstract
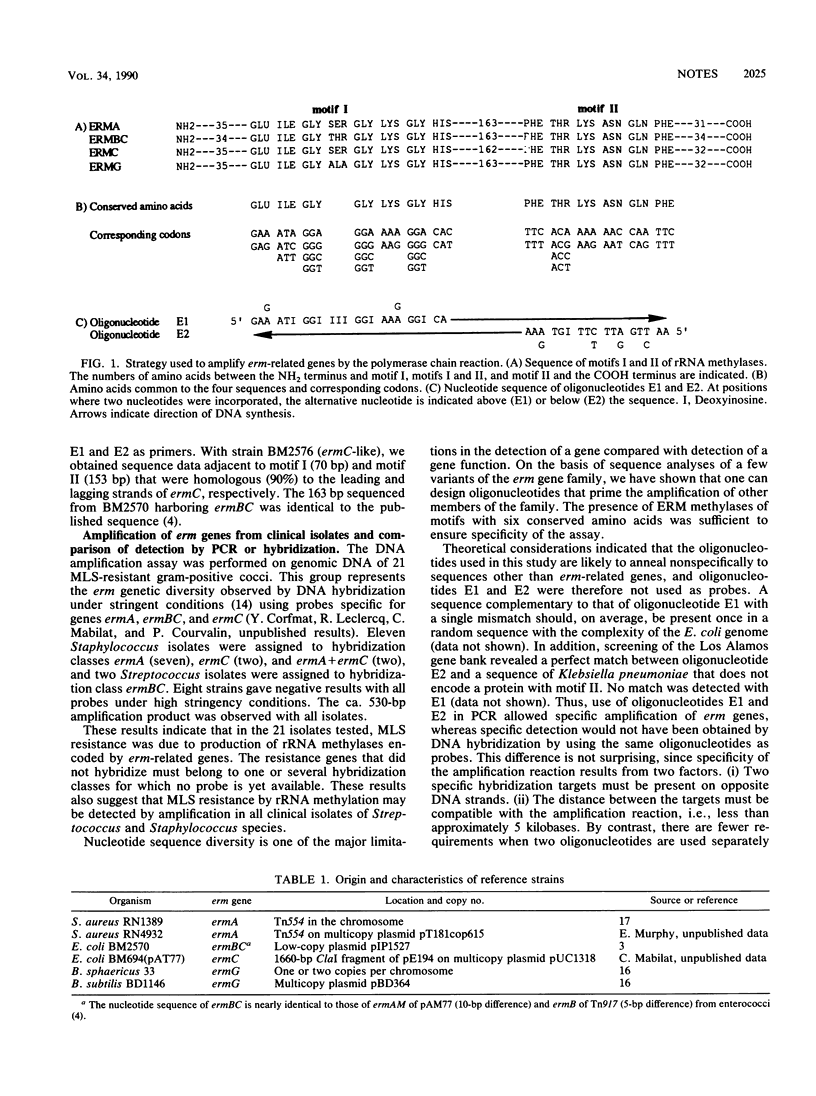
Genes belonging to different erm DNA hybridization classes were selectively amplified by polymerase chain reaction with a pair of oligonucleotides that corresponded to conserved amino acid motifs in known ERM methylases. Identification of the resistance mechanism was possible despite substantial nucleotide sequence diversity among the erythromycin resistance genes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur M., Andremont A., Courvalin P. Distribution of erythromycin esterase and rRNA methylase genes in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae highly resistant to erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):404–409. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Brisson-Noël A., Courvalin P. Origin and evolution of genes specifying resistance to macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin antibiotics: data and hypotheses. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):783–802. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Courvalin P. Contribution of two different mechanisms to erythromycin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):694–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Arthur M., Courvalin P. Evidence for natural gene transfer from gram-positive cocci to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1739–1745. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1739-1745.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M. J., PATTERSON D. L. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ORDERED COMPLEXES FORMED BETWEEN POLYINOSINIC ACID, POLYCYTIDYLIC ACID AND THEIR DEOXYRIBO-ANALOGUES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:410–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse W. B., Aymani J., Kennard O., Brown T., Jack A. G., Leonard G. A. Refined crystal structure of an octanucleotide duplex with I.T. mismatched base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):55–72. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel H. W., Soedirman N., Rost J. A., van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J. D. Transferability of macrolide, lincomycin, and streptogramin resistances between group A, B, and D streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.407-413.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire L., Arella M., Campione-Piccardo J., Lancaster W. D. Amplification of human papillomavirus DNA sequences by using conserved primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2660–2665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2660-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation: mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawase Y., Iwai S., Inoue H., Miura K., Ohtsuka E. Studies on nucleic acid interactions. I. Stabilities of mini-duplexes (dG2A4XA4G2-dC2T4YT4C2) and self-complementary d(GGGAAXYTTCCC) containing deoxyinosine and other mismatched bases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7727–7736. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B. Altered methylation of ribosomal RNA in an erythromycin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Courvalin P. Gene heterogeneity for resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins in Enterobacteriaceae. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;139(6):677–681. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Goussard S., Sougakoff W., Spencer R. C., Courvalin P. Direct sequencing of the amplified structural gene and promoter for the extended-broad-spectrum beta-lactamase TEM-9 (RHH-1) of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Plasmid. 1990 Jan;23(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Mohan S., Dubnau D. Cloning and analysis of ermG, a new macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance element from Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):340–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.340-350.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. Nucleotide sequence of ermA, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B determinant in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.633-640.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka E., Matsuki S., Ikehara M., Takahashi Y., Matsubara K. An alternative approach to deoxyoligonucleotides as hybridization probes by insertion of deoxyinosine at ambiguous codon positions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2605–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki I., Bertani G. Growth abnormalities in Hfr derivatives of Escherichia coli strain C. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):365–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker-Varia S., Jenssen W. D., Moon-McDermott L., Weinstein M. P., Dubin D. T. Molecular epidemiology of macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramin B resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):735–743. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker-Varia S., Ranzini A. C., Dubin D. T. Ribosomal RNA methylation in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli: effect of the "MLS" (erythromycin resistance) methylase. Plasmid. 1985 Sep;14(2):152–161. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Holder S. B., Halling S. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence common to staphylococcal and streptococcal plasmids which specify erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):990–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.990-998.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B. Inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin type B antibiotics: the resistance phenotype, its biological diversity, and structural elements that regulate expression--a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16 (Suppl A):63–90. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.suppl_a.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



